On Git, all the changes developers make, are stored in the Git log history. Users can view those changes whenever they want. However, sometimes, the commit history contains many unused commits that cause problems. So, it is preferable to delete the old history and keep the repository clean.
This article will explain the procedure of deleting all commit history in GitHub.
How to Delete/Remove all Commit History in GitHub?
There are different methods to delete commit history in GitHub, such as:
- Method 1: Deleting Commit History Using Orphan Branch
- Method 2: Deleting Commit History by Deleting the “.git” Folder
Method 1: Deleting Commit History Using Orphan Branch
To delete the commit history, first, switch to the local repository. Then, create a new temporary branch and navigate to it. Next, stage and commit all files in the temporary branch. After that, delete/remove the old “master” branch and rename the temporary branch to “master”. Lastly, update the GitHub branch forcefully.
Step 1: Navigate to the Local repository
First, redirect to the particular local repository using the below-listed command:
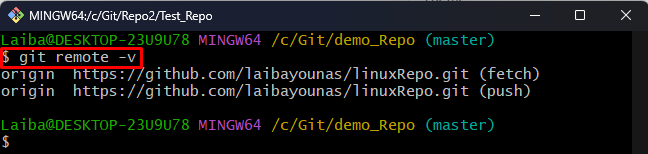
Step 2: Verify Remote Origin
Then, ensure that the local repository is linked to the remote repository:
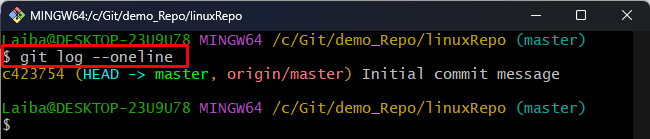
It can be observed that the current local repository is linked with the “linuxRepo” remote repository:
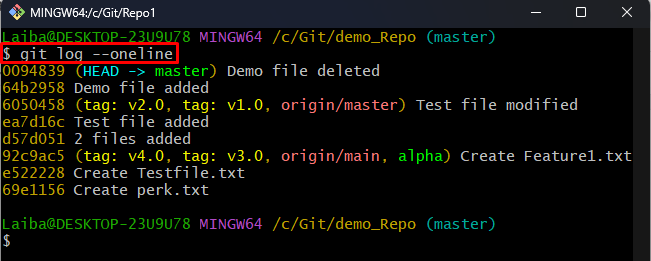
Step 3: View Commit History
Next, utilize the following command to display the commit history of the current repository:
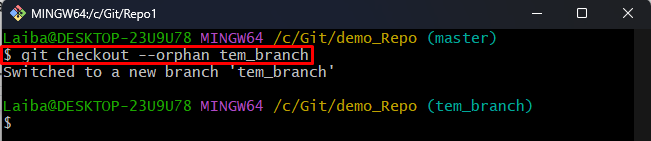
Step 4: Create and Switch to New Temporary Branch
Write out the “git checkout” command along with the “–orphan” option and desired new branch name to create and switch to it at once:
Here, “–orphan” option is used to create a “temp_branch” temporary branch with no history.
