What Will We Cover?
In this guide, we will explore deploying an AWS SAM application.
What Is AWS SAM?
AWS SAM is an Amazon cloud-based service for developing serverless applications. SAM, as well as SAM CLI, are both open-source projects. SAM defines the resources which are used in applications based on serverless architecture. It has short syntaxes to denote APIs, functions, databases, and event source mappings. The SAM syntaxes are transformed and expanded into AWS CloudFormation syntaxes. Applications can be modeled using YAML. In this way, serverless applications can be built rapidly.
The “sam deploy” Command
By default, the sam deploy command takes the current directory as the root directory for the project. First, the AWS SAM CLI looks for a template file named template.yaml inside the sub-directory “.aws-sam” was set up by running the sam build command.
Then, it looks for the same file (either template.yaml or template.yml) in the current directory. When a “—template” option is used with the deploy command, the default attitude of the AWS SAM CLI is overridden. It will then only deploy the specified AWS SAM template and local resources.
The sam deploy command also provides a guided interactive mode with the “—guided” option. In this mode, the user is prompted to different parameters needed for deployment.
Important SAM CLI Commands
sam-init: SAM CLI tool can initialize serverless applications using the AWS infrastructure templates. This is done using the “sam-init” command.
Sam-build: In the same way, the “sam-build” command is used for compiling, building, and packaging Lambda functions with the given runtime.
Sam-local: With Docker containers, “sam local” commands can locally test the SAM application by running it.
