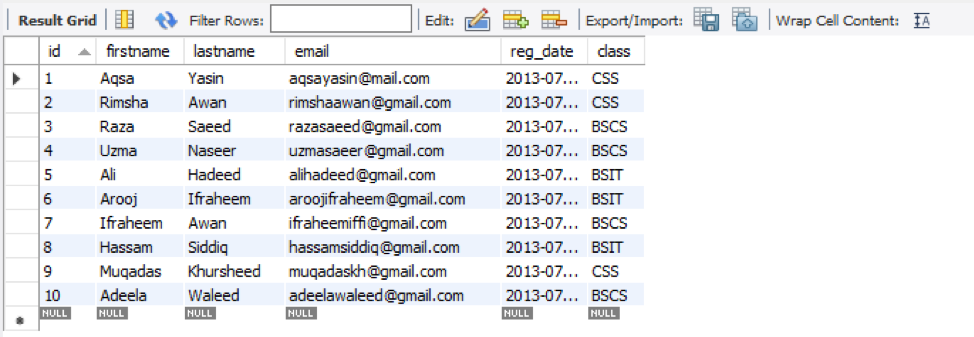
First of all, you must have some data in your database schema to perform queries on it. Let’s make a table named ‘student’ in the database ‘data’ using a CREATE query in MYSQL Workbench or Command-Line Client. The table ‘student’ has six columns: ‘id’, ‘firstname’, ’lastname’, ‘email’, ‘reg_date’, and ‘class’. We will be adding values to its columns using its grid view as below and click on the ‘Apply’ button to save changes. Now you can perform any update on these records.
Delete via Workbench Interface
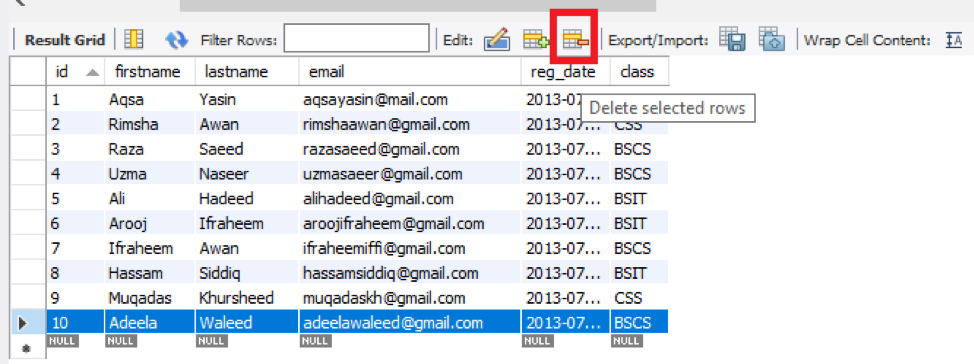
A very simple method to delete row/rows from the MySQL table is via the workbench grid view as we have a table ‘student’ with ten records in it. To delete a single row from a table, you have to select the particular row and press the delete-row icon from the grid window as we have selected the 10th row and pressed the highlighted icon below.
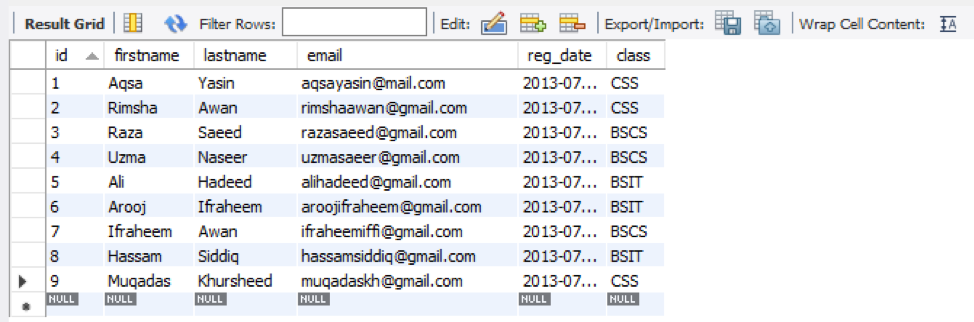
After tapping on the delete icon, you can see that the 10th row and its record have been deleted from the table ‘student’. If you want to delete more than one row, you have to select more than one row consecutively.
