So, before digging into details, let’s have a look at the syntax of the command:
How to use the cd command in Ubuntu
The syntax of the cd command is easy to understand and apply in the terminal: this section will provide a detailed guide to use the cd command in Ubuntu.
As the cd command is concerned with directories; so, we must know the current directory. Type the command stated below to check the present working directory
As you can see, the present working directory is “/home/adnan“.
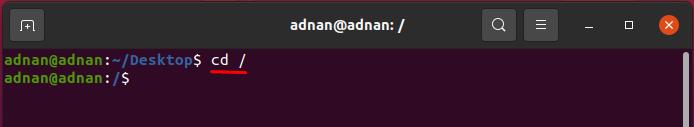
How to change the current directory to root directory using the cd command
It does not matter in which directory you are; if you want to move the terminal to the root directory, you must put “/” after the “cd” keyword. For instance, we are in the “Desktop” directory and want to go to the root directory, execute the command as given below:
How to change the current directory to home directory using the cd command
If you want to move the present working directory to the home directory, use the following symbol “~” (known as the tilde) with the “cd” keyword. Let’s say we are in the “Pictures” directory; use the following command to get back to the home directory:
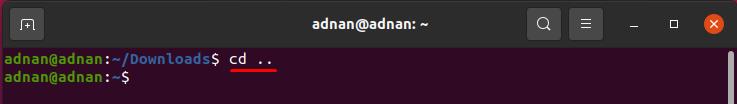
How to change the current directory to parent directory using the cd command
You can move to the parent directory of the pwd by executing the following command. For instance, we are currently in our “Downloads” directory and want to go back to the parent directory:
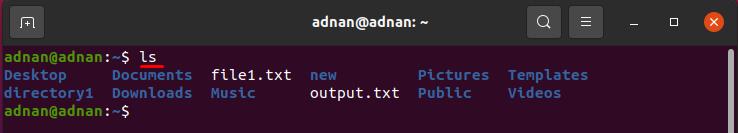
How to navigate to the sub-directory of a current directory using the cd command
Firstly, we will check the list of sub-directories. So, to get the list of sub-directories present in “/home/adnan”; execute the following command:
Let’s say we want to direct the terminal to the “Desktop” directory; you can do so by executing the following command as given below:
You can operate the terminal from any directory inside your drives; it is easy to use the “cd” command to move to one or two sub-directories, but what if we want to access a directory that is 4 to 5 directories away from our present working directory; it is possible to use “cd” as we have done above to access “Desktop“; however, it is easier to access the directory by giving the path to the “cd“:
Syntax: cd [path of the directory]
The syntax of the command given below will help to access the “final_dir” which is present in subdirectories of the “Desktop” directory.
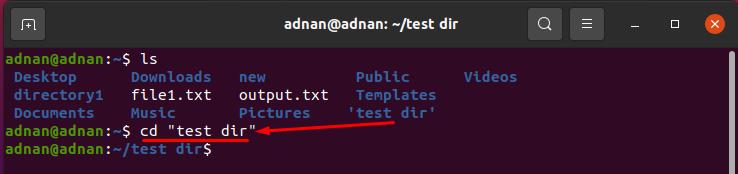
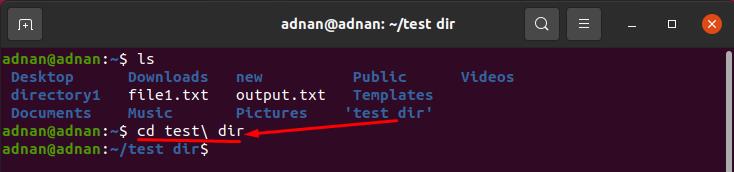
If you want to navigate to a directory that contains blank spaces, you must insert the directory name inside single or double-quotes. Otherwise, you won’t be able to get to that directory:
Syntax: cd [“name of directory”]
For example, there is a directory named “test dir” in our home directory; so, execute the following command to get to that:
Or the directory (with white spaces) can also be accessed using the following command:
Conclusion
Directory handling is the most used and important feature of any operating system; you can switch the directories using GUI and CLI. The Ubuntu command line terminal also supports commands to perform any action; whenever you open your Ubuntu terminal, it will open in the default(home) directory, and you can use the cd command to access other directories using the terminal. This article is all about the cd command of Ubuntu; we have briefly discussed the use of the cd command; this command can be executed in all the Linux distributions. You can change directories with the help of the cd command and can use its extensive support of available options to get filtered results.