This article will explain the procedure of cloning the Git repository with specific revisions.
How to Clone Git Repository With Specific Revision/Changeset?
To clone a specific revision of the Git repository, try out the below-stated steps:
- Go to the required local repository
- Set remote URL to the local repository
- Get the last commit hash of the remote repository
- Fetch the last commit with its hash
- Reset the repository to the desired commit
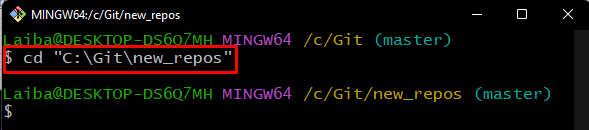
Step 1: Navigate to Repository
Move to the desired repository by utilizing the given command:
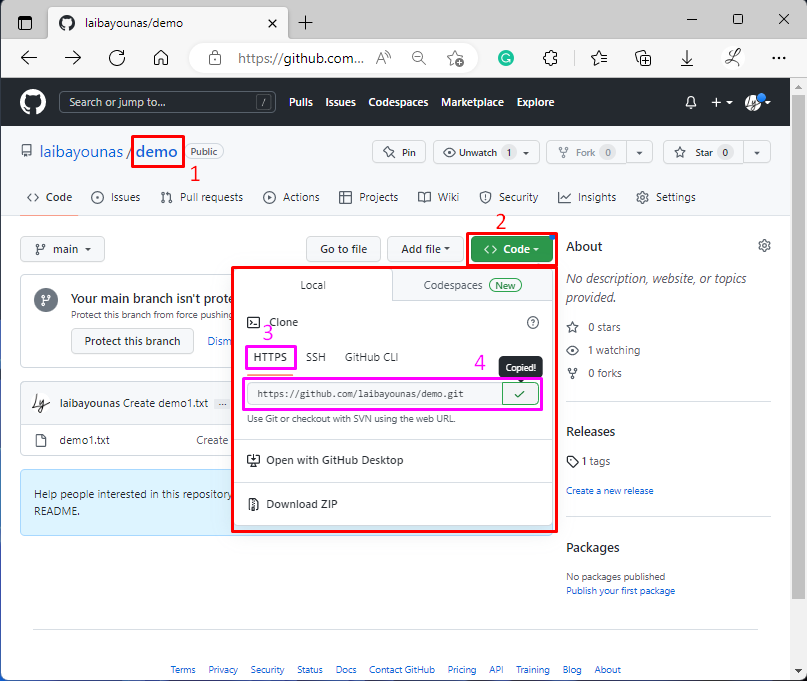
Step 2: Copy Remote URL
On GitHub, choose your desired remote repository and copy its “HTTPS” URL to the clipboard:
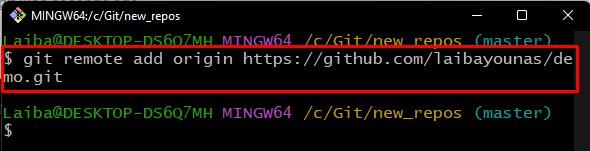
Step 3: Add Remote URL to Local Repository
Run the “git remote add” command to connect the remote repository with the local repository for further processing:
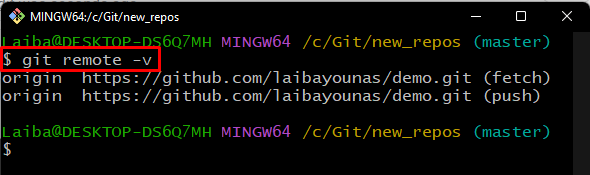
Step 4: Verify Added Remote Origin
Now, verify whether the remote origin has been added or not by executing the below command:
Step 5: Get Remote Repository Last Commit Hash
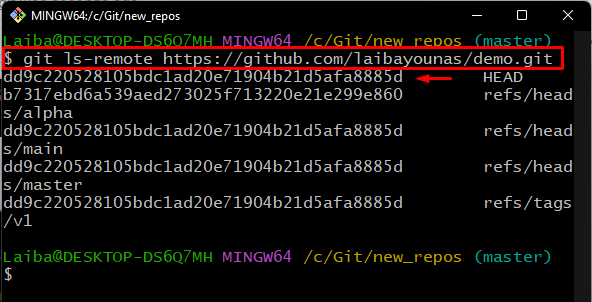
Utilize the “git ls-remote” command along with the remote URL to get the list of commit hashes from the remote repository:
The below output shows the list of all remote repository commits. Now, select the required commit hash. For instance, we have selected the “dd9c22…” remote commit hash:
Step 6: Fetch Origin With Commit Hash
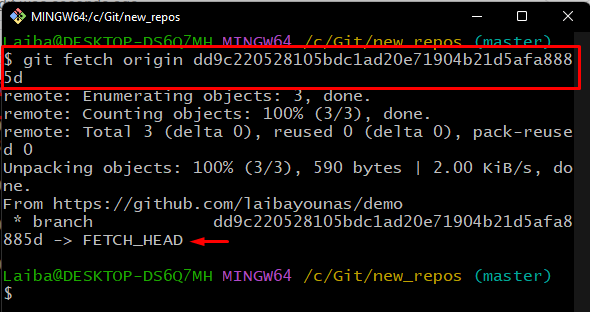
Then, download the content of origin by specifying the desired commit hash with the “git fetch” command:
As you can see the required commit hash revision is fetched successfully:
Step 7: Reset Repository to Commit
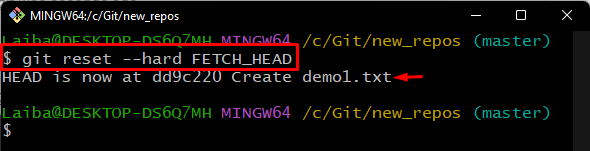
Lastly, run the “git reset” command along with the “–hard” flag and fetched HEAD pointer to reset the local repository pointer to the particular remote commit:
We have compiled the method of cloning the Git repository with a specific revision on the local repository.
Conclusion
To clone the Git repository with specific revisions, navigate to the local Git repository. Then, open GitHub, move to a desired remote repository and copy its URL. After that, connect the local repository to the remote repository by setting the remote URL. Get the last commit hash from the remote repository and fetch it with the help of “$ git fetch origin <commit-hash>”. Lastly, run the “$ git reset –hard FETCH_HEAD” command to reset the repository HEAD pointer to that specific commit. This article illustrated the process of cloning the Git repository with a specific revision/changeset.