Sam sync: The “sam sync” command provides a feature to synchronize and verify the modifications done in the cloud environment.
Sam-deploy: Finally, run the “sam deploy” command to deploy your SAM Application.
Deploying a HelloWorld Application
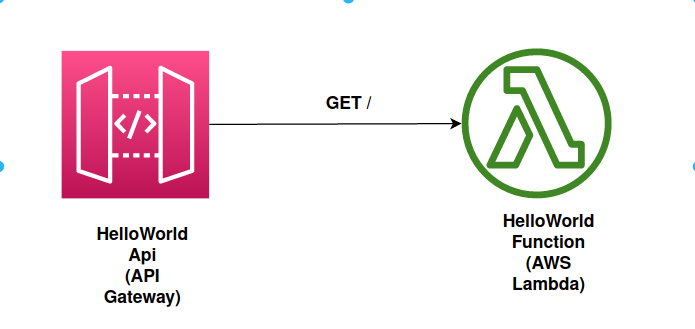
Let us take an example of AWS SAM deploy using a sample HelloWorld application. In this example, the HelloWorld application uses a basic API backend. Refer to the following diagram for the components used in this application:
The Lambda function is invoked when a GET request is received at the API Gateway endpoint. In response, a Hello World message is returned by the Lambda function.
Now, follow these steps to deploy this application:
1. Downloading the sample application
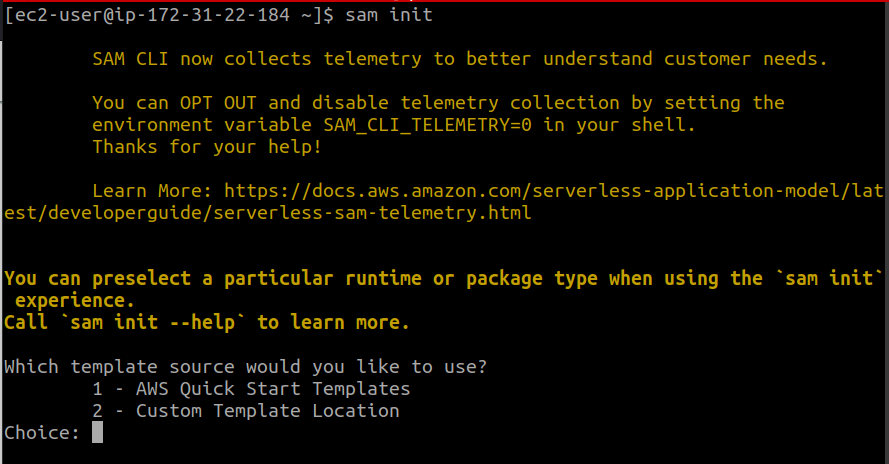
First, run the following command:
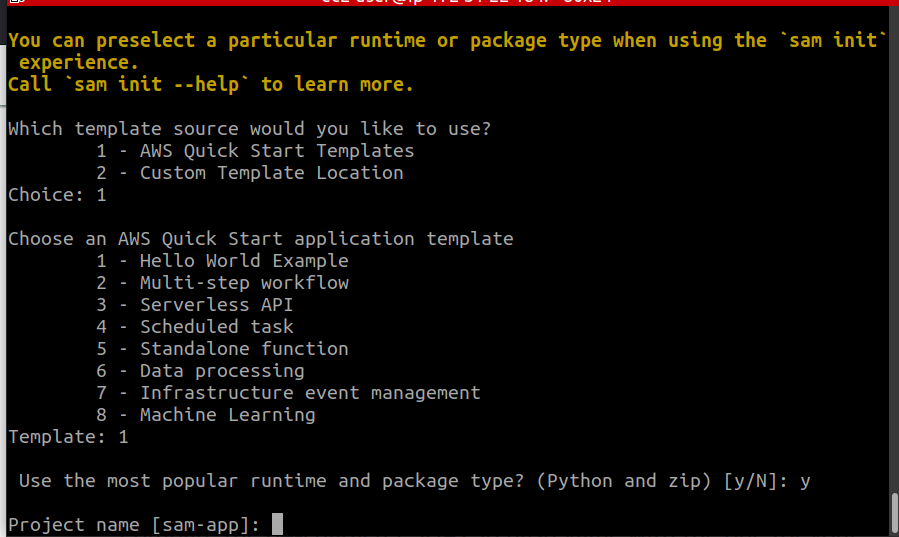
A series of prompts will appear on the screen. For the type of template, we are sticking to the AWS Quick Start Templates option followed by the Hello World template:
We are selecting the default option:Python runtime and Zip package type. Also, retain the project name to be the default one: “sam-app”.
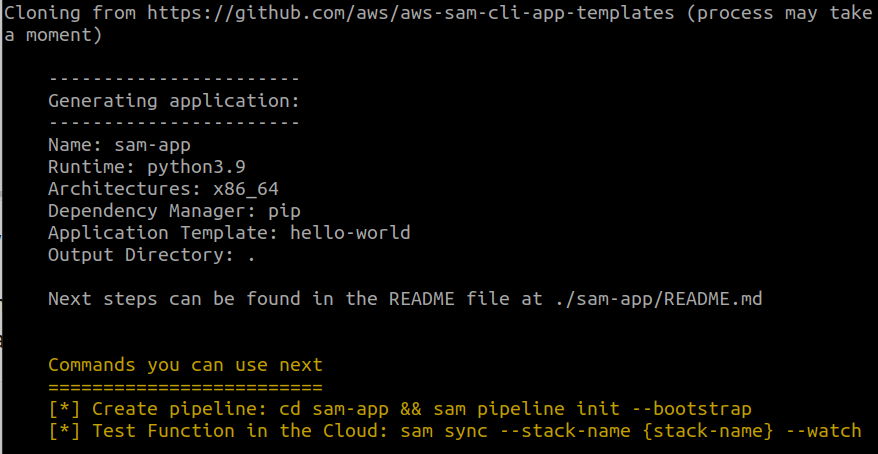
After executing the previous settings, you will see the basic summary of the application:
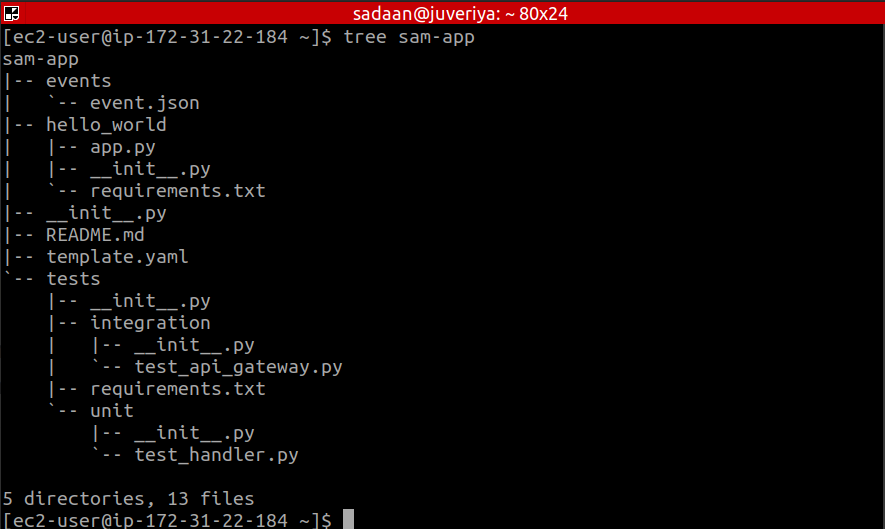
This sam-init command will cause a directory to be created with the same name as chosen for the project name. Also, note that the following directory contains many sub-directories and files:
These are the three most important files:
- The “template.yaml” includes the AWS SAM template, which describes the AWS resources comprising the application.
