For these rounding operations, the C language provides a set of functions included in the “math” library. To rounnd a variable to the nearest integer, there is the ceil() function. To round to the nearest integer, there is the floor() function.
In this Linux Hint article, you will learn all about using the function to round the fractional values to the nearest integer. To help you better understand and master this function, we created practical examples with code fragments and images that show its use with different types of input variables. We also give you a theoretical description of this function, its syntax, input and output arguments, and the data accepted in it.
Syntax of the Ceil() Function in C Language
Ceil() Function Description in the C Language
This function rounds to the next larger integer value of the numeric variable whcih is specified in its input arguments. The ceil() function is one of a set of functions provided by the “math” library and is defined in the “math.h” header. To use this function, we must include it in our “.c” file as follows:
Once the “math.hy” header is included, we can use ceil() to round up or the floor() to round down, as well as all the functions in the math libraries. To get the rounding of “x”, you must call this function by specifying the variable name in its input argument. The ceil() returns the result in “a”.
Example: How to Round a Fractional Integer with the Ceil() Function in Linux GCC
In this example, we will see how to round a fractional value to the next larger integer using the ceil function in gcc.
The following code snippet shows how to use the ceil() function to get the rounding of double “x” that has an assigned value of 3.1416. Then, the printf() function is used to output the result as “a” on the command console.
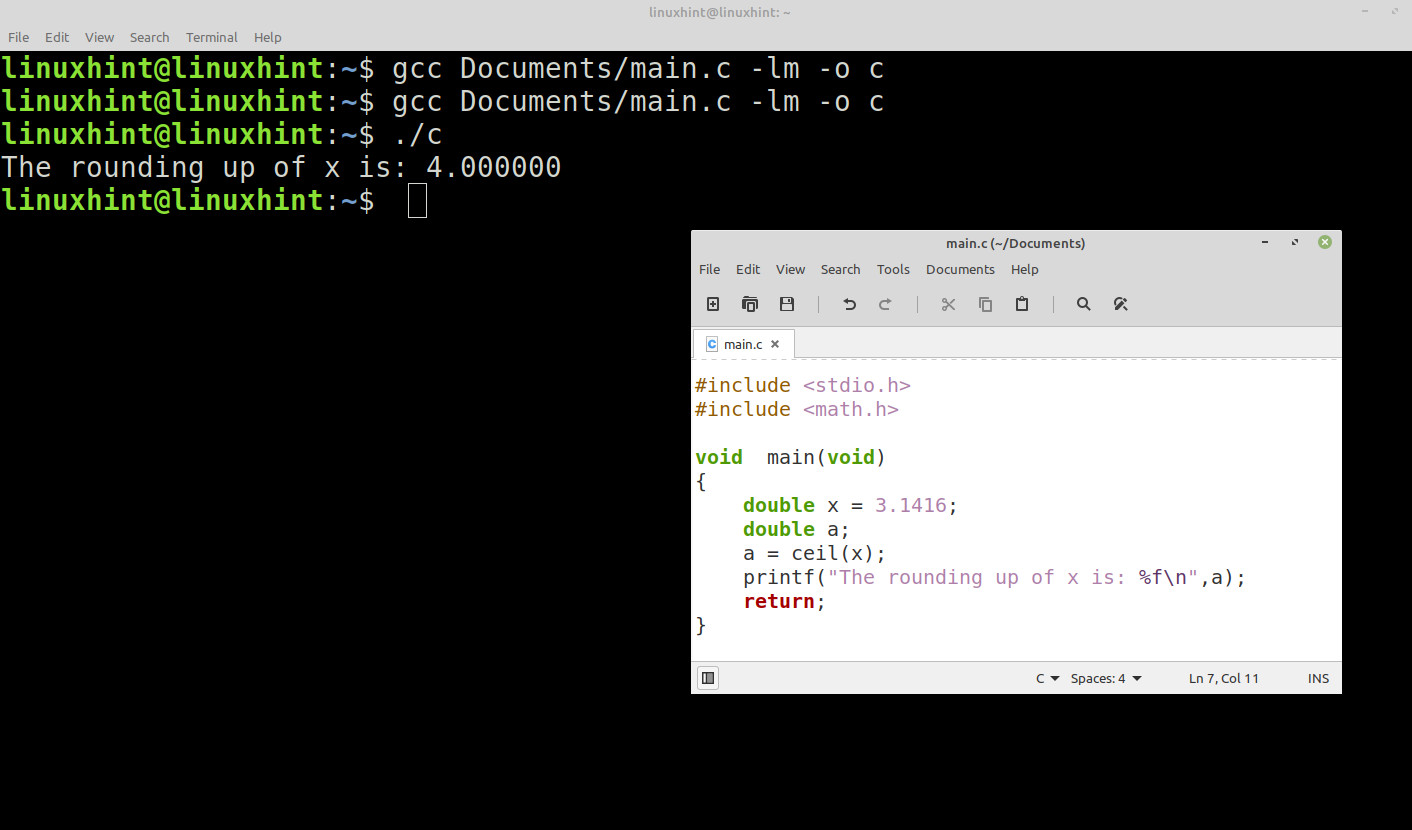
In the following image, we see the result in the command console. In this case, it is the rounding of 3.1416 is 4.00000:
