There are many choices available on the internet for system monitoring tools. Still, we have crafted a list of the best system monitoring tools for you by testing each tool in different circumstances. So, sit back and enjoy the ride to find the best system monitoring tool for Ubuntu that matches your requirements.
1. htop
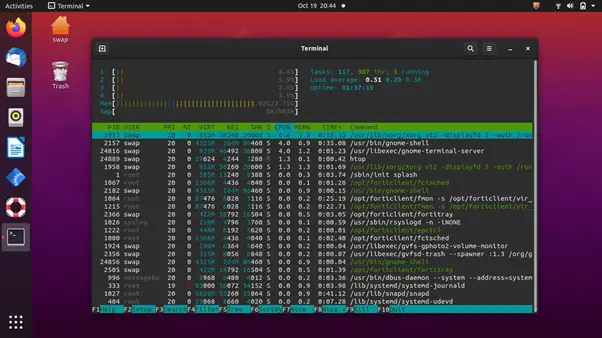
htop is a cross-platform system monitor, process viewer, and process manager and a reliable alternative to top, which is also a system monitoring tool for Linux and its distros. It is specially designed and developed for consoles and terminals; hence, it supports text mode.
It is a feature-rich system monitoring tool that can be used on Linux, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, and macOS. Talking about the features, it offers information based on various parameters, such as tasks, load average, and uptime. You can change color preferences on its UI to match your requirements.
For Linux and its distros, it provides a delay account matrix and offers support for custom scripts and real-time signals. Since it is open-source and free, it makes it one of the best system monitoring tools for Linux systems.
2. Glances
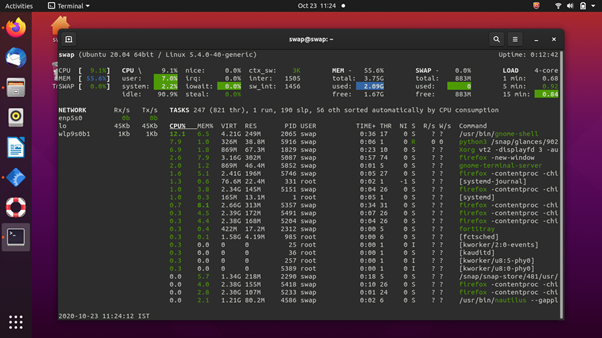
Written in Python, Glances is another cross-platform system monitoring tool on our list. It uses a web-based interface to give you maximum system information in the minimum possible space. Depending on terminal size, it automatically adjusts itself and displays all the information in a single window.
It can also be used in client/server mode, and remote system monitoring could be done through the web interface or terminal. You getting all the important information in one place is one of the positives of this tool.
The thing I like most about this system monitoring tool is that you can keep track using its web interface, which allows remote monitoring. Linux running on low-end or older computers might find it tough to run this tool smoothly as it demands higher CPU resources.
3. Stacer
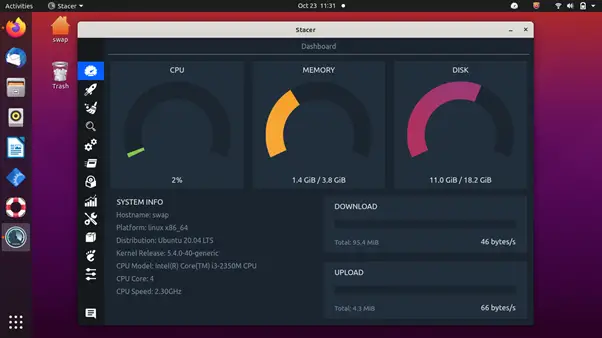
Stacer is an open-source system monitor and optimization tool, which helps system administrators manage system resources and tasks under one roof. It is a modern tool with an excellent user interface that makes you feel at home even on first use.
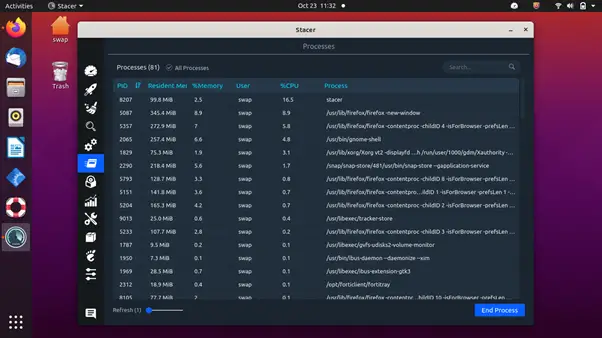
It has feature-rich tools that let you manage startup apps, clean unnecessary package caches, crash reports, application logs, application caches, and trash under the system cleaner tab, and start or stop services quickly. Sort processes based on process id (PID), CPU, and memory usage, find a particular process easily using its name in the search bar, and uninstall applications that are not required anymore.
The resource tab displays CPU, RAM, Disk, CPU load average, and network activity for the last 60 seconds. It also comes with an APT repository manager, which you can use to activate, disable or delete any repository. Ubuntu users can use this feature to edit the package repositories.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install stacer
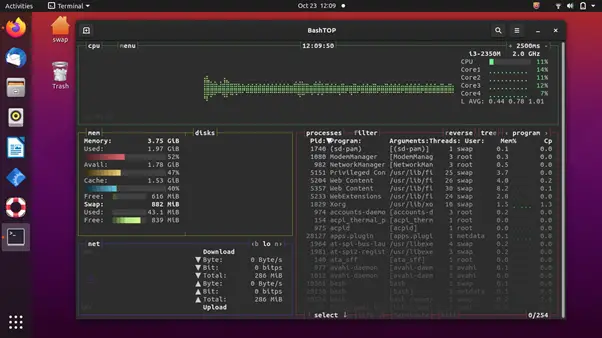
4. BashTOP
BashTOP is another cool and reliable system monitoring tool for Linux and its distros, such as Ubuntu. It displays the usage stats for processors, memory, disks, network, and other resources.