- “app.py” inside the hello_world folder, which includes the code for handling the Lambda function.
- “requirements.txt” inside the hello_world folder, which includes dependencies required by the application.
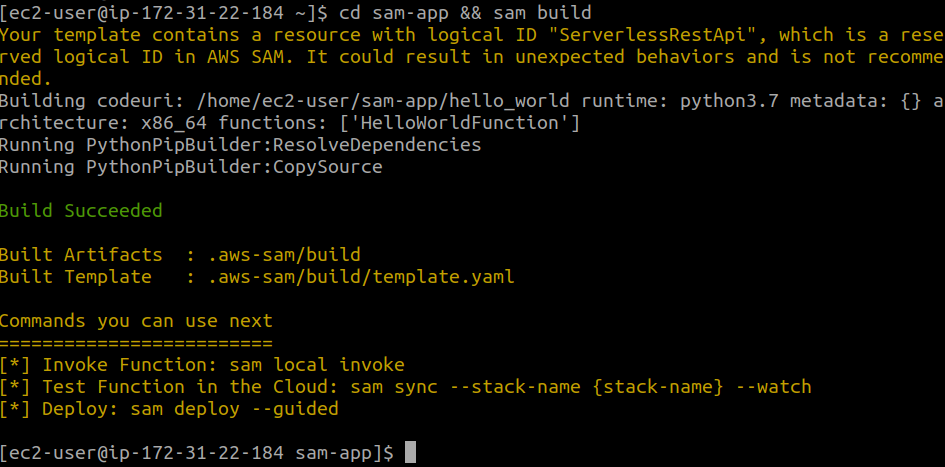
2. Building the application
Before building the application, navigate the project directory containing the template.yaml file and then run the build command. Here is how to do this in one step:
Note: Please use the required version of Python. Otherwise, the build command may fail.
3. Deploying the application
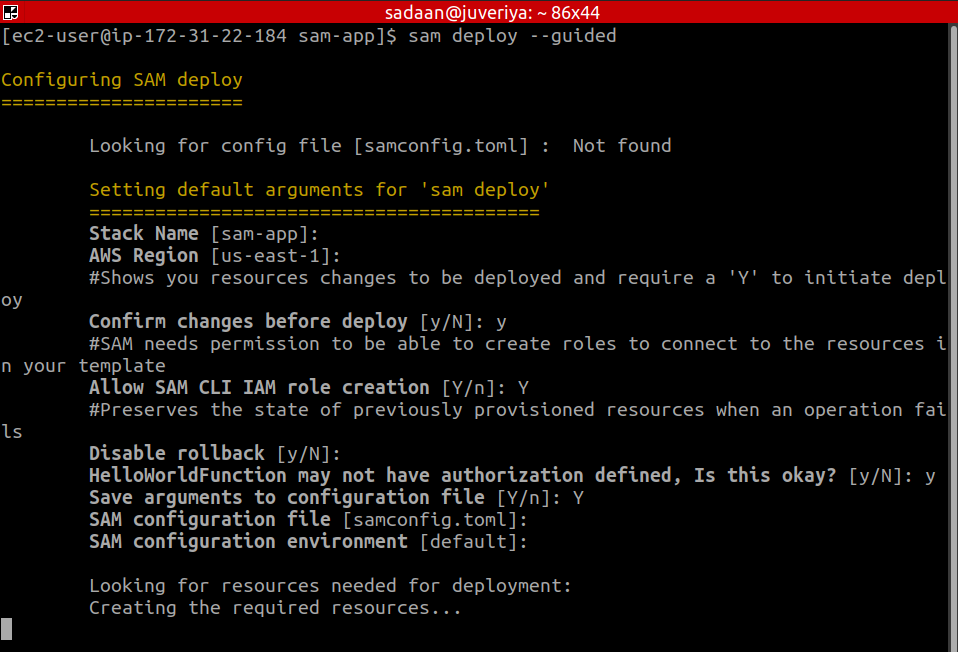
Finally, to deploy the application with an interactive wizard, run the following command:
Acknowledge a question by entering “Y” and press enter to choose a default option.
