Copying Files in Linux
You can use the graphical interface or command line to copy the files in Linux.
Method 1: Graphical Way
For anyone who is not comfortable with the command line, you can simply right-click on the file that you want to copy and select the copy option. Then, navigate to where you want to copy the file, right-click, and select the paste command.

Alternatively, you can use the “copy to” which opens the file system for you to navigate to your target directory.
Method 2: Command-Line Way
Copying the files in Linux is best when using the command line. Besides, Linux offers the cp command that you can use to copy the files from one directory to another by specifying its path.
There are various options that you can use with the cp command. The following is a quick cheat sheet:
- -v: Added to make the cp command verbose.
- -i: Added to make the cp command interactive, especially when copying the files into a directory that contains files with the same filename.
- -p: Added to copy a file and its attributes, such as access permissions and modification dates.
- -b: Added to create a backup of the file being copied to the destination folder, but with a different extension.
- -r: It specifies recursiveness and is used when you want to copy all files in a directory.
Let’s see how the cp command is used to copy the files.
Copying Files in the Same Directory
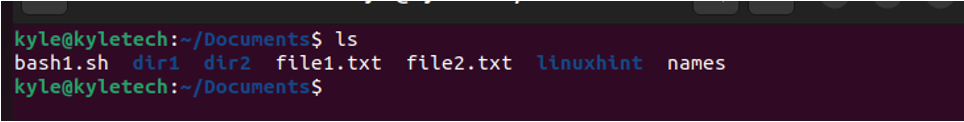
Suppose you want to copy the files to another directory in the same location. In that case, you only need to specify the file name or pattern and the target directory. We will use the files in the following image for this example:
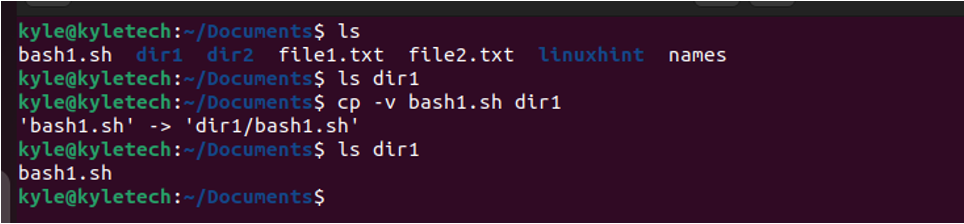
In the given image, if we needed to copy the bash1.sh to the folder dir1, the command would be:
Note that we added the -v option for verbose.
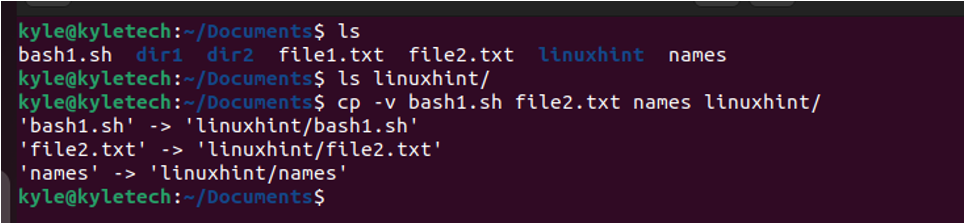
Also, if we need to copy more than one file, you must separate the file names with a space and list all the files that you want to copy.
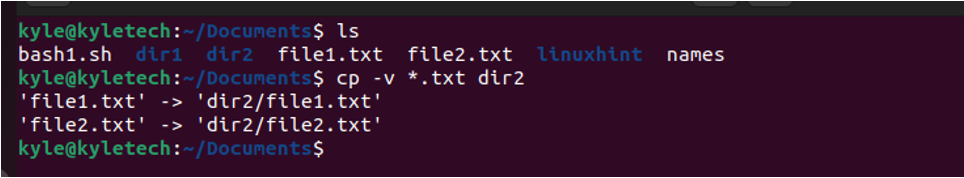
If you need to copy the files with the same extension, you can use the wildcard to match a given pattern. For instance, you could use the following command to copy all the text files. All files that match the pattern get copied to the specified directory.
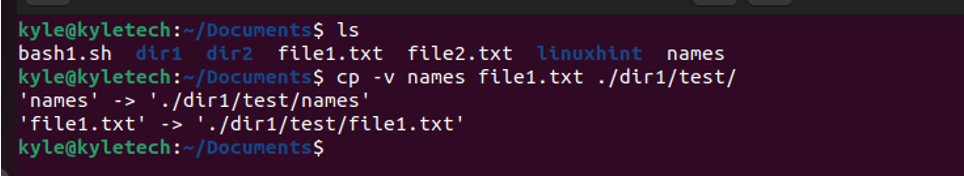
Suppose you wanted to copy the files to a subdirectory in the current directory; you must specify the path. For instance, if dir1 has a subdirectory named test and you want to copy a file to it, we could use the following command:
If you copy the files to a directory that contains the same filename, you will end up overwriting the existing files unless you add the -i option for interactivity.