Common Problems with the Ceil() and Floor() Rounding Functions and How to Solve Them
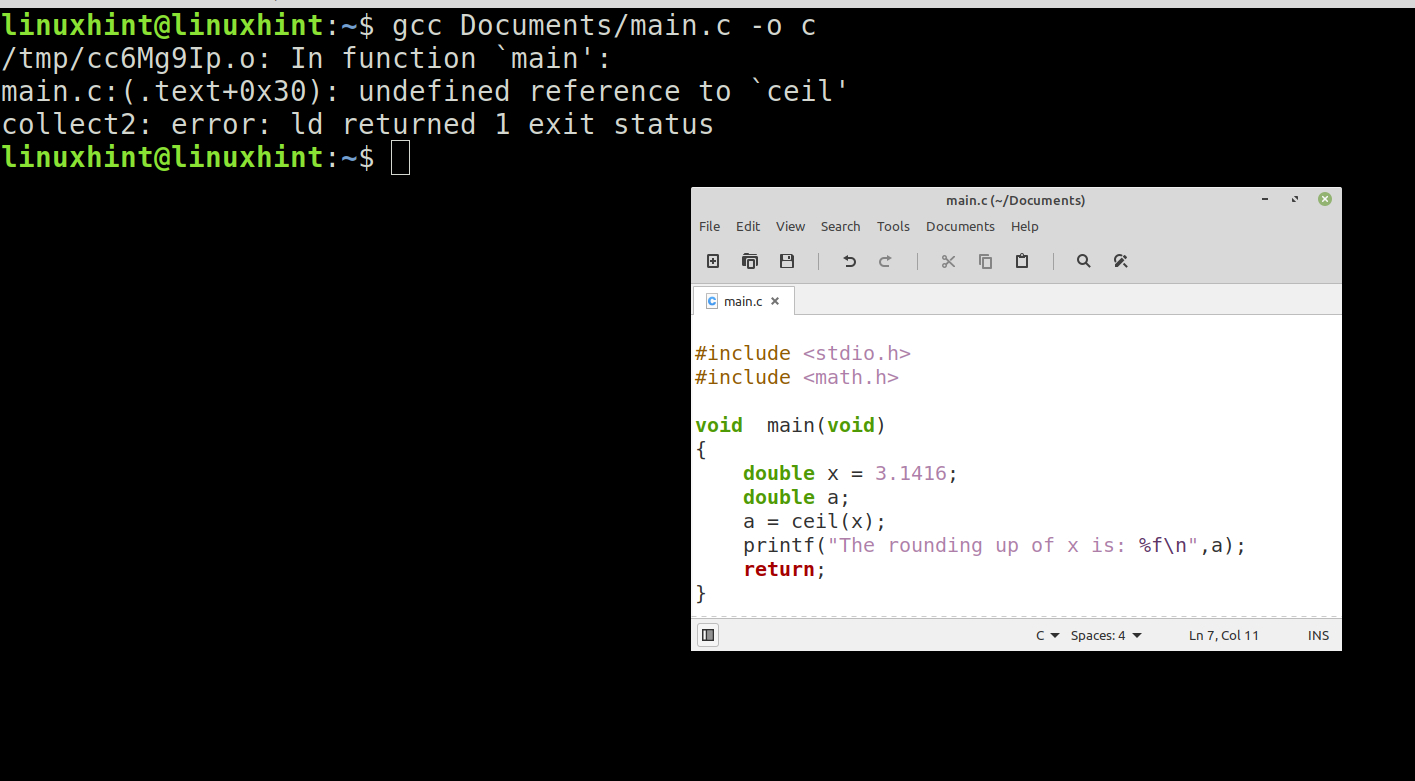
When we use the functions and compile our code, it often happens that the compilation gives the following error:
This causes us to look for syntax errors or undefined variables in our “.c” or “.h” code since everything indicates that our problem lies there. But this leads to a loss of valuable time since our problem lies in the linking of the libraries and the data compatibility of these functions.
For programmers who like to know the reason for a problem and not just solve it, we will explain this error step by step to make the programming work more fluent and avoid loading unnecessary libraries for our code.
To explain this, we compile the code from the previous example as follows. In the following figure, we see the compilation of our code and the error that is referred to in this section:
This is because since C99, gcc splits its libraries into two parts – libc and libm. Although the library we refer to in our code is found in both, the data types that these functions accept in each of their versions are different, and that is the source of the problem. If the ceil() function is called with an int as input, the error disappears, although the rounding down occurs.
These problems are fixed at compile time by invoking the libm library on the command line that we use to compile. The following is the path:
Conclusion
In this Linux Hint article, we showed you how to use the ceil() function to round the fractional values to the nearest integer. We explained step by step on how to load the “math” library to use this function. We also showed you one of the most common errors when using this function and how to fix it to get a smooth programming task. We hope that you found this C language article helpful. See other Linux Hint articles for more tips and information.