The outcomes of this post are:
- What is the Difference Between “git rebase master” vs. “git rebase origin/master”?
- How to Use “git rebase origin/master”?
- How to Use “git rebase master”?
What is the Difference Between “git rebase master” vs. “git rebase origin/master”?
The “git rebase <remote-name>/master” command is utilized for rebasing the particular branch from the developer’s upstream “master” branch. On the other hand, the “git rebase master” command shows that users can rebase from the tracking branch of the remote URL “origin”.
How to Use “git rebase origin/master”?
Try the following instructions to use the above-listed command.
Step 1: Navigate to Root Directory
Type out the “cd” command with the root directory path and switch to it:
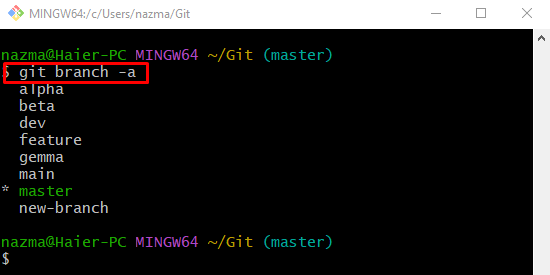
Step 2: List Remote and Local Branches
Then, show all branches by utilizing the “git branch” command along with the “-a” flag for all:
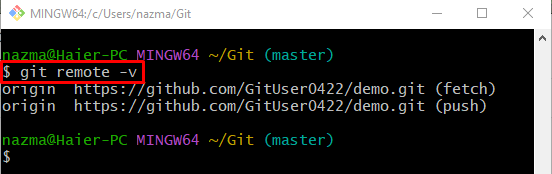
Step 3: Verify Remote URL
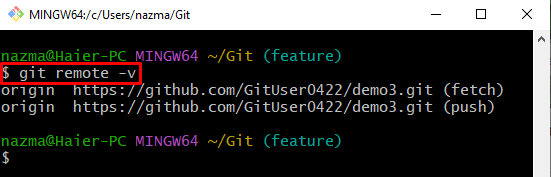
Now, to ensure that the remote URL exists in the local repository for tracking purposes or not, execute the “git remote” command:
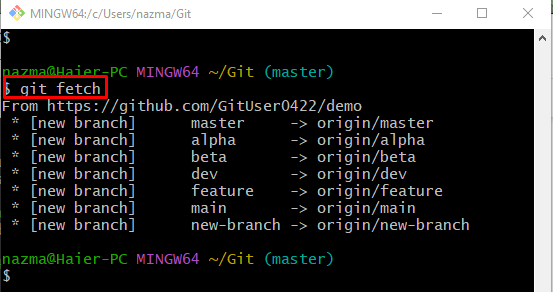
Step 4: Download GitHub Branches
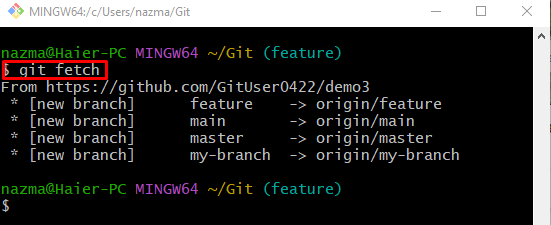
Next, fetch the newest version of the GitHub branch locally, run the below-stated command:
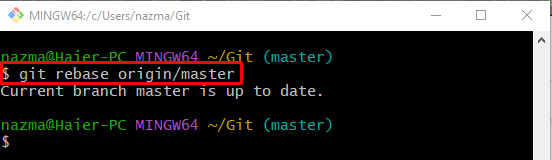
Step 5: Run ‘git rebase origin/master’
Finally, use the “git rebase” command along with the remote branch name:
According to the following output, the “master” branch is up-to-date because we have merged the GitHub branch content into the particular local:
How to Use “git rebase master”?
To use the above-stated command, check the below-given steps.
Step 1: Check Remote URL
First, view the remote URL list by running the “git remote” command:
Step 2: Fetch Remote Repository Content
To fetch the GitHub repository, which is set as the remote URL, utilize the “git fetch” command:
Step 3: Rebase Local Branch
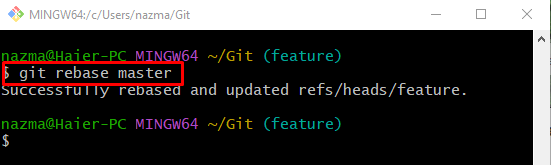
Finally, execute the provided command to perform the rebase operation locally:
It can be observed that the local “master” branch is rebased successfully, and the HEAD reference is updated:
We have differentiated between the “git rebase origin/master” and “git rebase master”.
Conclusion
The “git rebase origin/master” command is used to rebase the desired branch from the developer’s upstream “master” branch. On the other hand, the “git rebase master” command indicates that developers can rebase from the tracking branch of the remote URL “origin”. This post elaborated on the “git rebase master” and “git rebase origin/master” commands.