Delete Single Row via Command-Line
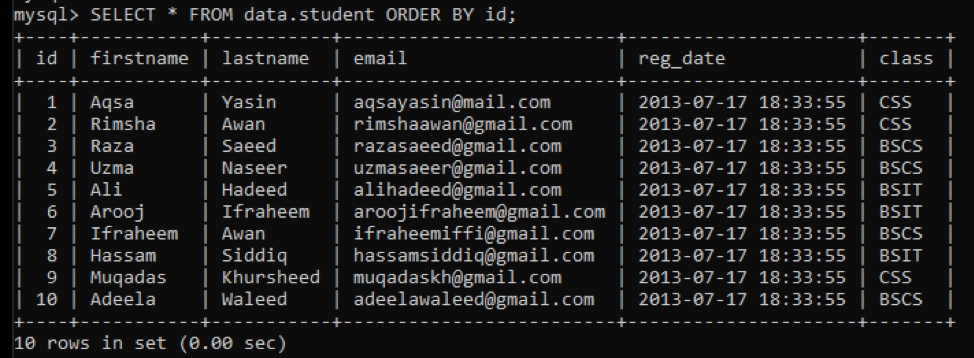
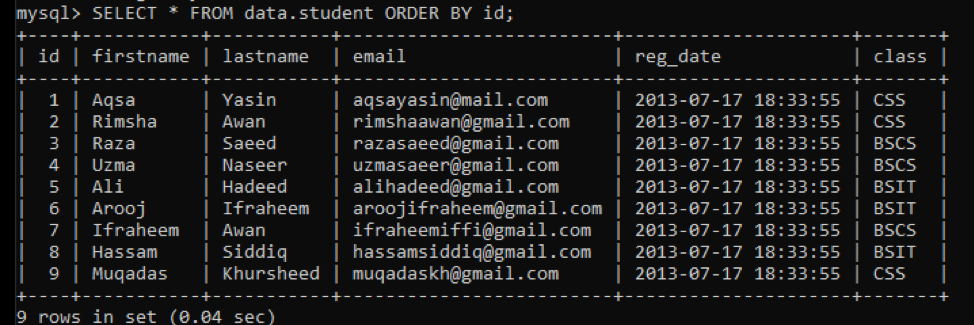
Another simple method to delete a row from the MySQL schema is through the command-line client. Open the MySQL command-line client under the newly installed ‘MySql’ via the ‘window’ button. First of all, check and display all the records of table ‘student’ using the ‘SELECT’ command as below.
Example 01: Using One Condition in WHERE Clause
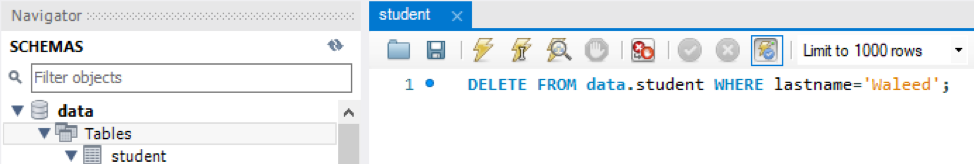
Let’s delete a single row using the ‘WHERE’ clause in the ‘DELETE’ query. We are deleting the row where the ‘lastname = Waleed’, which is row number 10 as above. Let’s try it as:
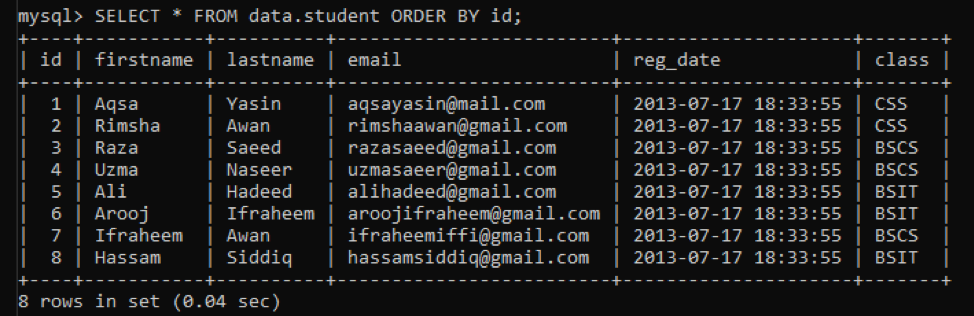
It has been deleted successfully as it displays that ‘Query OK, 1 row affected’.
On display all the rows of table ‘student’, we can see that the record of the 10th row has been deleted from the table.
Use the same ‘DELETE’ query in the navigator of the workbench to delete a record as shown.
Example 02: Using More than One Condition in WHERE Clause
You can also delete the single row from the table, using more than one condition in the ‘DELETE’ query of MySQL. We are using two conditions in the ‘WHERE’ clause, e.g., ‘lastname = khursheed’ and ‘id > 7’. This query will only delete the row which has an id greater than ‘7’, and its lastname is ‘khursheed’. In our case, it is the 9th row.
