Why Check Disk Space?
It is essential to monitor disk usage frequently since insufficient disk space might cause numerous services on your system to break. Furthermore, there are regular updates in Linux distributions that need adequate space for installation. As a result, you must ensure that sufficient disk space is accessible.
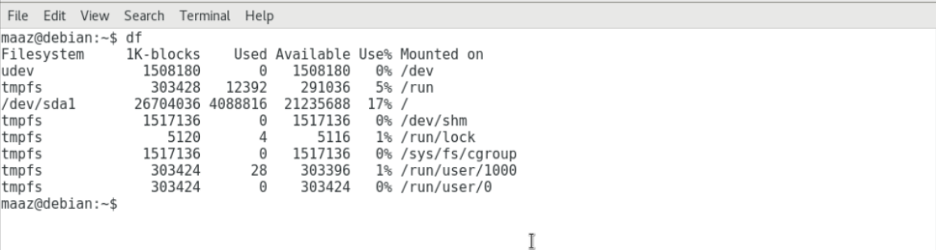
One can check Disk Space using the df command.
This command gives information about the total space consumed and available on your disk.
The syntax for the command is:
If no option is given, this command outputs the space used and available on all the file systems.
Below is the table showing the meaning of each column in the above command
| Column Name | Valid Field Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Filesystem | source | This column displays the mount point source. This is usually an external device. |
| 1K-blocks | size | Display the total quantity of blocks present in the disk. |
| Used | used | Displays the number of blocks used. |
| Available | avail | Displays the number of available blocks. |
| Use% | pcent | Displays percentage of used space |
| Mounted on | target | Specifies the mount point. |
To get disk information of a particular file, use the following command.
Output
/dev/sda2 69872174 57721420 12150754 82.6% /home
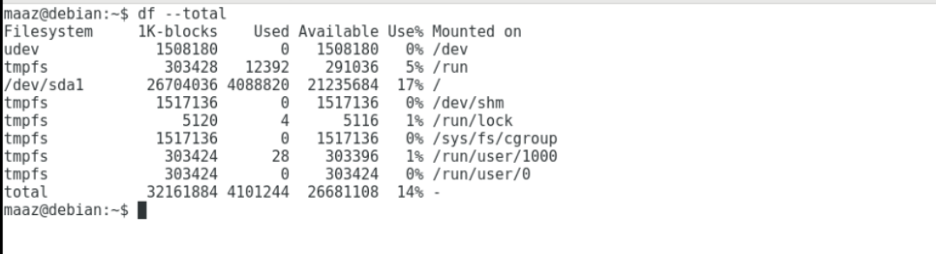
To get total space usage and availability on our disk, use the –total option with the command.
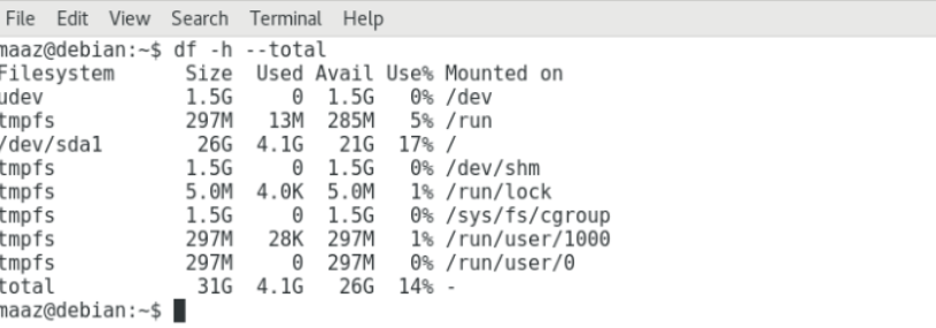
To check disk space in powers of 1024, use the -h option with the command.
Conclusion
This article went through a detailed discussion regarding checking disk usage in your Debian Operating System. We discussed the df command to extract information about the disk. This command provides detailed information on the file systems through various options.