This study will explain the methods for creating a Java object.
How to Create an Object in Java?
To create an object in Java, you can utilize the below-listed methods:
Let’s look at the working of these methods one by one.
Method 1: Create an Object Using “new” Keyword
One of the most used approaches for creating an object or instance of the class is to use the “new” keyword. Almost all objects are created in this manner. It uses a constructor with or without passing any arguments.
When you use the new keyword to create an instance of a class, memory is allocated for the newly created object, and a reference to that object’s memory is also returned.
Syntax
Follow the given syntax to create an object in Java:
Example
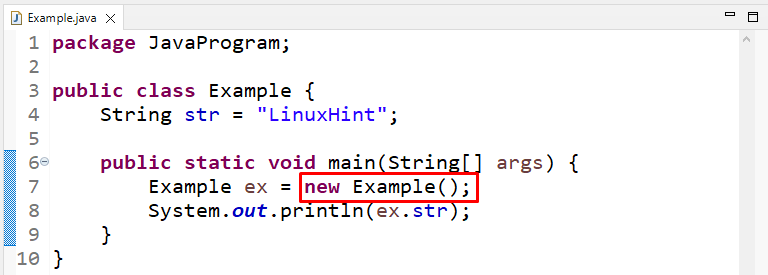
In this example, we will firstly create a String type variable named “str”:
Next, we will create an object “ex” of the “Example” class using the “new” keyword:
Then, we will print the value of String variable str using the created object:
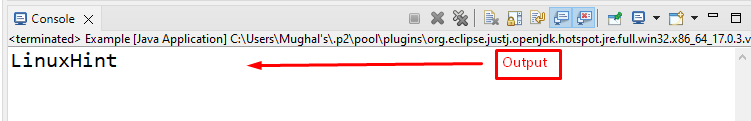
The output indicates that the object is successfully created, and it accessed the String value “LinuxHint”:
Let’s move to the next method for creating an object of the class.
Method 2: Create an Object Using clone() Method
Another method for creating an object is the “clone()” method that belongs to the “Object” class. It copies an object and returns it. When the clone() method is called, the JVM creates a new object. It copies the entire content of the previously created object into a new one. Keep in mind that it does not invoke any constructors.
Syntax
To create an object in Java using the “clone()” method, follow the syntax provided:
Example
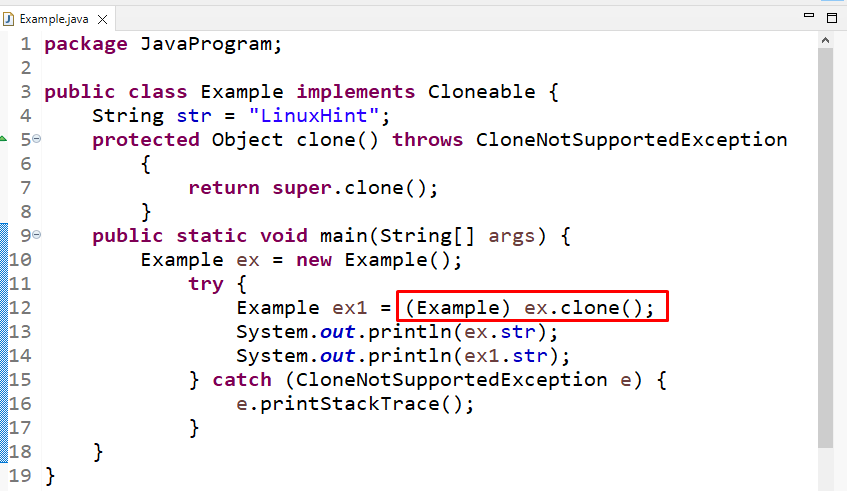
For cloning an object, we will first implement our class with the “Cloneable” class, and then we will override a “clone()” method by throwing the exception “CloneNotSupportedException” and then call the clone() method of the Cloneable class using “super” keyword which refers to the super class:
Then, in the main() method, first, we will create an object “ex” of the class, then clone the created object using the clone() method and print the string with both the object “ex” and the cloned object “ex1”:
Example ex = new Example();
try {
Example ex1 = (Example) ex.clone();
System.out.println(ex.str);
System.out.println(ex1.str);
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
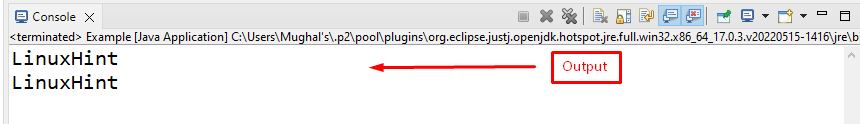
The output indicates that the object is successfully cloned and it copies the same result as an object:
Method 3: Create an Object Using newInstance() Method
In this section, you will learn how to create an object using the “newInstance()” method that belongs to the java.lang.Class. For creating the object, it calls the default constructor and returns a newly created instance of the class called the object of a class. It utilizes the Constructor class’ newInstance() method implicitly.
