This guide will cover how to:
- Grant Create Materialized View Privilege
- Create a Materialized View
- Refresh a Materialized View
- Set the Size for a Materialized View
- Monitor the Refresh Time for a Materialized View
- Rebuild a Materialized View
Configuring for Materialized Views
To start with the configuration for materialized views you need to login to the Oracle database as a system administrator. To do that, use the “SQLPLUS” command or the “SQL developer” tool.
How to Grant Create Materialized View Privilege?
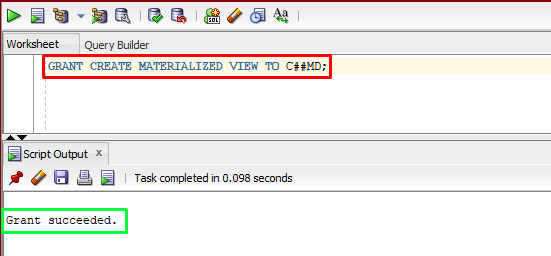
To grant the create materialized view privilege to any specific user, the “GRANT” command with the “CREATE” statement can be used. The example is given below:
In the above example, “C##MD” is the user.
Output
The output showed that a privilege has been granted to the user.
How to Create a Materialized View?
In Oracle, the “CREATE” statement can be utilized to create a materialized view.
Example 1: Creating a Materialized View
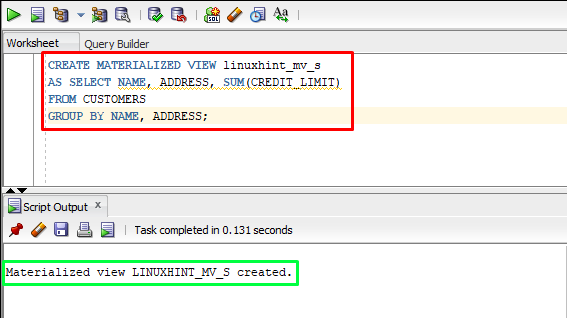
Let’s see an example of creating a simple materialized view:
AS SELECT NAME, ADDRESS, SUM(CREDIT_LIMIT)
FROM CUSTOMERS
GROUP BY NAME, ADDRESS;
In the above example, “linuxhint_mv_s” is the materialized view of the “CUSTOMERS” table. Various columns including the NAME, ADDRESS, and CREDIT_LIMIT along with the SUM() function are specified in the select list.
Output
The output depicts that the materialized view of the CUSTOMERS table has been successfully created.
Example 2: Creating a Materialized View With a Specific Condition
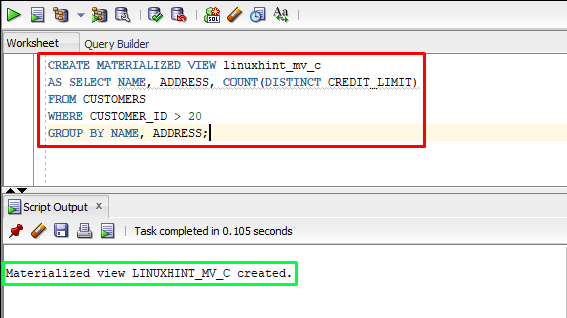
Let’s see another example of creating a materialized view, with a particular condition:
AS SELECT NAME, ADDRESS, COUNT(DISTINCT CREDIT_LIMIT)
FROM CUSTOMERS
WHERE CUSTOMER_ID > 20
GROUP BY NAME, ADDRESS;
In the above example, only those rows will be included in the materialized view where the value of CUSTOMER_ID is greater than 20.
Output
The output showed that the materialized has been created under a specific condition.
How to Refresh a Materialized View?
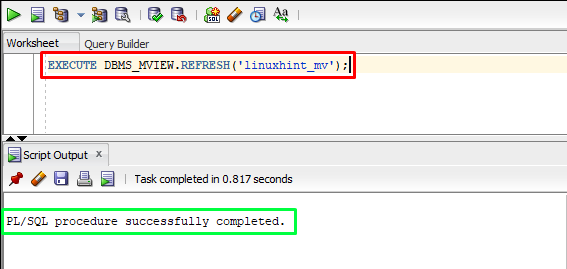
To refresh a materialized view “DBMS_MVIEW.REFRESH” can be used which is a PL/SQL procedure in the Oracle database. The command to refresh a materialized view is given below:
In the above command, “linuxhint_mv” is the materialized view.
