In programming, file management allows us to store and access any type of information whether in user-created databases, system files for running programs, executable files, and so on.
The C language provides, among other things, the open() function to create or open files. This function opens or creates a file specified in the input arguments by its absolute or relative path.
When we use this function, we have the possibility to specify via flags the attributes that the file to be opened or created must have, for example. whether it should be read-only, read-write or both.
In this Linux Hint article, you will learn how to specify the read and write attributes of files using the O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY, and O_RDWR flags.
We will look at a theoretical description of these flags and then implement their use in examples that include code snippets and images where we set read and write attributes with these flags.
Description of the Flags O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY and O_RDWR.
The flags O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY and O_RDWR are used in the open() system function to specify the opening mode of a file. To better understand what these flags are about, let us look at the syntax along with a brief description of this function.
The open() function opens the file specified in the path in one of the following three modes specified in the flags:
O_RDONLY: Open or create a read-only file
O_WRONLY: Opens or creates a write-only file.
O_RDWR: Opens or creates a file with read and write access.
The open() function also uses additional flags such as O_ CREAT, to create a file or
O_ APPEND, to add text to it. In cases where more than one flag is used in the flags input argument, a logical OR operation must be performed between them.
These flags and the functions that use them are defined in the “fcntl.h” header. Therefore, we must include them in our “.c” file as follows in order to use them:
How to Open a File with Read and Write Permission Using the open() Function and the O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY, and O_RDWR Flags in the C Language.
In this example, we will show you how to open a file with read and write permissions. To do this, we use the open() function, specifying the path and name of the file in the path input argument and the O_RDWR read and write flag in the input flags. Here is the code:
#include <fcntl.h>
void main()
{
int fd open ( "Documents/example.txt", O_RDWR );
}
In this way, open() returns the fd descriptor which we can use with the read() and write() functions to read and write the file.
How to Create a File and Set the Read and Write Attributes with the Flags O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY and O_RDWR in the C Language.
In this example, we create a file named “example.txt” and save it in the “Documents” directory with the read only attributes using the O_RDONLY flag.
To do this, we add the header “fcntl.h” to our file and call the open() function specifying the relative path and the name of the file in the path input argument, which in this case is “Documents/example. txt”.
Since we want to create the file, we use the O_ CREAT flag. And since we want to give it read-only attributes, we use the O_RDONLY flag. So, we need to perform a logical OR operation between these two flags. Here is the code for this example:
#include <fcntl.h>
void main()
{
int fd open ( "Documents/example.txt", O_CREAT | O_RDONLY );
}
We compile the code in the Linux command console using GCC, specifying the path and name of the “.c” file and the name of the output, as shown below:
And we execute the output with the following command:
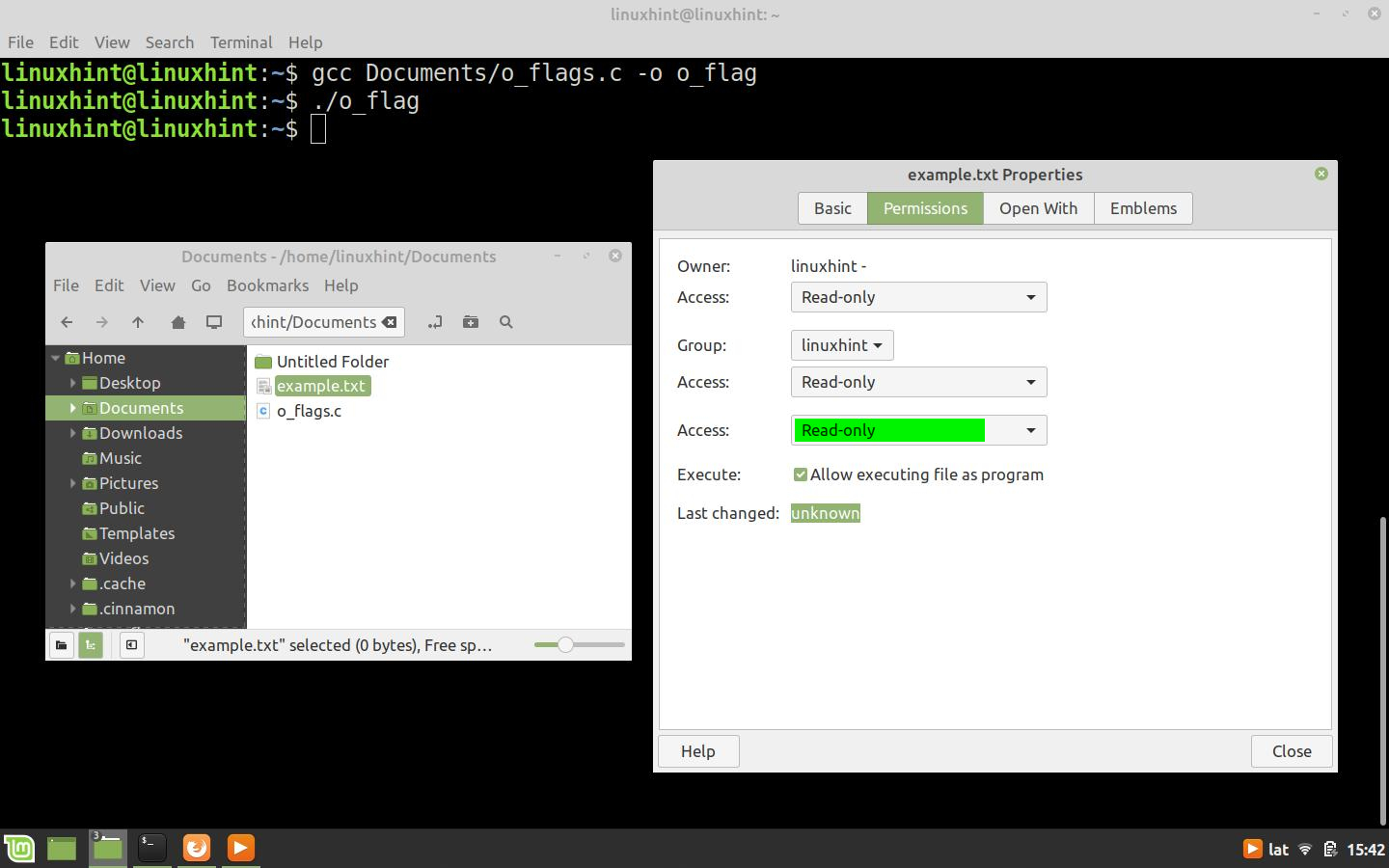
When you run this code, the open() function will create a file with read-only attributes. In the following figure, we can see the file created in the Linux file manager and its read-only attributes in its properties.