Syntax
For creating an object in Java with the “newInstance()” method, use the following syntax:
Example
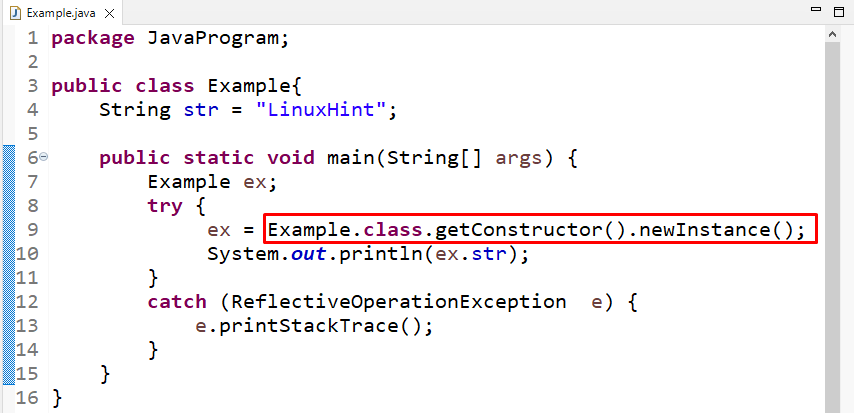
In the main() method, we will create an object of the Example class:
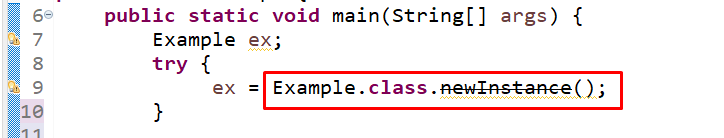
Here, we will use a try-catch block to handle exceptions. First we will call the “class.newInstance()” method, but in Java 9, the “newInstance()” method is deprecated:
To fix it, we will invoke the newInstance() method with the “getConstructor()” method:
In the catch block, we will pass the “ReflectiveOperationException” that creates a new exception with null as its detailed message. The cause is not initialized and may be initialized later with a Throwable called “Throwable. initCause(Throwable)”:
e.printStackTrace();
}
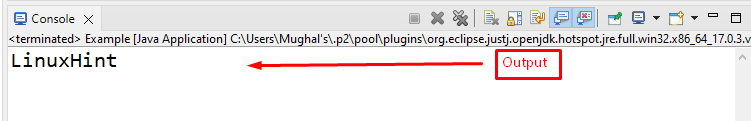
Output
We offered different ways for creating an object in Java.
Conclusion
For creating an object in Java, you can use different methods, including new keyword, clone() method, and newInstance() method. The new keyword is the most commonly used method for creating an object. The object can be copied using the clone() method. The class.newInstance() method of the Java Class is deprecated in Java 9; however, you can use it with the getConstructor() method. In this study, we explained the ways to create an object in Java.