Single line comment:
You can explain the function of each line of the script by adding a single line comment on the above or side of the line. ‘#’ symbol is used to comment on a single line in the bash script. The following example shows the use of single-line comments. The script will calculate the sum of two integer numbers, and the value of the addition will be printed. The single-line command has been added before each script line that will be ignored after executing the code.
Example-1: Single line comment
The ‘#’ symbol is used to add single-line comments in the bash script. Create a bash script with the following code to check the way to add a single-line comment in the script. Two numeric numbers will be added and printed after executing the script. Here, all comments have been added before each line of the script to describe the purpose.
#Print a simple text
echo "Working with bash comments"
#Add 10 with 20 and store the value in n
((n=10+20))
#Print the value of n
echo $n
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
Example-2: Inline comments in bash script
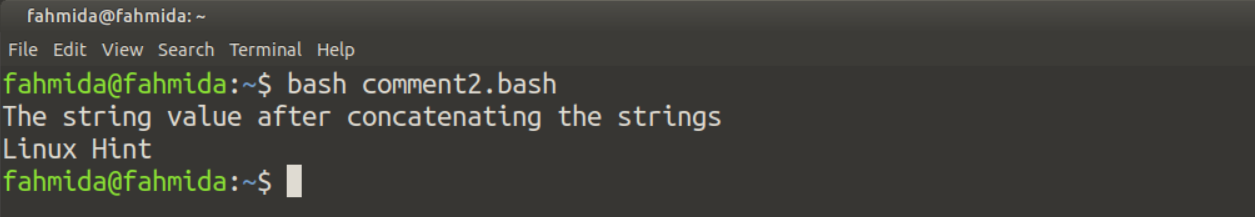
The single-line comment can also be added after the end of the script that is called an inline comment. Create a bash file with the following script to check the use of inline comments. The following script will combine two string values and print the combined value. Four inline comments have been added in the script that will be ignored at the time of execution.
str1="Linux" # Initialize the first string value
str2=" Hint" # Initilaize the second string value
str=$str1$str2 # Combine the string values
echo "The string value after concatenating the strings"
echo $str # Print the combined string
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
Multiple line comment:
There is no direct option to comment on multiple lines in the bash script like other programming languages. You can use other features of bash to comment multiple lines in a script. One option is using ‘here document’, and another option is using ‘:’. The uses of both options are shown in the following examples.
Example-3: Multi-line Comment using here document
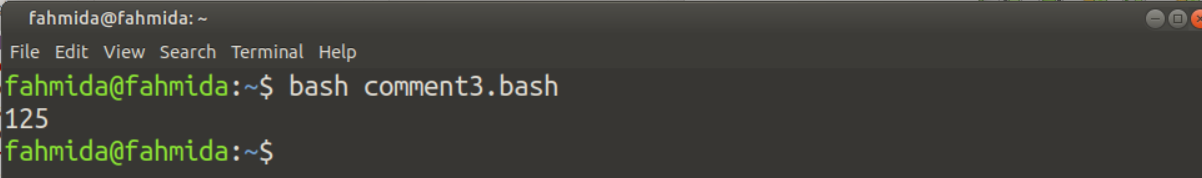
A delimiter is used at the beginning of the comment with << symbol, and the same delimiter is used at the end of the comment to add a multi-line comment in bash script. Create a bash file with the following script to check the way to add a multi-line comment using here document. Here, LongComment has been used as the delimiter of here document to add the multi-line comment. The script will calculate and print the value of 53 as output. One multi-line and three single-line comments have been used in the script.
<<LongComment
This script is used to
Calculate the cube of
a number with value 5
LongComment
#Set the value of n
n=5
#Calculate 5 to the power 3
((result=$n*$n*$n))
#Print the area
echo $result
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
Example-4: Multi-line comment using ‘:’ command
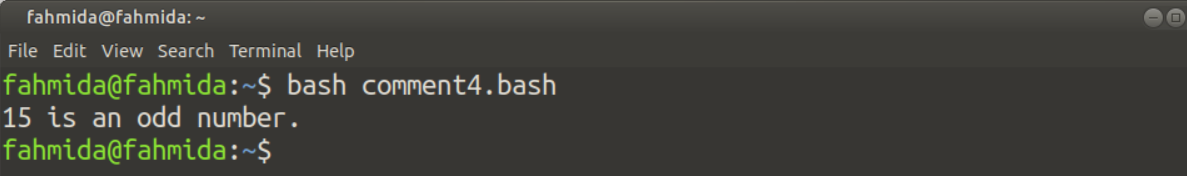
Using colon (:) with the single quote is the most simple way to add a multi-line comment in bash script. The multi-line comment will be added within a single quote(‘) after the colon(:). The use of multi-line comments has shown in the following example. The script will check a number is odd or even. Here, one multi-line comment has been used in the script to describe the script’s main purpose.
#Initialize the variable n with a number
n=15
: '
The following script will check the number is
Even or odd by dividing the number by 2 and checking the remainder value
'
echo -n "$n "
if (( $n % 2 == 0 ))
then
echo "is a even number."
else
echo "is an odd number."
fi
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above code.