The below output indicates that the new branch has been created and we have switched to it:
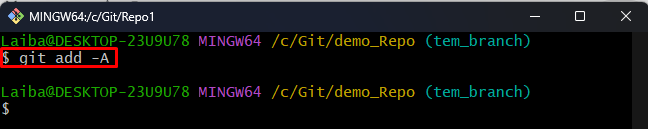
Step 5: Stage All File
Now, run the below-stated command to add all files to the Git index:
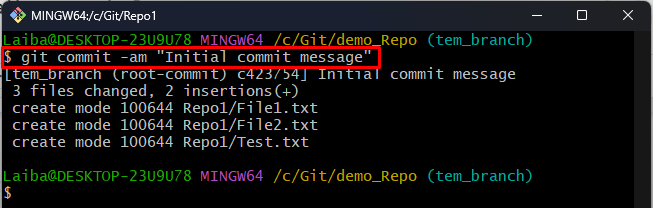
Step 6: Commit Changes
Then, commit modification in the temporary branch:
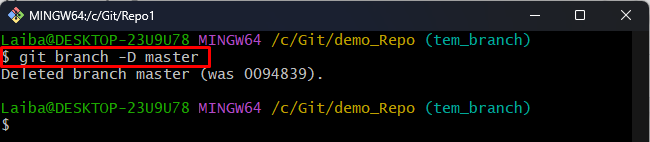
Step 7: Delete Old “master” Branch
To delete the old master branch, utilize the “git branch” command with the “-D” option and “master” branch name:
As you can see the “master” branch has been deleted:
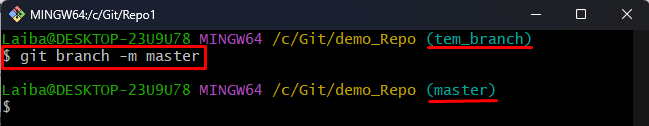
Step 8: Rename Temporary Branch to “master”
Now, use the given-provided command to rename the temporary branch to “master”:
It can be seen that the “temp_branch” has been renamed to “master”:
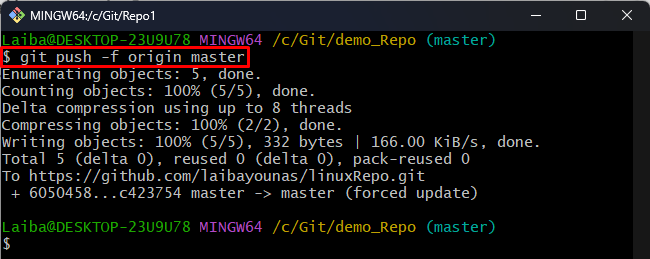
Step 9: Update Remote Repository
After that, push the new local changes to the remote repository and update it:
Step 10: Navigate to Remote Repository
Redirect to the cloned GitHub repository:
Step 11: Verify Changes
Lastly, execute the provided command to verify whether the commit history of the GitHub repository has been deleted or not:
It can be observed that all the old commit history of the “linuxRepo” repository has been deleted successfully:
Method 2: Deleting Commit History by Deleting the .git Folder
The “.git” folder has all the commit history. So, deleting the “.git” folder will delete all the Git commit history. To do so, follow the provided instructions.
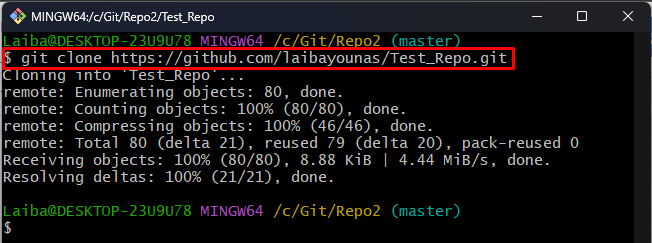
Step 1: Clone GitHub Repository
First, write out the below-listed command to clone the particular remote repository in the local repository:
Make sure to replace the <username> with the username of the repository owner.