Output
The output showed the materialized view has been refreshed.
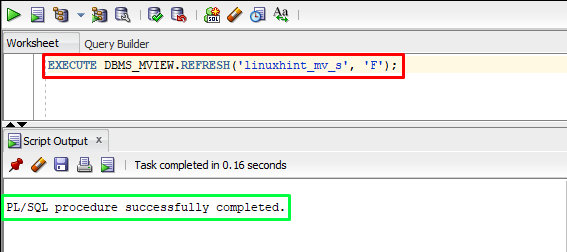
If the user wants to perform a fast refresh for a materialized view, then pass the “F” flag as the argument to the “DBMS_MVIEW.REFRESH”. This will refresh the materialized view based on the changes that have occurred in the base tables since the last refresh, which makes it faster than a complete refresh. The example is given below:
In the above example, “linuxhint_mv_s” is the materialized view.
Output
The output portrays the materialized view has been successfully refreshed.
How to Set the Size of a Materialized View?
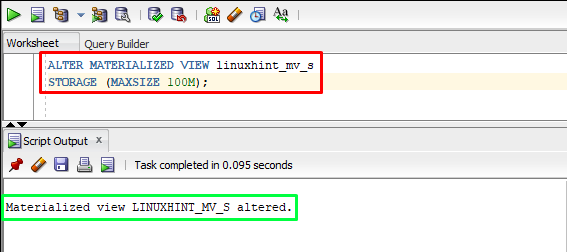
To set the size for a materialized view, the “ALTER” command can be used with the “STORAGE” clause. This clause allows you to specify the amount of disk space that the materialized view should use. The example of setting the maximum size for a materialized view is given below:
STORAGE (MAXSIZE 100M);
In the above example, the “linuxhint_mv_s” is a materialized view.
Output
The output depicts that the materialized view has been altered.
How to Monitor the Refresh Time for a Materialized View?
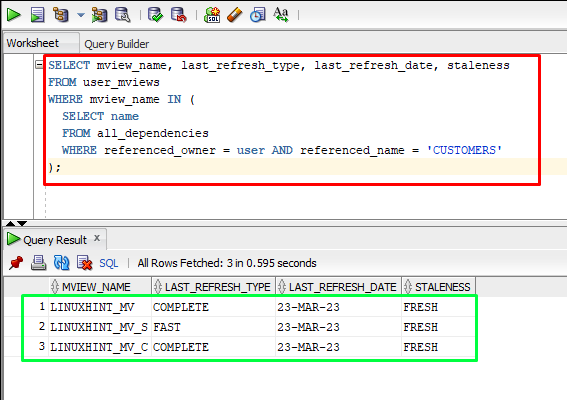
To monitor the refresh time for a materialized view simply use the “SELECT” statement to display the information of “user_mviews”. The command is given below:
FROM user_mviews
WHERE mview_name IN (
SELECT name
FROM all_dependencies
WHERE referenced_owner = user AND referenced_name = 'CUSTOMERS'
);
Output
The output showed the refresh time for a materialized view.
How to Rebuild a Materialized View?
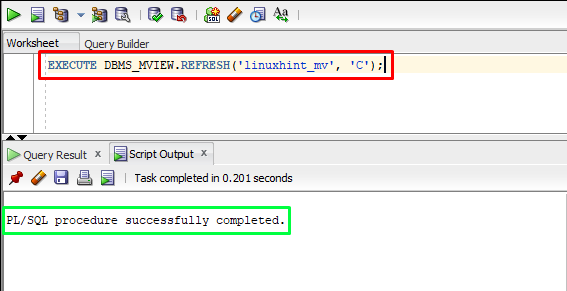
To rebuild a materialized view, you can perform a complete refresh by using the “C” flag in the DBMS_MVIEW.REFRESH, as given below:
Output
The output depicts that the materialized view has been refreshed.
Conclusion
The configuration of materialized view includes granting the create materialized view privilege, creating a materialized view, refreshing a materialized view, setting the size for a materialized view, monitoring the refresh time for a materialized view, and rebuilding a materialized view. This guide explained the steps to configure for materialized views.