This blog will define the methods for creating Java ArrayList.
How to Create an ArrayList in Java?
The ArrayList in Java implements the List interface, it extends the Collection interface, and also it is a subclass of AbstractList. As a result, we have the following options for declaring an ArrayList object:
Let’s go through the working of these approaches and how they help in creating an ArrayList in Java.
Method 1: Create an ArrayList in Java Using Collection Interface
In this section, we will create an ArrayList using a “Collection” interface that belongs to the java.util.Collections package. It converts all the elements of one collection to another one by one.
Syntax
Use the below syntax for creating an ArrayList using Collection Interface:
Here, “name” represents our ArrayList that is created using Collection Interface.
Example
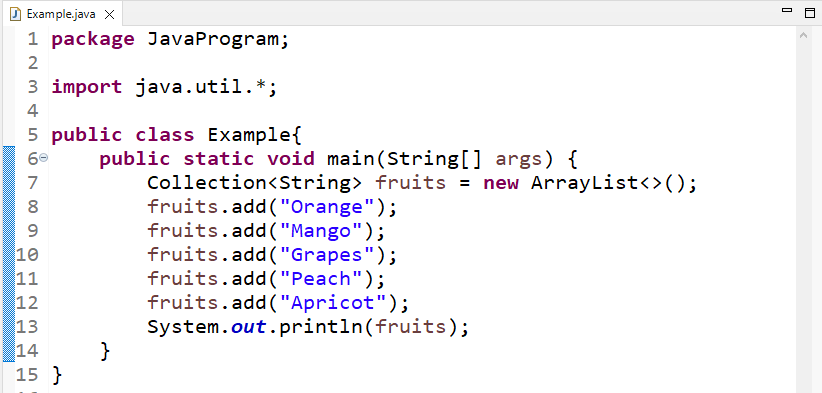
Using Collection Interface, we will create an ArrayList called “fruits“:
Then, add the elements in the ArrayList using the “add()” method:
fruits.add("Mango");
fruits.add("Grapes");
fruits.add("Peach");
fruits.add("Apricot");
Lastly, print the ArrayList on the console with the “System.out.println()” method:
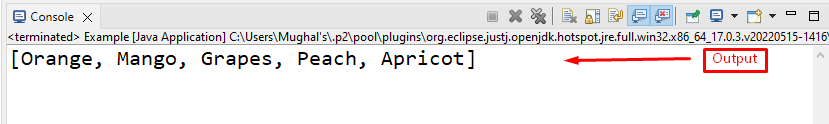
The output shows that the ArrayList is successfully created using Collection Interface:
Let’s try the List interface for the creation of ArrayList in Java.
Method 2: Create an ArrayList in Java Using List Interface
We will use the List interface for creating an ArrayList. It implements classes such as LinkedList, ArrayList, Stack, and so on. The List interface belongs to java.util, and it is a child interface of Collection. Like an Array, it is also index-based and permits you to store duplicate values.
Syntax
Follow the below-given syntax for using List to create an ArrayList:
Here, “name” represents our ArrayList that is created using List Interface.
Example
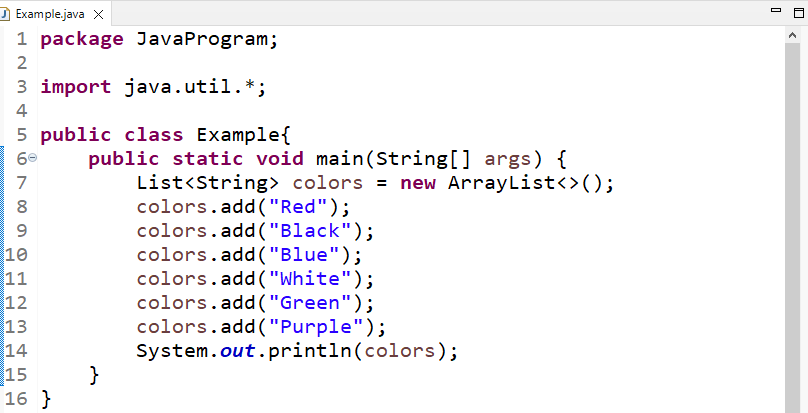
Create an empty ArrayList named “colors” using the List interface:
Call the “add()” method to add the elements in the ArrayList:
colors.add("Black");
colors.add("Blue");
colors.add("White");
colors.add("Green");
colors.add("Purple");
Finally, we will print the ArrayList elements on the console:
Output
If you want to create an ArrayList using the ArrayList class, then follow the below section:
Method 3: Create an ArrayList in Java Using ArrayList Class
In this section, we will create an ArrayList using the ArrayList class. The ArrayList class belongs to java.util package. This approach stores an element in a dynamic array with no size restriction. You can utilize all of the List interface’s methods because it implements the List interface. Moreover, the ArrayList keeps track of the insertion order implicitly.
Syntax
The following provided syntax will be used for the creation of an ArrayList using the ArrayList class:
Here, “name” represents our ArrayList that is created using the ArrayList class.
Example
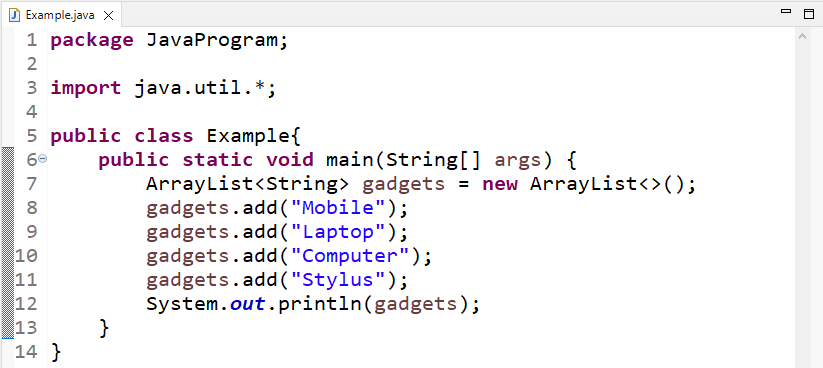
We will create a “gadgets” ArrayList using the ArrayList class:
Then, add elements in the ArrayList using the “add()” method:
gadgets.add("Laptop");
gadgets.add("Computer");
gadgets.add("Stylus");
Lastly, we will print the elements of ArrayList passing the ArrayList to the “System.out.println()” method:
Output
We have provided different approaches for creating an ArrayList in Java.
Conclusion
For creating an ArrayList in Java, you can use the Collection interface, List interface, and ArrayList class. All these approaches successfully created an ArrayList. The most commonly used approach by programmers for creating an ArrayList is utilizing the ArrayList class. In this post, we have provided different approaches for creating an ArrayList in Java with detailed examples.