$ nano array.sh
Example 1
Starting from the first example, we will be demonstrating the very basic and most-used known syntax of declaring arrays in Bash. Thus, we have added the Bash support in our program code i.e. “#!/bin/bash”. After this, we have used the variable “Array” with an assignment sign to make it an empty array using the simple brackets “()”. This is how a simple array-like structure in Bash can be defined. As this is an array-type variable, the echo statement will take it as a variable. So, we have used it with the “$” sign and within the curly brackets as per the program.
The code is saved properly and we have executed it on the shell with the “bash” instruction. It turns out that the array is empty.
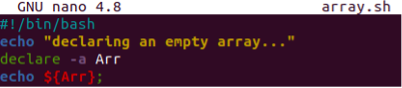
Just like the above syntax, the Bash provides us the “declare –a” method to declare an array in a Bash program. Let’s see how we do it. So, we have started this program with Bash support and added an echo statement within the first line to display a message that we will be displaying an empty array on the shell. We have been using the keyword “declare” along with the option “-a” to declare an array named “Arr”. We haven’t assigned any value to it which means this array will be empty for sure. The echo statement has been using this array variable “Arr” within the curly brackets held by the “$” sign to display on the shell.
We have saved this updated code and executed it on the Bash terminal using the Bash instruction. It turns out the same as we got in the first example of syntax i.e., empty array.
Example 2
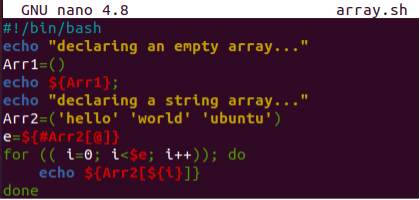
The above example was all about the use of a simple assignment operator and the “declare –a” method to declare an empty array in a Bash script. Now, we have updated the last code and used the assignment operator method to declare an empty array “Arr1” first and display it via the echo statement using the “$” sign.
After this, we have tried the same assignment operator method to create a new array “Arr2” with three string values in it. Simply putting the values in the brackets between the single quotes is enough. After this, we have created a new variable “e” that has been getting the total size of this array “Arr2” using the “@” operator within its index. The “for” loop has been utilized to iterate the array and display each of its string values at the Bash shell using the “echo” statement and index “I”. Let’s save this code first.
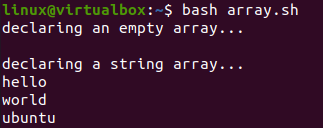
Executed this Bash code on the terminal and got the below result. It displays the empty array as an “empty line” and the other array values are displayed one by one on separate lines.
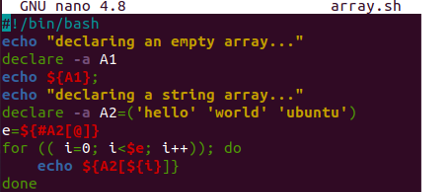
Let’s use the “declare” method with the “-a” option to declare an array with values. So, we have updated the same code shown below. We have been using echo statements to display that the empty and string array will be going to display at the shell. We have been using the keyword “declare” along with the “-a” option to declare an empty array “A1”. We are displaying it using the echo statement utilizing “$” with the array name in curly brackets. After this, we have initialized another array “A2” with the declare keyword followed by the “-a” option. This array contains the same three string values and the rest of the code has been the same.
Now, it’s time to run this code on our shell. So, we have been running this code with the Bash command and got the very same result as we have got with the simple assignment method.
Example 3
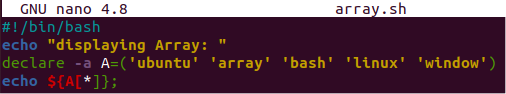
Let’s take a look at another example to use the “-a” option with the declare keyword to initialize an array in the Bash code and display it. This time, we will be displaying it with a unique method. So, we have started this bash script with the echo statement stating “displaying array:”. After this, we have used the very same method to declare a method with the “-a” option to initialize an array “A” with 5 string values as presented below. After this, we have used the “*” sign in the square brackets to display all values of array “A” on the shell.
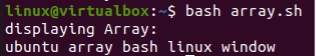
After running this simple Bash code, we have got the array values displayed on a single line in the Bash terminal instead of displaying at separate lines as in the above examples.
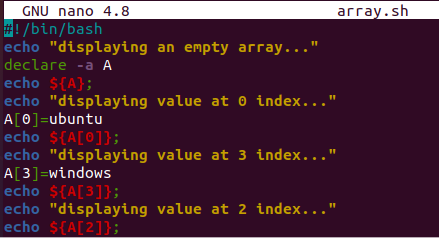
You can also assign the values to an empty array separately one by one at a specific index using the assignment method below. We have assigned values to index 0 and 3 as shown.
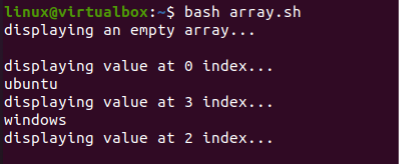
After running this code, the empty array, values at index 0, 3, and 2 (empty) are displayed.
Conclusion
This is all about the use of the “declare” keyword along with the “-a” option in Bash to declare arrays. This method is very effective when it comes to declaring or initializing arrays because the traditional methods of declaring arrays don’t work in Bash.