This tutorial will illustrate the methods for converting the collection to a list in Java.
How to Convert Collection to List in Java?
For converting a collection to a list in Java, Java provides different methods listed below:
Let’s check out all of these methods one by one.
Method 1: Convert Collection to List in Java Using asList() Method
In this section, we will use the predefined “asList()” method of the “Array” class to convert a collection into a List.
Syntax
The provided syntax is used for the conversion of collection to list using the “asList()” method:
Example
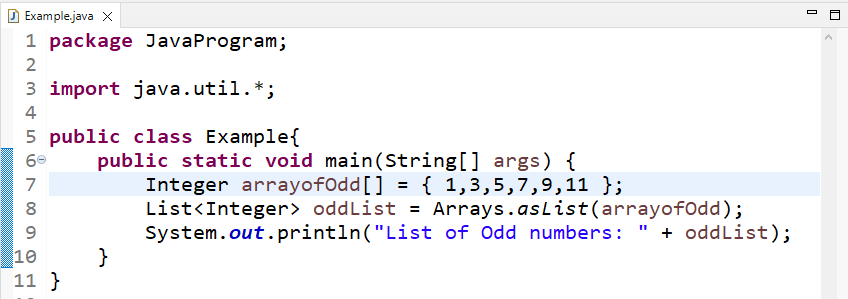
In this example, we will convert an array to a List that belongs to the Collection framework. To do so, we will create and initialize an Integer type array named “arrayofOdd”:
Call the “Arrays.asList()” method and pass “arrayofOdd” as an argument:
Finally, we will print the converted array to list on the console:
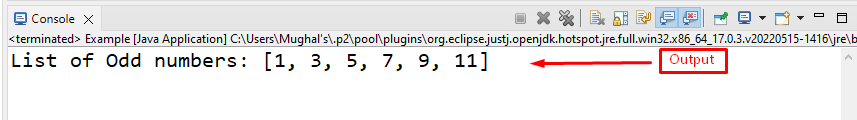
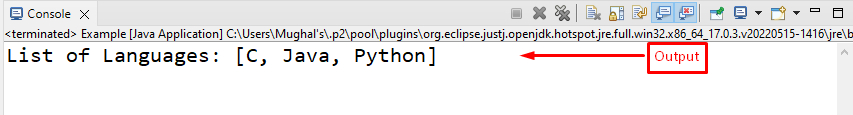
The output displays the list of Odd numbers:
Let’s move to another predefined method of Java for conversion of collection to list.
Method 2: Convert Collection to List in Java Using copyOf() Method
Here, we will use a “copyOf()” method of the “List” interface for converting a collection into a list. This method copies the elements of the collection into a list. It gives the unmodifiable list of the specified collection.
Syntax
Use the given syntax for “copyOf()” method to convert collection to list:
Example
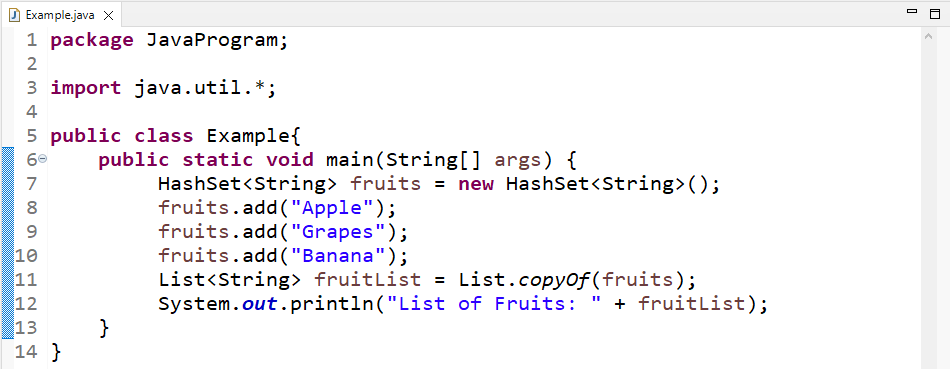
We will convert a HashSet collection into a list using the “List.copyOf()” method. Firstly, we will create a HashSet named “fruits”:
Then, we will add the elements in HashSet using the “add()” method:
fruits.add("Grapes");
fruits.add("Banana");
Call the “List.copyOf()” method by passing a HashSet in it as an argument:
Lastly, we will print the converted List from HashSet:
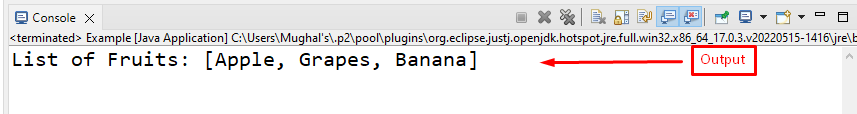
The output shows the list of fruits:
There is one more predefined method that belongs to the collection framework. So, let’s see how it works.
