One thing that tends to be a little confusing for beginners is the concept of MySQL collation and character sets. Although it is not a complex feature, it trips a few people, especially No-SQL developers. This is because No-SQL databases do not have such features.
In this article, we will explore the concept of MySQL collation and how we can check the collation type of a given input string.
What is Collation in MySQL?
A collation refers to a set of rules defining how MySQL database characters are compared and sorted. Each character set in MySQL is mapped to its unique collation within the MySQL engine. However, a character set can have one or more collations.
If you wish to explore the documentation of character sets and what each represents, check out the IANA resource below:
https://www.iana.org/assignments/character-sets/character-sets.xhtml
MySQL View Available Collations
To view the collations that are available in your system, you can use the command shown below:
Start by loggin in to your MySQL shell:
Enter password: *****
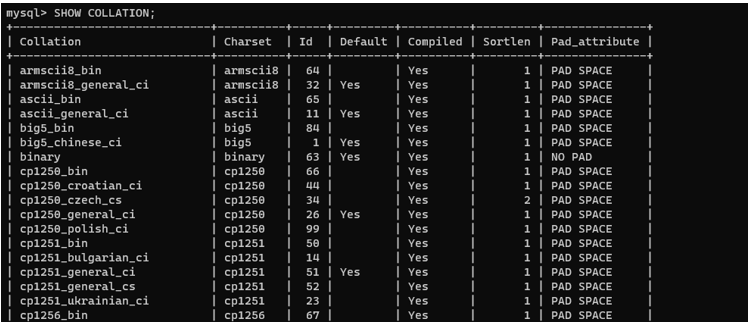
Once logged in, run the query below to list all the collations on the server.
The query lists a table with the various collations’ information and attributes.
Note that the above image has been truncated to fit the purpose of this tutorial. This is because MySQL provides a wider range of collations than illustrated above.
MySQL Check String Character Set
Sometimes, you may want to determine a specific string’s character set or collation. For example, in MySQL, we can use the charset() function to determine the string of a particular function.
To illustrate, create a table as shown:
str CHAR(10) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci
);
The query above creates a table called sample_table with the character set of utf8 and the collation of utf8_general_ci.
You can change either the character set or collation as you see fit.
We can then insert some data as shown:
sample_table(str)
values
('HÉLLO'),
('HÊLLO'),
('HËLLO');
The code above inserts some sample strings into the table.
To check the character set of a string, we can run:
charset('HËLLO');
The code above should return the character set of the provided string as:
To list the character set of the strings in the table, we can run:
charset((select str from sample_table));
Similarly, the code should return the character set of the strings in the table:
MySQL Check String Collation
We can also use the collation function to get the collation of a specific string, as shown in the example below:
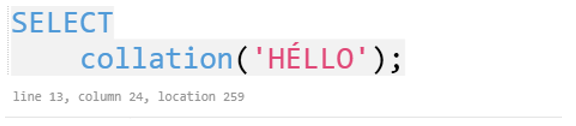
collation('HÉLLO');
The code should return the output as shown:
To get the collation of the strings in a table, we can run the code:
collation((select str from sample_table));
The code above should return:
Conclusion
This article covered the basics of MySQL collation and character set features. We also discussed how you could determine a given string’s character set and collation.