Method of Assigning Output to a Variable in Bash:
Note: We will be demonstrating this method on Ubuntu 20.04. You can also use any other Linux distribution if you want.
In this method, we will be explaining to you how you can assign the output of a command to a variable in Bash directly via the terminal. For getting this work done through this method, you will have to perform the following steps:
Since we are not creating a Bash script for this method, therefore, we should directly launch the terminal in Ubuntu 20.04. You can also take a look at the terminal window from the image shown below:
Method of Storing the Value of “date” Command to a Variable:
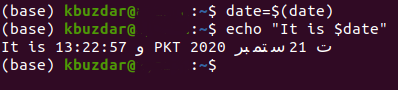
Once you have launched the terminal, you need to save the output of a command to a variable. For this particular example, we will be using the date command of Linux and we will be assigning its output to the date variable. This can be done by typing the following command in your terminal and then pressing the Enter key:
Here, the first date refers to the variable that we have created. You can have any name of your choice for this variable. Whereas the second date followed by the “$” and enclosed in the round brackets indicate the date command of the Linux operating system. Running this command will simply fetch the current system date and will save it to the date variable. This command can also be seen in the following image:
Now type the following command in your terminal and then press the Enter key:
Here, the echo command will be responsible for displaying the current date on your terminal by printing the value of the date variable. You can also use the printf command to achieve the same purpose. This command can also be witnessed from the image shown below:
As soon as the execution of the echo command will complete, you will be able to see the current date stored in the date variable on your terminal as shown in the following image. However, the echo command used in this method is not mandatory. It is used just to show you that the output of the date command has been successfully saved to the date variable so that you can easily verify it. Otherwise, you can even skip this step.
Method of Assigning the Value of “who” Command to a Variable:
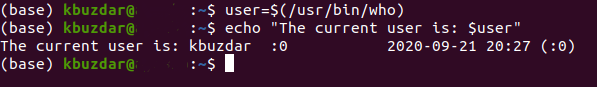
You can also assign the output of the “who” command to a variable. The “who” command is used to find out the currently logged in user of the system. You only need to type the following command in your terminal:
The details of the current user reside in the /usr/bin directory, therefore, this path is mentioned before the “who” command. Running the above-mentioned command will assign the output of the “who” command to the variable named user.
After doing this assignment, you have to run the echo command to print this value as shown in the image below:
The execution of the echo command will display all the information regarding the currently logged in user along with the current system date and time on your terminal as shown in the following image:
Method of Saving the Value of “pwd” Command to a Variable:
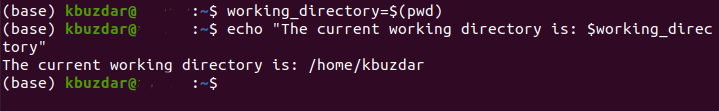
You can even find out the current working directory of your Ubuntu 20.04 system and store it in a variable. All you have to do is to run the command shown below:
Running this command will store your current working directory in the working_directory variable.
After assigning the current working directory to your desired variable, you can display the value of this variable on the terminal by making use of the echo command:
Executing the echo command will display the current working directory on your terminal as shown in the following image:
In the very same manner, you can assign the outputs of even the complex commands to any variable of your choice.
Conclusion:
By following the easy and simple steps described in this article, one can conveniently store the output of any command in Bash to the desired variable. This variable can then be used for printing the output of that command or even using it for any further processing.