Step 2: Redirect to Remote Repository
Then, use the “cd” command with the remote repository name and navigate to it:
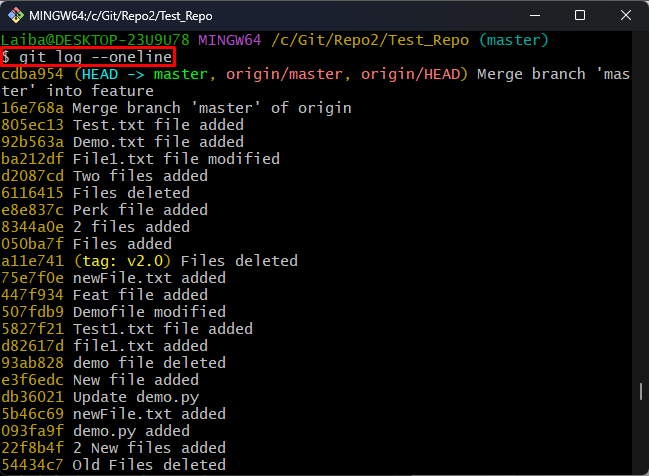
Step 3: View Commit History
Next, display the commit history of the remote repository:
In the below output the commit history of the GitHub repository can be seen:
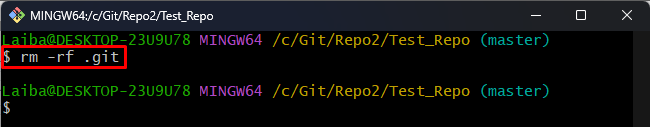
Step 4: Delete “.git” Folder
Now, delete the “.git” folder with the help of the below-stated command:
Step 5: Reinitialized the Repository
Use the provided command to reinitialize the repository:
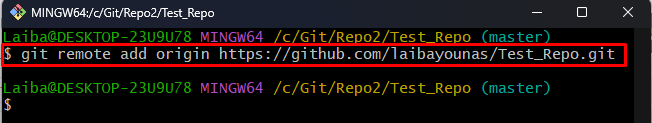
Step 6: Add Remote URL
Then, add the remote URL in the current repository:
Make sure to replace the <username> with the username of the repository owner.
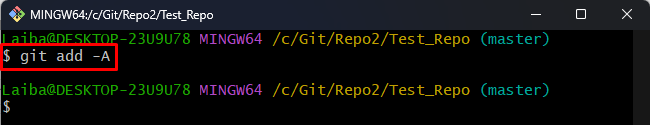
Step 7: Stage All Files
Next, add all files to the Git index:
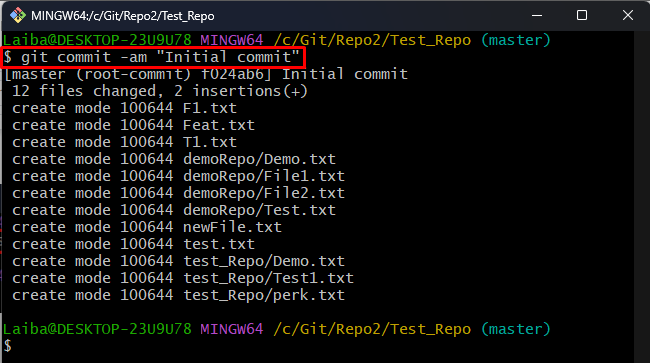
Step 8: Commit Changes
To commit all changes, enter the below-provided command:
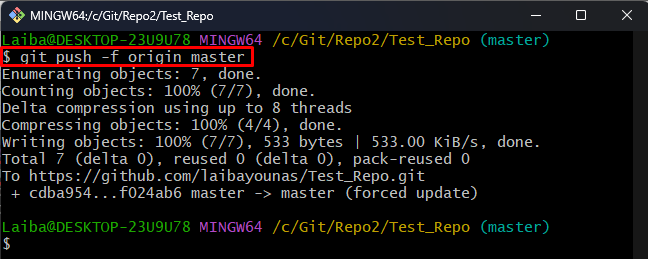
Step 9: Update Remote Branch
Lastly, push changes to the GitHub “master” branch and update it:
Step 10: Ensure Changes
To verify whether all the commit history of the GitHub repository has been deleted or not, run the following command:
As you can see, all the old commit history of the GitHub repository has been deleted:
We have efficiently explained the methods of deleting all the commit history in GitHub.
Conclusion
Different methods can be used to delete commit history in GitHub, such as using the orphan branch or deleting the “.git” folder. However, sometimes, deleting the “.git” folder can cause some problems in the repository. So, it is safe to create or make an orphan branch. It will delete all the log history and keep the code in its present state. This article explained methods of deleting all commit history in GitHub.