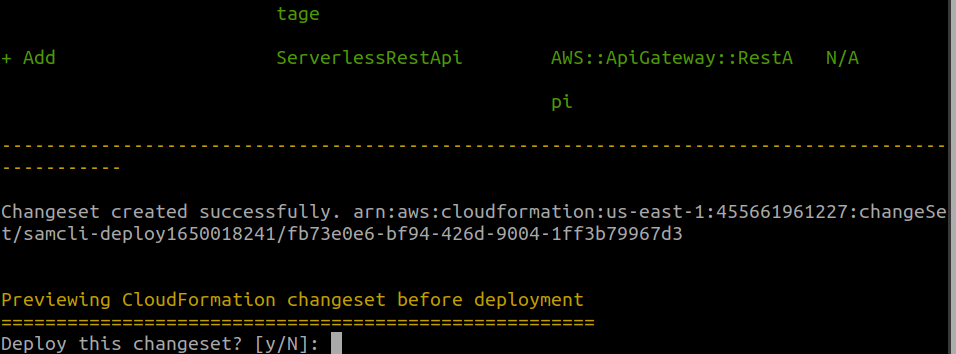
When asked to deploy the changes, enter “y”:
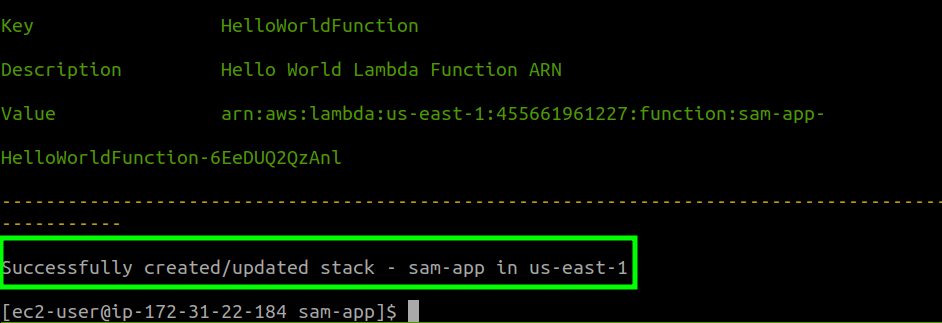
After some processing, you should see a successful message:
Testing the Application
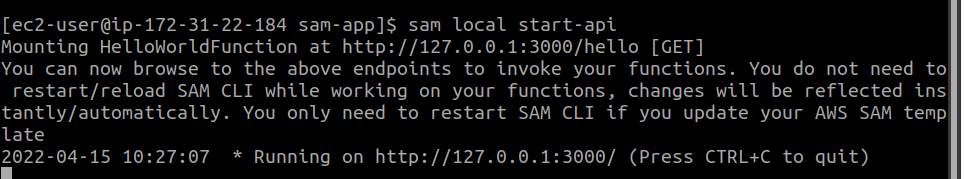
Use the “sam local” command to test the hello world application with Docker containers:
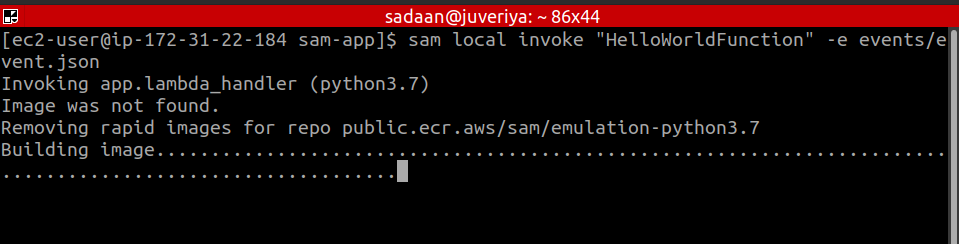
Another way to test the application is to call the lambda function with:
Conclusion
In this guide, we have covered how to build and deploy an AWS SAM application using a sample AWS SAM template. Next, you can try to develop and deploy your own AWS SAM application. We hope you found this article helpful. Check other Linux Hint articles for more tips and tutorials.