Bash OR Operator
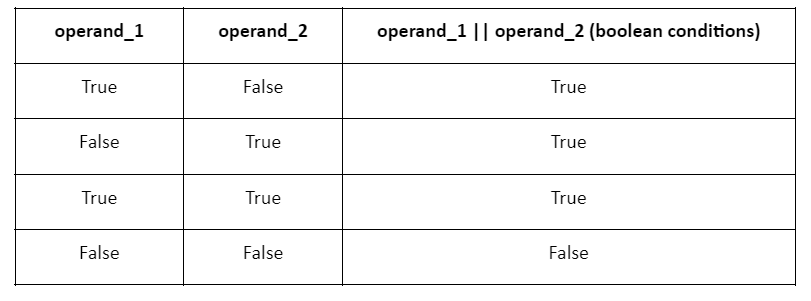
The OR operator takes two operands (logical expressions) and returns true if either of the operands is true; otherwise, it returns false. In Bash scripts, the OR operator is used through double pipes. The following is the truth table of the Bash logical OR operator which helps you to understand everything better:
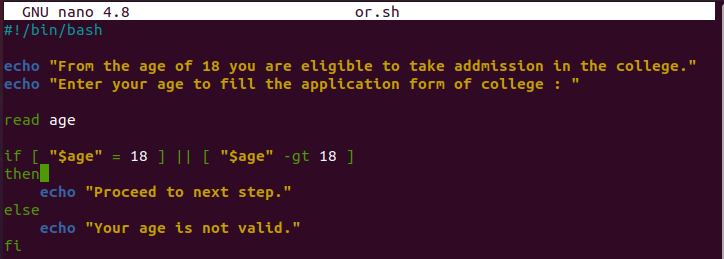
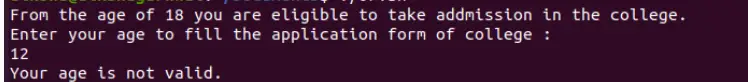
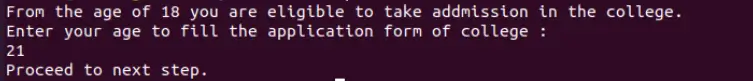
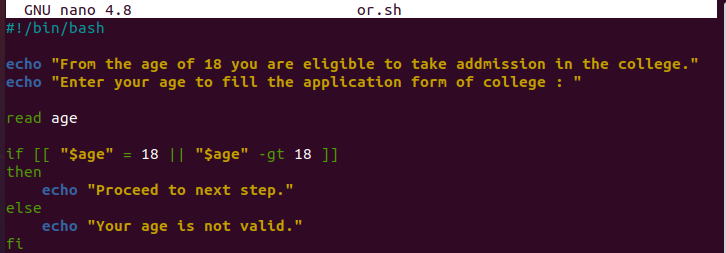
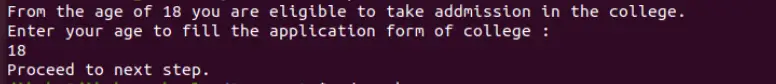
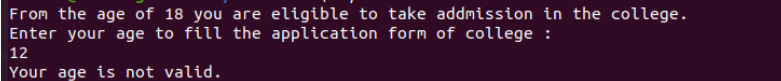
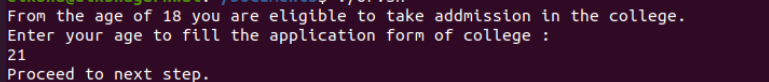
Let’s take an example where we create a script that gives a specific result after entering a particular number. For example, for college admission, any person should be 18 years or more to be admitted to college. We put two conditions – first, if the candidate’s age is equal to 18 years and second, if their age is over 18 years. It asks you to proceed if either condition is true. However, if both conditions are false, it tells you that your age is invalid.
Output:
In the previous example, you can see that we used an OR logical operator in our script using pipes with square brackets. You can also use an OR operator in Bash using double square brackets. The syntax is as follows:
Output:
Through both types of syntax, you can see that you get the same output. In this way, you can use any two of the two methods according to your convenience.
-O Logical Operator
You can also use the -o flag for the OR operator to replace the double pipe. This flag also works similarly, and it returns a true statement if any of the conditions is true. Otherwise, it displays a false statement. Its syntax is something like this:
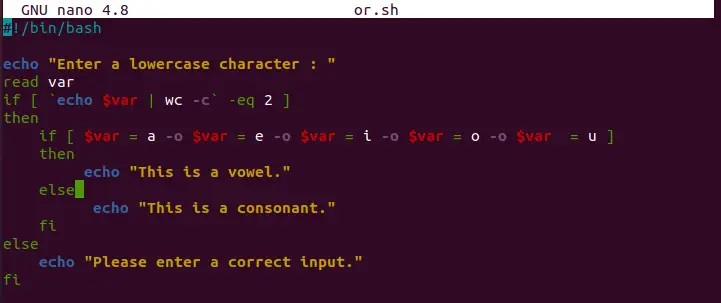
In the following example, we will see which character is a vowel and which is consonant through the OR operator:
Output:
In this way, you can also use the OR operator through the -o flag.
Conclusion
This is all about the OR logical operator which you can use in the Bash script. Many Bash users believe that the OR logical operator and -o logical operator is different, but it is not. These two are the same, but the only difference is that there is a specific way to use both, as shown in the given examples. Using both methods and running them in the terminal give the same output.