In this guide, you will learn to configure the sources.list on Debian11.
What is sources.list File in Debian Linux
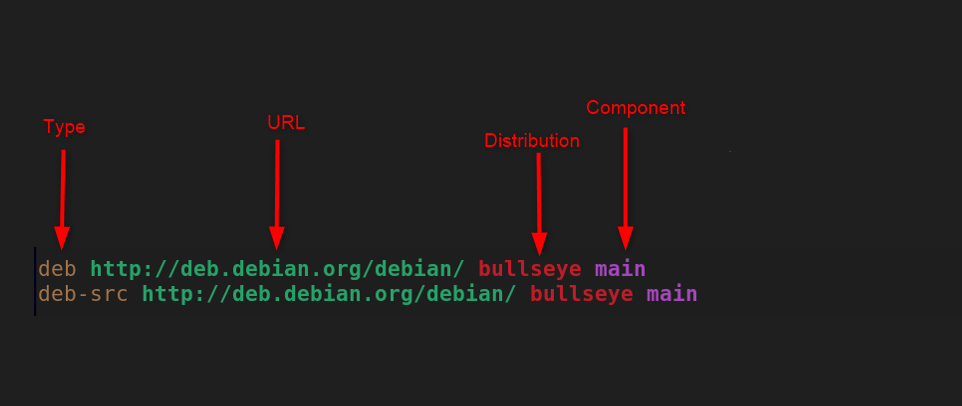
In Debian, the sources.list file is a configuration file that includes the list of repositories that a certain package requires during the installation. It allows users to directly install a package from the source repository of the Debian system. Whenever you run the apt or apt-get command, the package management system uses the information in the sources.list file and check whether the given package is available in the source repository. If it’s available, the package manager will install it on your Debian system. The repositories inside the sources.list file has the following format:
The source repository consists of:
1: Archive Type
The first term in the above format is the archive type. On Debian-based systems, you will find only two archive types including deb and deb-src. The deb is the repository of binaries and the deb-src is the repository of the packages in the source file format.
2: URL
The URL is the server that stores all the files of the packages and databases. This represents the location of the package from where you are downloading it.
3: Distribution
The third format distribution represents the release code name of a version of your Debian system.
4: Component
The last is the information type of the repository. You will find four types main, universal, multiverse, and restricted.
Debian users can modify the sources.list file according to their choice by adding or removing repositories, enabling, or disabling any repository in the system, and more. It will help users install a specific package version on the system.
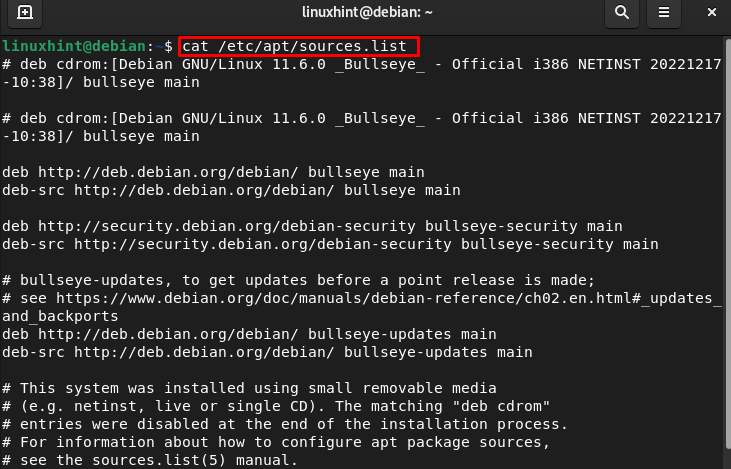
You can check the sources.list in Debian 11 by executing the following command:
Open the sources.list on Debian
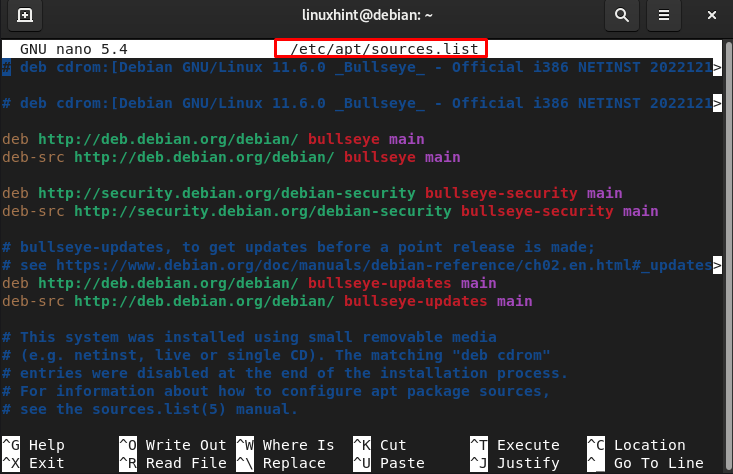
You can open the file /etc/apt/sources.list file in nano or any other editor in the terminal:
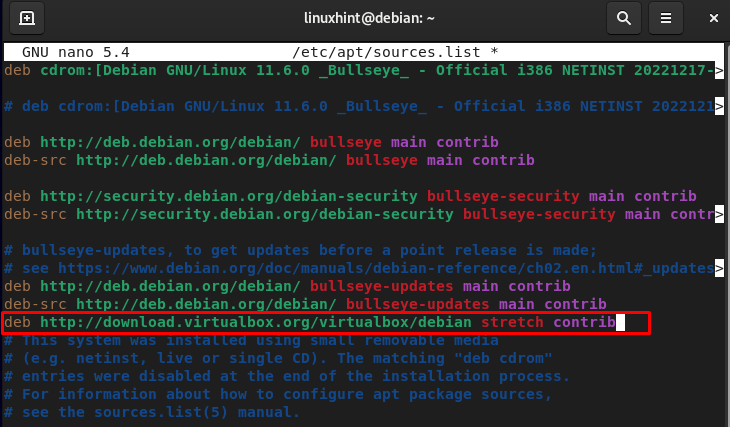
How to Add a Repository Using the sources.list File
Once you open the sources.list file on the terminal, you can edit it. For example, you want to add the virtual box repository in the file, then copy and paste it into the file and save it.
After adding the repository, save the file using Ctrl+X, add Y and press enter. Then run the following command to successfully update the added repository into the system.
After that, you can install a package associated with that repository.
Bottom Line
The sources.list supports the active sources and variety of source media and .d provides the way to add sources.list in a separate file. Debian uses the APT package manager. Apt is configured via the /etc/apt/sources.list, you can edit and make changes to this list by opening it on the terminal using nano editor.