Example-5: Comment multiple lines in Visual Studio Code
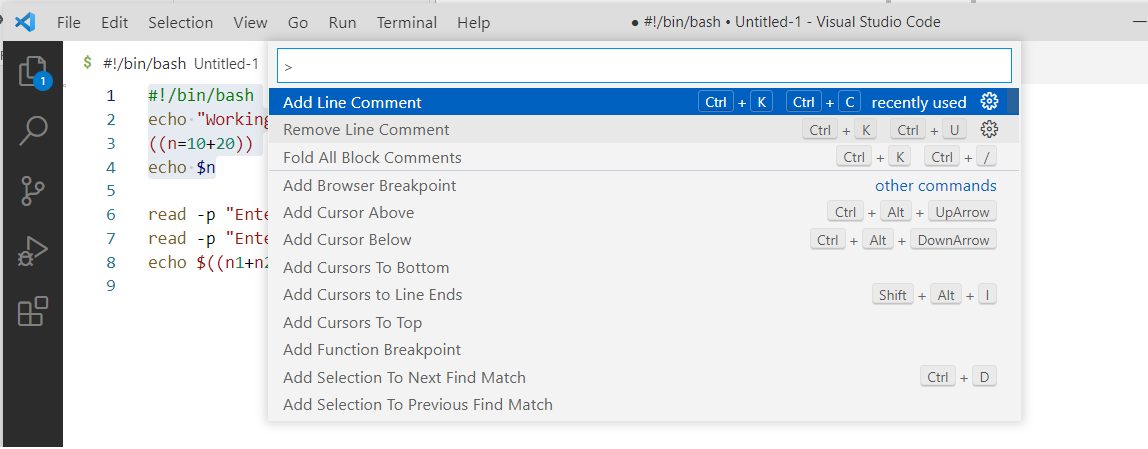
The ways to add a comment in multiple lines at a time using ‘#’ in Visual Studio Code has shown in this example. The ways of adding comments in previous examples can be applied to all types of editors. But if you are using any standard code editor like Visual Studio Code, commenting multiple lines or removing the comment from multiple lines is easier than a normal text editor. You have to install this editor in your system to check this example. Create a bash file with the following script using the visual studio code editor.
echo "Working with bash comments"
((n=10+20))
echo $n
read -p "Enter the first number: " n1
read -p "Enter the second number: " n2
echo $((n1+n2))
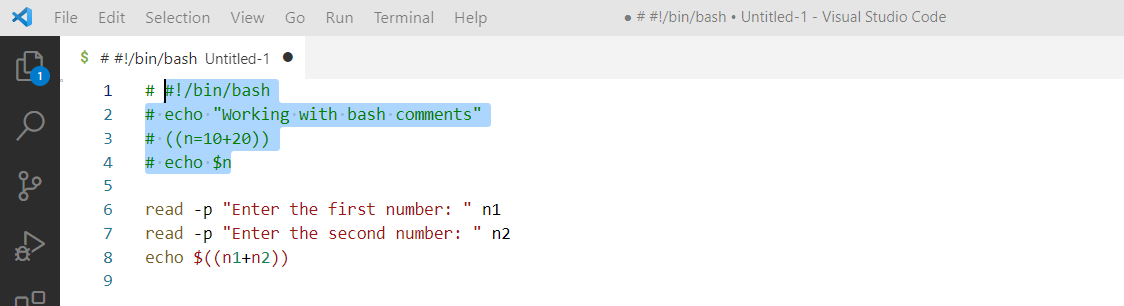
Select the lines you want to comment out, right-click on the selected lines, and select Add line comment from the command palette.
After the selection, the selected lines will be commented with ‘#’ like the following image.
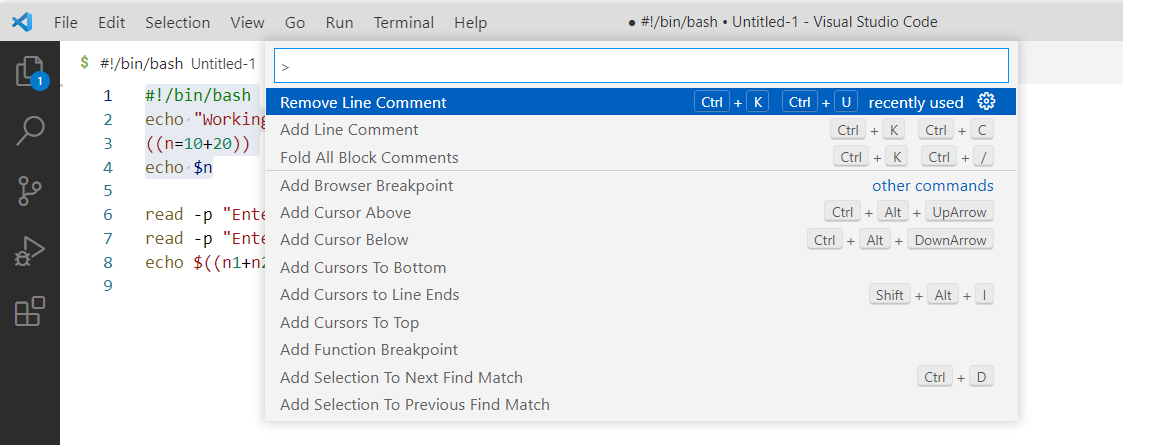
Select the lines that you want to uncomment out and right-click on the selected lines, and select Remove Block Comment from the command palette to remove the ‘#’ from the lines that were commented before.
Conclusion:
Different ways to add single and multi-line comments in bash script have been shown in this tutorial by using multiple examples. Adding multi-line comments is not simpler in bash like other programming languages when using a text editor. This tutorial will help you learn and apply single and multiple line comments in your bash script.