Binary Tree in C
In C, a binary tree is an instance of a tree data structure with a parent node that may possess a maximum number of two child nodes; 0, 1, or 2 offspring nodes. Every single node in a binary tree has a value of its own and two pointers to its children, one pointer for the left child and the other for the right child.
Declaration of Binary Tree
A binary tree can be declared in C using an object called struct that depicts one of the nodes in the tree.
datatype var_name;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
Above is a declaration of one binary tree node name as a node. It holds three values; one is the data-storing variable and the other two are the pointers to the child. (left and right child of the parent node).
Facts of Binary Tree
Even for large sets of data, using a binary tree makes searching easier and quicker. The number of tree branches is not limited. In contrast to an array, trees of any kind can be made and increased based on what is required of an individual.
Binary Tree Implementation in C
The following is a step-by-step guide to implementing a Binary Tree in C.
Step 1: Declare a Binary Search Tree
Create a struct node that has three types of data, such as data, *left_child, and *right_child, where data can be of integer type, and both *left_child and *right_child nodes can be declared as NULL or not.
{
int data;
struct node *right_child;
struct node *left_child;
};
Step 2: Create New Nodes in Binary Search Tree
Create a new node by creating a function that accepts an integer as an argument and provides the pointer to the new node created with that value. Use the malloc() function in C for dynamic memory allocation for the created node. Initialize the left and right child to NULL and return the nodeName.
{
struct node* nodeName = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
nodeName->data = value;
nodeName->left_child = nodeName->right_child = NULL;
return nodeName;
}
Step 3: Insert Right and Left Childs in Binary Tree
Create functions insert_left and insert_right that will accept two inputs, which are the value to be inserted and the pointer to the node to which both children will be connected. Call the create function to create a new node and assign the returned pointer to the left pointer of the left child or the right pointer of the right child of the root parent.
root->left = create(data);
return root->left;
}
struct node* insert_right(struct node* root, datatype data) {
root->right = create(data);
return root->right;
}
Step 4: Display Nodes of Binary Tree Using Traversal Methods
We can display trees by using three methods of traversal in C. These traversal methods are:
1: Pre-Order Traversal
In this traversal method, we will go through the nodes in a direction from parent_node->left_child->right_child.
if (root) {
printf("%d\n", root->data);
display_pre_order(root->left);
display_pre_order(root->right);
}
}
2: Post-Order Traversal
In this traversal method, we will go through the nodes in a direction from the left_child->right_child->parent_node->.
if (binary_tree) {
display_post_order(root->left);
display_post_order(root->right);
printf ("%d\n", root->data);
}
}
3: In-Order Traversal
In this traversal method, we will go through the nodes in a direction from left_node->root_child->right_child.
if (binary_tree) {
display_in_order(root->left);
printf("%d\n", root->data);
display_in_order(root->right);
}
}
Step 5: Perform Deletion in Binary Tree
We can delete the created Binary Tree by deleting both the children with the parent node function in C as follows.
if (root) {
delete_t(root->left);
delete_t(root->right);
free(root);
}
}
C Program of Binary Search Tree
The following is the complete implementation of Binary search tree in C programming:
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node {
int value;
struct node * left, * right;
};
struct node * node1(int data) {
struct node * tmp = (struct node * ) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
tmp -> value = data;
tmp -> left = tmp -> right = NULL;
return tmp;
}
void print(struct node * root_node) // displaying the nodes!
{
if (root_node != NULL) {
print(root_node -> left);
printf("%d \n", root_node -> value);
print(root_node -> right);
}
}
struct node * insert_node(struct node * node, int data) // inserting nodes!
{
if (node == NULL) return node1(data);
if (data < node -> value) {
node -> left = insert_node(node -> left, data);
} else if (data > node -> value) {
node -> right = insert_node(node -> right, data);
}
return node;
}
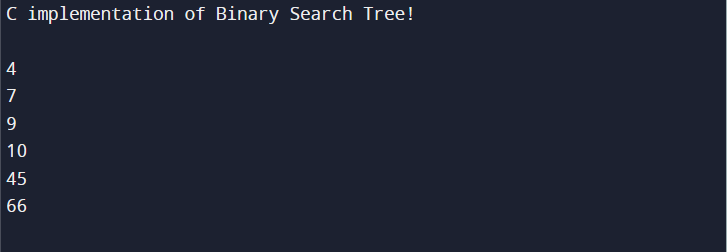
int main() {
printf("C implementation of Binary Search Tree!\n\n");
struct node * parent = NULL;
parent = insert_node(parent, 10);
insert_node(parent, 4);
insert_node(parent, 66);
insert_node(parent, 45);
insert_node(parent, 9);
insert_node(parent, 7);
print(parent);
return 0;
}
In the above code, we first declare a node using struct. Then we initialize a new node as “node1” and allocate memory dynamically using malloc() in C with data and two pointers type children using the declared node. After this, we display the node by printf() function and call it in the main() function. Then the insertion_node() function is created, where if node data is NULL then node1 is retired, else data is placed in the node(parent) of the left and right child. The program starts execution from the main() function, which generates a node using a few sample nodes as children and then uses In-Order traversal methods to print the node contents.
Output
Conclusion
Trees are frequently employed to keep data in a non-linear form. Binary trees are types of trees where each node (parent) has two offspring the left child and the right child. A binary tree is a versatile method of transferring and storing data. It is more efficient as compared to Linked-List in C. In the above article, we have seen the concept of a Binary Tree with the step-by-step implementation of a Binary Search Tree in C.