It is an excellent tool for desktop and computer users who are generally personal users. However, system administrators and server users won’t find this tool useful as their demands will be higher. Also, it is a little bit slower compared to other system monitoring tools, such as Htop.
It is an easy-to-use tool and sports a beautiful user interface with everything placed perfectly.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install bashtop
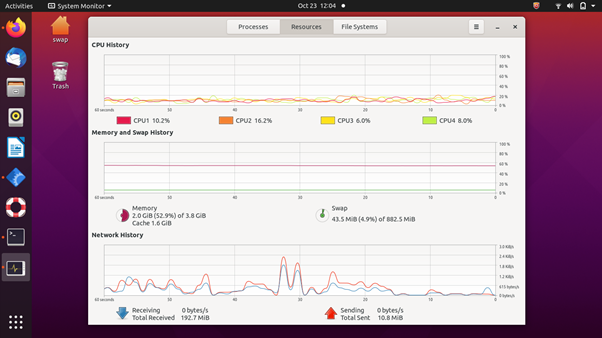
5. GNOME System Monitor
It is a simple system monitoring tool that comes pre-installed on various Linux distros running the GNOME desktop environment. This tool shows which programs are running, how much processor time, memory, and disk space are used.
As you can see in the screenshot, it has a clean and simple user interface. Every information and stats are placed perfectly in the user interface, which makes it easy to read and understand.
The CPU history tab shows how much processor capacity is used for each CPU, and the memory and history tabs show how much of your computer’s memory (RAM) is being used. Under the network tab, you see the download and upload speed of the network over the last 60 seconds.
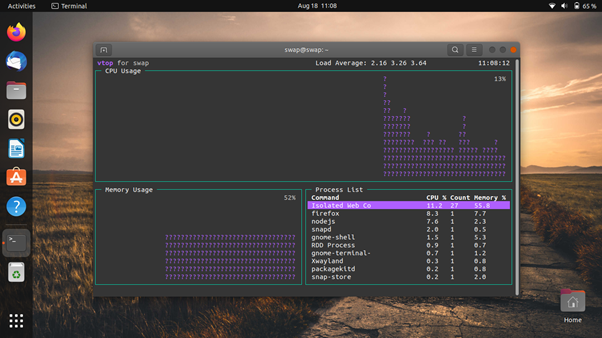
6. vtop
vtop is a free and open-source system monitoring tool for Ubuntu and other Linux distros. Using vtop, not only can you monitor system resources, but also you can manage them.
It is a command-line tool written in node.js. Hence, you must first install node.js and npm packages before installing vtop. Using this tool, you can easily monitor CPU usage and memory usage, something you can do in other command-line tools like top.
$ sudo apt-get install npm
$ sudo npm install -g vtop
7. nmon
nmon is a simple-to-use system monitoring tool for Linux and its distros, such as Ubuntu. It gives you a quick overview of what’s going on with your server.
This monitoring tool displays the usage stats of CPU, memory, network, disks, file system, NFS, top processes, and resources. The best thing is you can select what the nmon displays, and what you have to do is simply press specific keys to toggle stats.
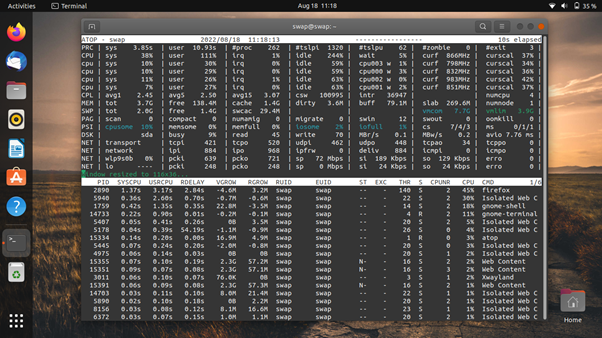
8. atop
atop is an advanced interactive system and process monitor that displays the load on the Linux system. It shows the stats of the most critical hardware resources, such as CPU, memory, disk, and network.
You can log resource utilization permanently if you want it for long-term analysis.
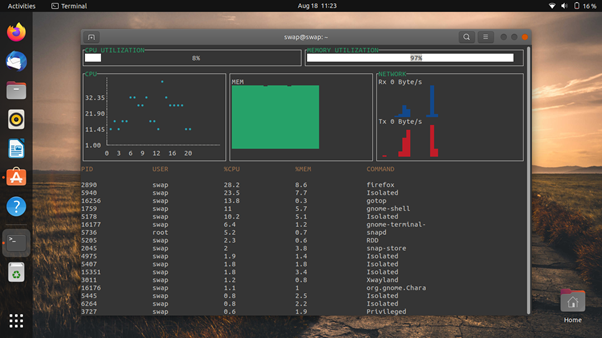
9. gotop
gotop is another command-line graphical system monitoring tool for Ubuntu and other Linux distros. Along with Linux, gotop is also available for macOS.
It is inspired by vtop and gtop. But unlike them, it does not use node.js. Instead, it is written in Go. You can monitor CPU usage, disk usage, CPU temperature, memory usage, network usage, and process table.
Conclusion
These are the best system monitoring tools you can use on your computers running Linux and its distros. Some other tools are available for Ubuntu, but the ones listed above are tested and presented to you.