Syntax:
The syntax of this function is given below. This function takes the specific position as an argument value and returns the value of that position if the position value exists.
vector.at(position)
Example-1: Read each element of a vector
The way to print each element of the vector by using at() function has shown in the following example. A vector of string values has been defined in the code.
The ‘for’ loop has been used to iterate the vector based on the vector size and print each value of the vector in each line by using at() function. The size() function has been used to count the total number of elements of the vector.
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Declare a vector of string values
vector Str = {"Welcome", "to", "LinuxHint"};
//Iterate the string using loop
for(int i=0; i<Str.size(); i++)
{
//Print the character
cout<< Str.at(i) << "\n";
}
cout<< "\n";
return 0;
}
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above code. There are 3 elements in the vector that have been printed in the output.
Example-2: Calculate the sum of the vector values
The way to calculate the sum of all values of a vector that contains integer numbers has shown in the following example. A vector of 10 integer numbers has been declared in the code. The first ‘for’ loop has been used to print the values of the vector and the second ‘for’ loop has been used to calculate the sum of all values of the vector. Next, the result of the summation has been printed.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
//Declare a vector of integer numbers
vectorintVector {7, 4, 9, 2, 1, 0, 8, 3, 5, 6};
//Initialize an integer variable
int sum = 0;
//Print the values of the vector
cout<< "The values of the vector:\n";
for (int i=0; i<intVector.size(); i++)
cout<< ' ' << intVector.at(i);
cout<< '\n';
//Calculate the sum of the vector values
for (int i=0; i<intVector.size(); i++)
sum += intVector.at(i);
//Print the sum value
cout<< "The sum of all vector values is:" << sum << "\n";
return 0;
}
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above code. The sum of all values (7 + 4 + 9 + 2 + 1 + 0 + 8 +3 +5 + 6) is 45 that has printed in the output.
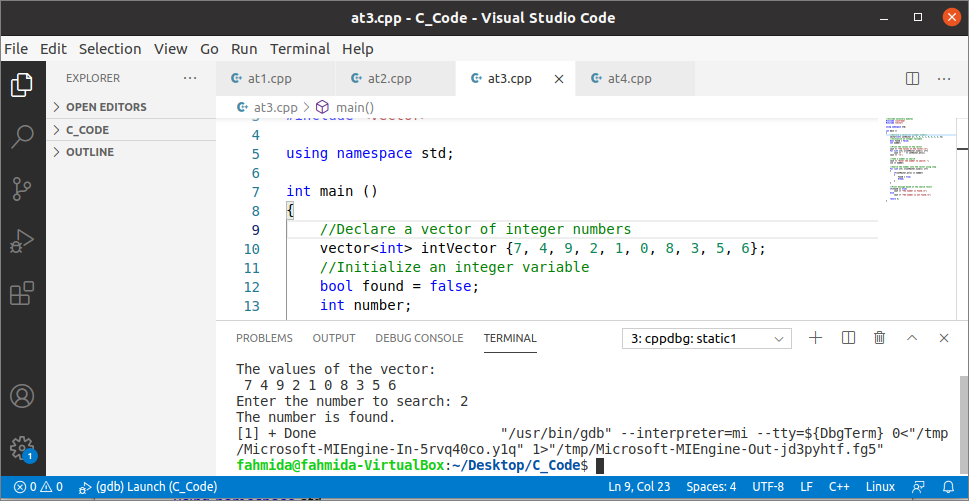
Example-3: Search a particular value in the vector
The way to search a particular value in a vector using at() function has shown in the following example. A vector of 10 integer numbers has been used in the code like the previous example. The values of the vector have been printed by using a ‘for’ loop and at() function.
The searching value will be taken from the user. Another ‘for’ loop has been used to search the input value into the vector and set the value of the variable, found to be true if the input value exists in the vector.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
//Declare a vector of integer numbers
vectorintVector {7, 4, 9, 2, 1, 0, 8, 3, 5, 6};
//Initialize an integer variable
bool found = false;
int number;
//Print the values of the vector
cout<< "The values of the vector:\n";
for (int i=0; i<intVector.size(); i++)
cout<< ' ' << intVector.at(i);
cout<< '\n';
//Take a number to search
cout<>number;
//Search the number into the vector using loop
for (int i=0; i<intVector.size(); i++)
{
if(intVector.at(i) == number)
{
found = true;
break;
}
}
//Print message based on the search result
if(found == true)
cout<< "The number is found.\n";
else
cout<< "The number is not found.\n";
return 0;
}
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above code. The value 2 exists in the vector, and the message, “The number is found” has been printed.
The value 11 does not exist in the vector and the message, “The number is not found” has been printed.
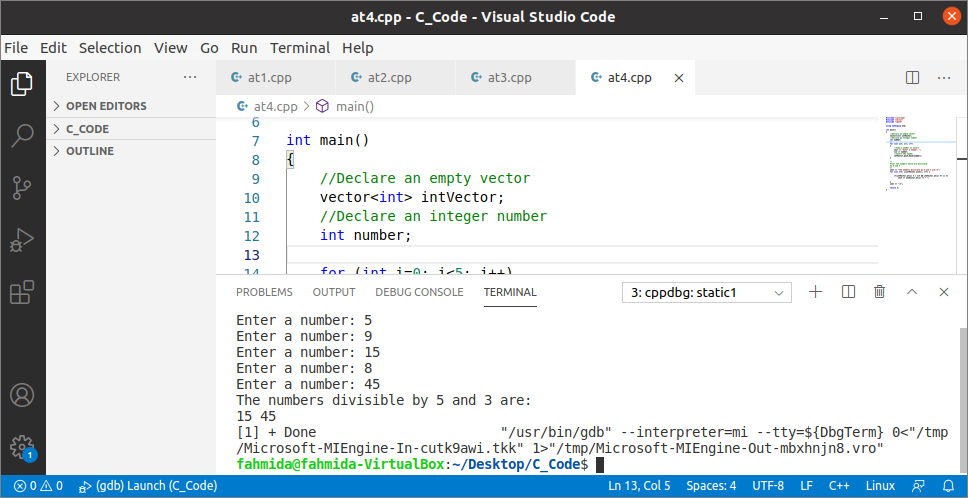
Example-4: Search value based on conditions in the vector
The way to find out those values from the vector that are divisible by 5 and 3 has shown in the following example. Five integer values will be taken from the user and inserted into an empty vector by using the push_back() function. After insertion, each value of the vector will be divided by 3 and 5. If the remainder values of both divisions are zero, then that value of the vector will be printed.
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Declare an empty vector
vectorintVector;
//Declare an integer number
int number;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
//Take a number to insert
cout<>number;
//Insert the number
intVector.push_back(number);
}
/*
Print the numbers which are divisible
by 5 and 3
*/
cout<< "The numbers divisible by 5 and 3 are:\n";
for (int i=0; i<intVector.size(); i++) {
if(intVector.at(i) % 5 ==0 && intVector.at(i) %3 == 0)
cout<< intVector.at(i) << " ";
}
cout<< "\n";
return 0;
}
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above code for the input values, 5, 9, 15, 8, and 45. Here, 15 and 45 are divisible by 3 and 5.
Conclusion:
Different uses of at() function in C++ vector have been described in this tutorial by using multiple examples. The at() function can also be used for string data type. I hope the reader will be able to use this function in vector for various purposes after reading this tutorial.