The “cat” command is a versatile Linux command that you can use for various purposes which varies from creating and merging files to writing a text to a file. It is one of the simplest commands which you must know as a beginner.
However, many Linux users don’t know about the feature of the “cat” command which writes a text to a file. In this quick blog, we will explain the various examples on how to use the “cat” command to write a text to a file in Linux.
Cat Command to Write a Text to a File
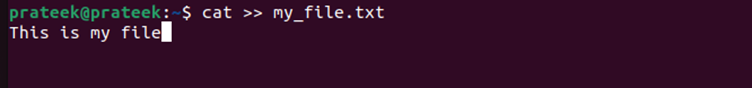
Let’s start with creating a “my_file.txt” text file using the “cat” command:
After running the previous command, you can add any line accordingly. For example, let’s add the following line:
You can add more lines below the line. Once you’re done adding the text that you wish to add to your file, press “Ctrl+C” to end the command.
The Difference Between “>” and “>>”
While you can use both “>” and “>>” while working with the “cat” command, there’s a difference between the two that you need to understand.
While using “>”, you must ensure that the name you use for the file is unique. That’s because if a file with the supplied name is already available, the “>” symbol will overwrite the existing content in that file.
Conclusion
The “cat” command has a range of applications and can be used for various tasks including adding a text to the files directly from the Linux terminal. The provided explanation will help you to work better with files using the Linux “cat” command. We recommend you to press the “CTRL” and “C” keys. Otherwise, you cannot exit the “cat” command.