Method 3: Convert Collection to List in Java Using addAll() Method
Another method for converting a collection to a list is the “addAll()” method that belongs to the java.util.Collection package. It converts all the elements of one collection to another.
Syntax
Follow the given syntax of the “addAll()” method:
The method takes two arguments as a parameter, one is the converted collection, and the other one is the collection that needs to be converted.
Example
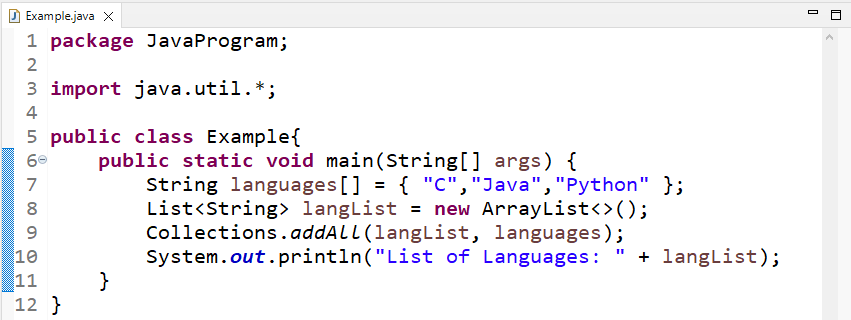
In this example, we will create a String type array named “languages”:
Next, we will create an ArrayList named “langList” that will store the elements of the String array:
Now, in the Collections.addAll() method, we will pass the array “languages” and the list “langList” as arguments:
Finally, we will print “langList” on the console using the “System.out.println()” method:
Output
Is there any method except predefined methods of Java for converting collections to lists? Yes! Follow the next given section.
Method 4: Convert Collection to List in Java Using for Loop
Except for Java predefined methods, we can also convert the collection to a list using the “for” loop. It is the most basic and easy method of conversion.
Syntax
The following syntax is used for the conversion of a collection to a list using the “for” loop:
Example
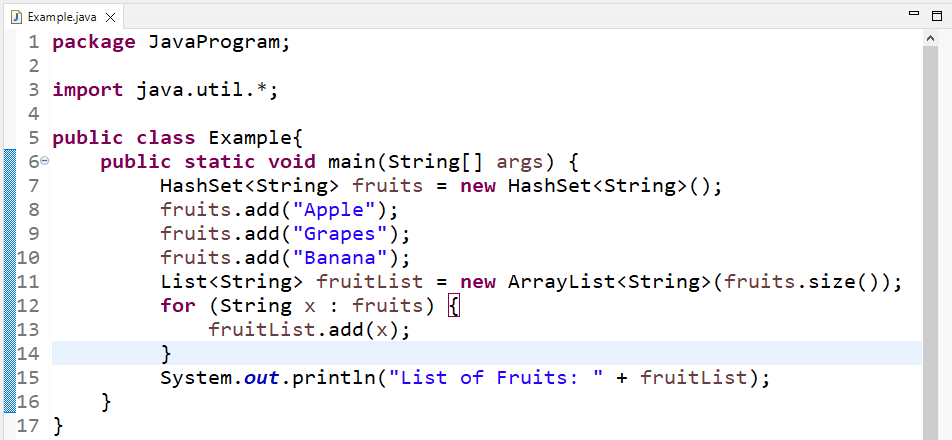
We will now convert the already created HashSet to a list using a “for” loop. First, we will create a list equal to the size of the HashSet in which the HashSet elements will be stored:
In the for loop, we will add the elements of “fruits” HashSet to the list using the “add()” method:
Finally, we will print the list converted from HashSet:
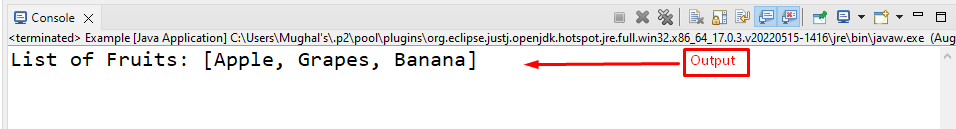
Output
We gathered all the methods for the conversion of collection to list in Java.
Conclusion
For converting collection to list, Java provides multiple predefined methods, including Arrays.asList(), List.copyOf(), Collections.addAll(), and a for loop. Using a for loop is the simplest and beginner-level method that can be understandable for everyone. In this tutorial, we illustrated the different methods of converting a collection to a list in Java with detailed examples.