If we want to create a file with read and write access, we must use the O_RDWR flag as shown below:
#include <fcntl.h>
void main()
{
int fd open ( "Documents/example.txt", O_CREAT | O_RDWR );
}
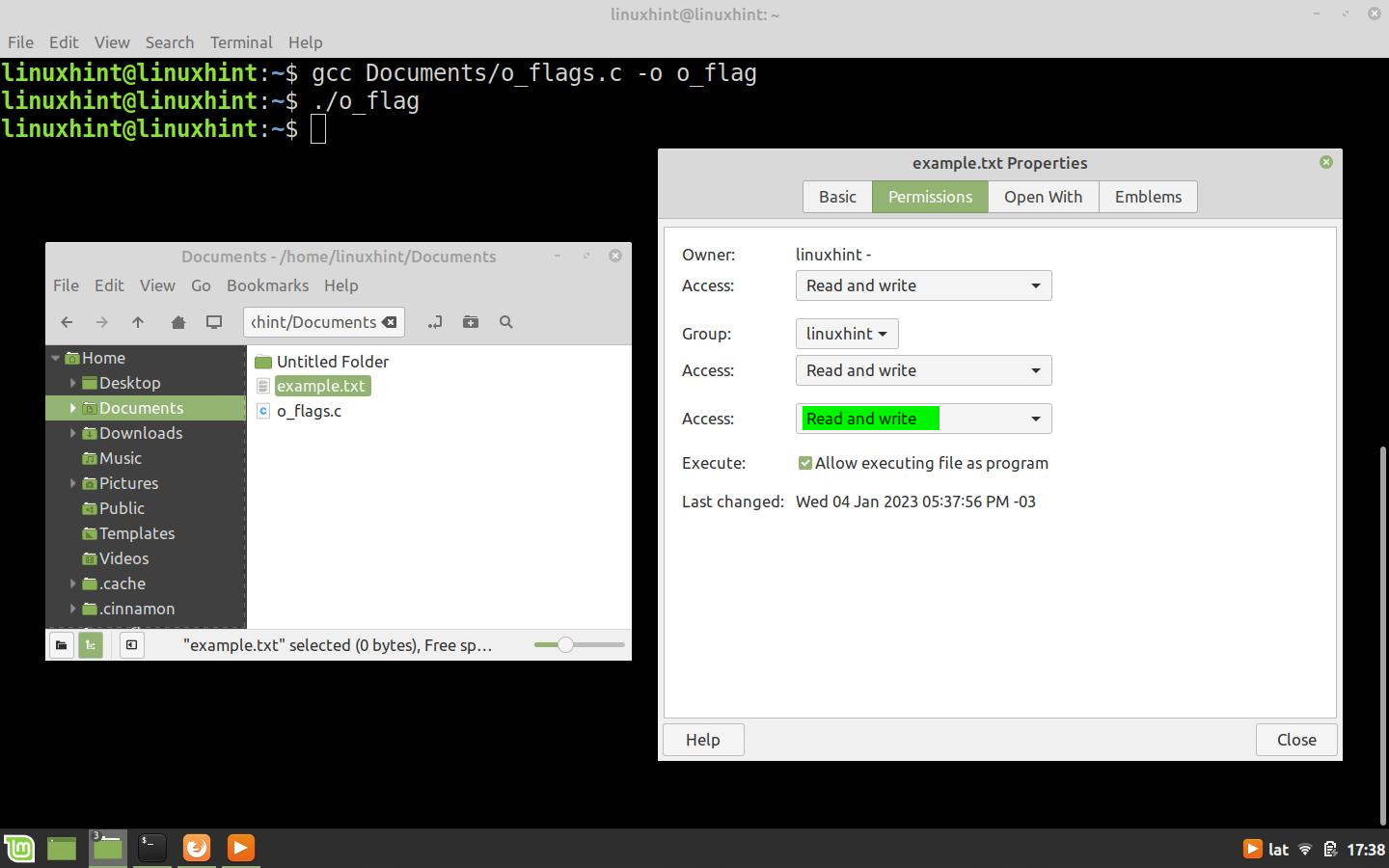
In this case, the open() function creates a file with read and write attributes as shown in the following figure.
Conclusion
In this Linux Hint article about the C language, we explained how you can use the O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY, and O_RDWR flags to select the open mode of a file when you use the open() function.
We also showed you how to create files using the open() function and the O_ CREAT flag, and how to assign read and write permissions by performing a logical OR operation between it and the O_RDONLY and O_WRONLY flags.
We hope that you found this article useful. For more articles about the C language and Linux tips, use the search engine on our website.