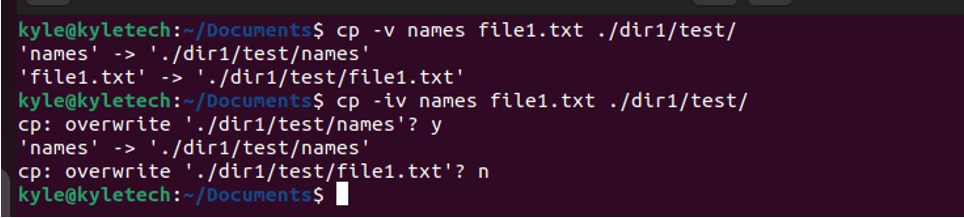
Let’s try to repeat the command in the previous example to see the error it raises and how you can choose to overwrite the existing files or not.
In the previous image, if you want to overwrite the files having the same names in the target directory, you must type y to the terminal, then press the enter key. If you don’t want to overwrite, press n.
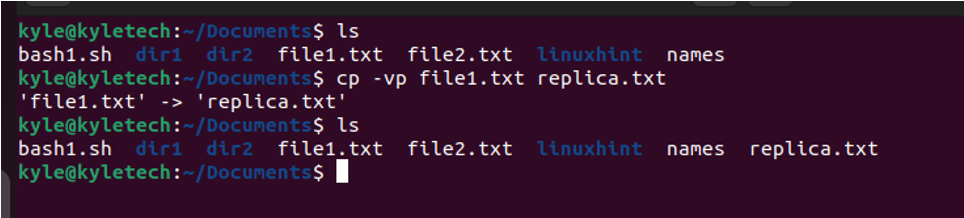
If you want to create a copy of a file in the same directory, you must specify the target file and the name of the replica file. For instance, let’s create a copy of our file1.txt called replica.txt, and let’s retain its attributes. In that case, the command would be as shown in the following:
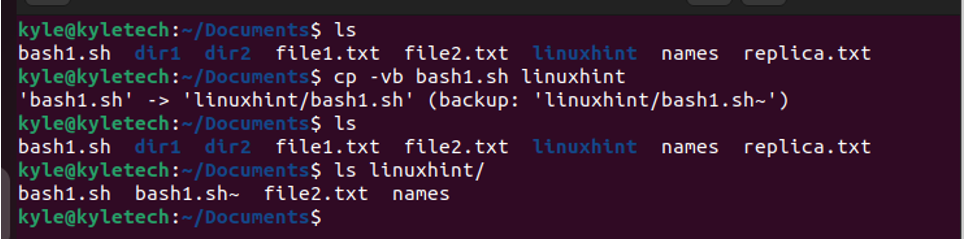
To create a backup of the file that you are copying, add the -b flag and note the new backup file that is created with a different extension. Let’s create a backup of bash1.sh to our destination folder. We now have a new backup named bash1.sh-
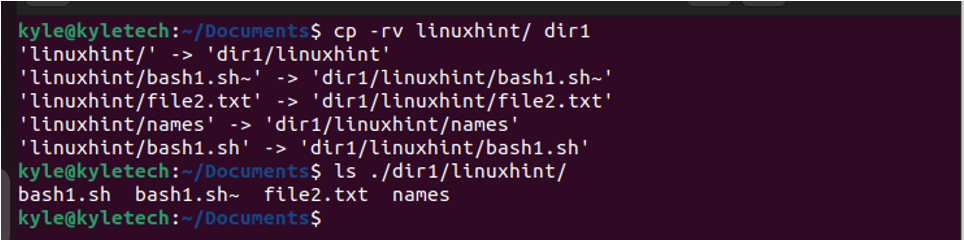
If you want to copy a directory and all the files, add the -r option and specify the path. For instance, in the following image, wecopied the linuxhint folder and all its contents to dir1.
Copying Files in Different Directories
When you must copy the files located in different directories, use the following syntax:
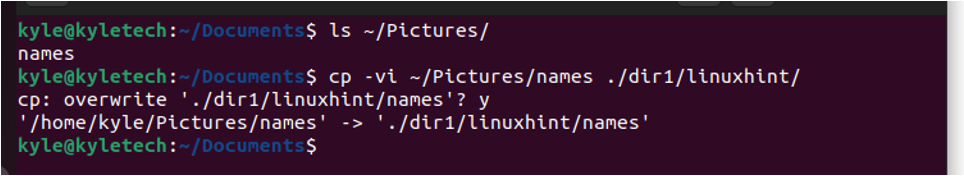
For instance, the command is shown in the following if we needed to copy a file in the /Pictures into the linuxhint sub-directory in the dir1.
The trick is to specify the exact path of the source file and the destination.
Conclusion
We’ve seen the various options that you have when it comes to copying the files in Linux. The commands described only need a little practice, and soon you will master how to copy the files in Linux using the command line.