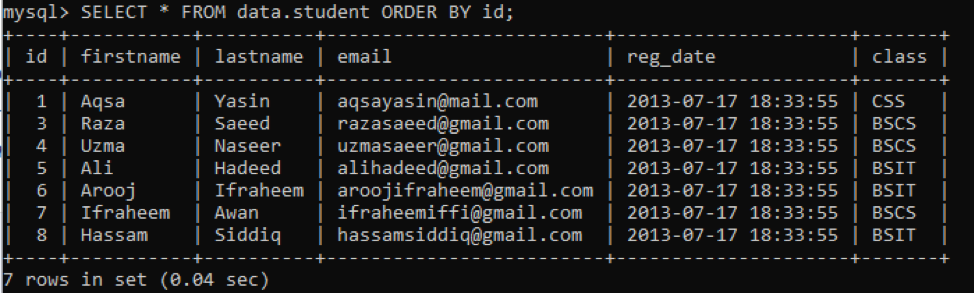
The 9th row has been deleted successfully as it says that ‘Query OK, 1 row affected.’
On checking, we have only 8 rows left within the table. The 9th row has been wiped away from the table, as shown below.
Example 03: Using LIMIT Condition in WHERE Clause
We can also delete a single row via the ‘LIMIT’ clause in the ‘DELETE’ query. In this query, we have to define a limit as ‘1’ for a single row to be deleted. We have defined a limit value as ‘1’ in the ‘WHERE’ clause of the ‘DELETE’ query. It will only delete the first row from all the records having ‘lastname = Awan’, which is row number 2.
Use the ‘SELECT’ query to check the updated table. You can see that the 2nd row is nowhere in the table as displayed below, and we have only 7 rows left.
Delete Multiple Rows via Command-Line
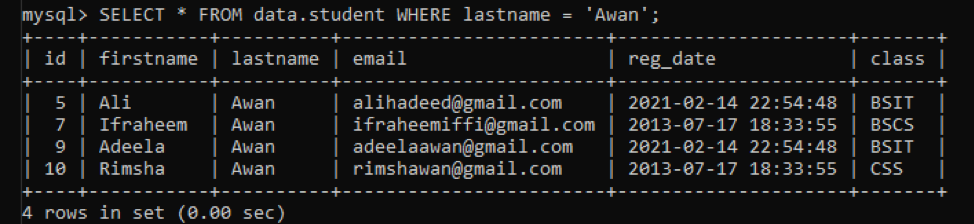
Let us update the table ‘student’ first by adding some records to it so we can delete multiple rows. Let’s display the records of a table where the lastname is ‘Awan’, using the ‘SELECT’ query with the only WHERE clause. This query will display only 4 rows, as we have only 4 records for the column ‘lastname = Awan’.
Example 01: Using LIMIT Condition in WHERE Clause
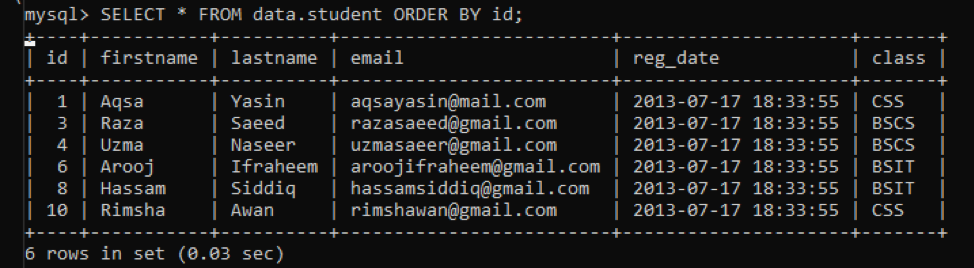
To delete multiple rows from a table, we can be using the ‘LIMIT’ condition in the ‘WHERE’ clause of the ‘DELETE’ query. We just have to define the ’LIMIT’ other than 1 or any negative number. So, we have been defining ‘LIMIT’ as ‘3’, to delete 3 rows from the table. It will delete the first three rows of the record having the ‘lastname’ as ‘Awan’.
Display the remaining records of the table using the ‘SELECT’ query. You will see, there is only 1 record left for ‘lastname’ having the value ‘Awan’, and three rows have been deleted.
Example 02: Using More than One Conditions in WHERE Clause
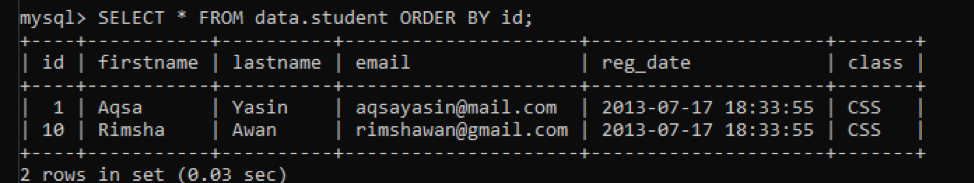
We are using the same above the table and defined two conditions in the ‘WHERE’ clause to delete rows having ‘id’ greater than 2 and less than 9 as follows:
We have only 2 rows left in the table while checking the records.
Example 03: Delete All Rows
You can delete all the rows from the table ‘student’ using the below simple query in the command line as:
While trying to display the records, you will get an empty set of tables.
Conclusion
We have taken a glimpse of different ways to delete single and multiple rows from a table while working in MySQL via the workbench and command-line client interface.