This blog will demonstrate the usage and implementation of the “Arrays.asList()” method in Java.
What is the “Arrays.asList()” Method in Java?
The “Arrays.asList()” method transforms the provided array into a “list”. This method can transform an array of strings, integers, or class objects into a list.
Syntax
In this syntax, “arr” corresponds to the array that needs to be converted into the list.
Example 1: Utilization of “Arrays.asList()” Method Upon Strings Array in Java
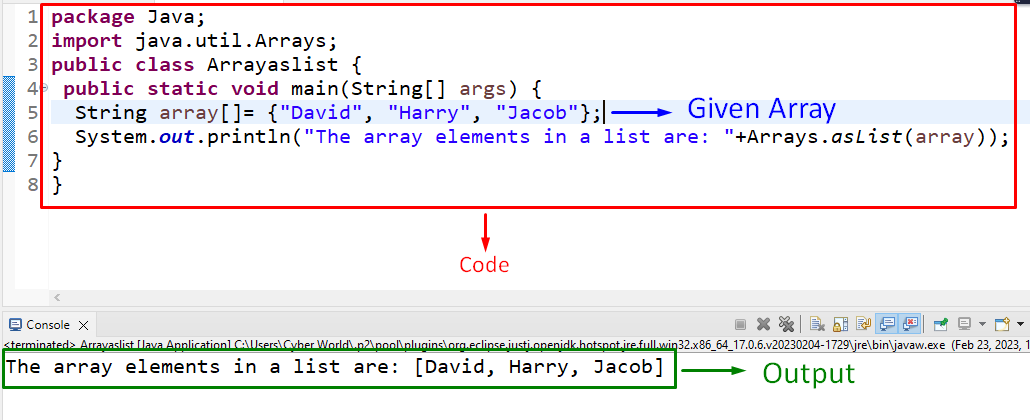
In this example, the “Arrays.asList()” method can be used to transform an array of strings into a list.
Before moving to the example, make sure to include the following library to work with “Arrays”:
Now, add the below-provided code in the “main()” method:
In the above code block:
- Firstly, declare an array of strings having the given string values.
- In the next step, apply the “Arrays.asList()” method accumulating the specified array as its parameter.
- This will result in converting the string array into a list.
Output
In this output, it can be observed that the strings array is converted into a list (identified by the square brackets in the output).
Example 2: Utilization of “Arrays.asList()” Method Upon Integer Array in Java
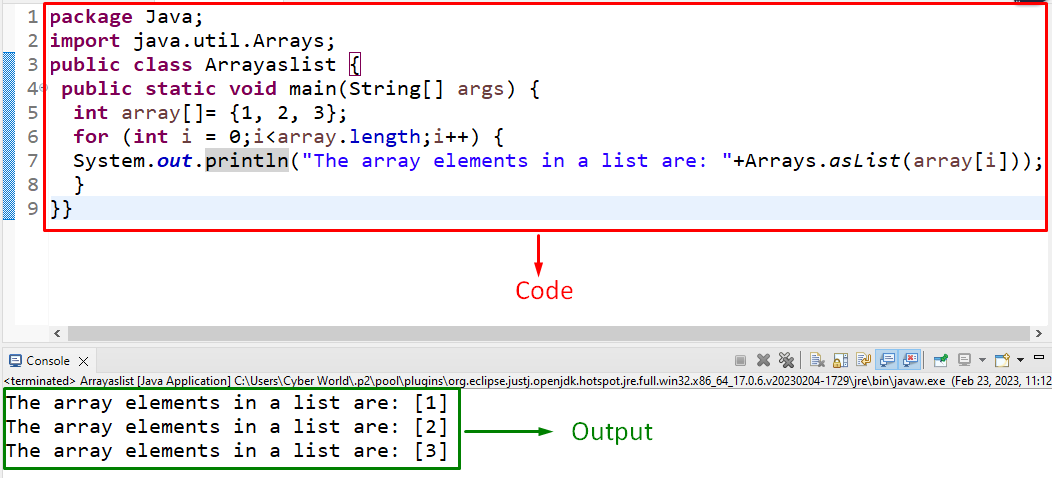
In this particular example, the discussed method can be implemented to transform an integer array into a list by iterating through the list elements one by one.
Now, let’s move on to the below-stated code snippet:
Apply the following steps as given in the above code:
- Initialize an array of integers.
- After that, apply the “for” loop to iterate through the array elements via the “length” property.
- Lastly, return the iterated integers one by one as a “list” via the “Arrays.asList()” method.
Output
In this outcome, it can be observed that the integers are appended in the list step by step since the “for” loop is utilized.
Example 3: Utilization of “Arrays.asList()” Method Upon Class Object in Java
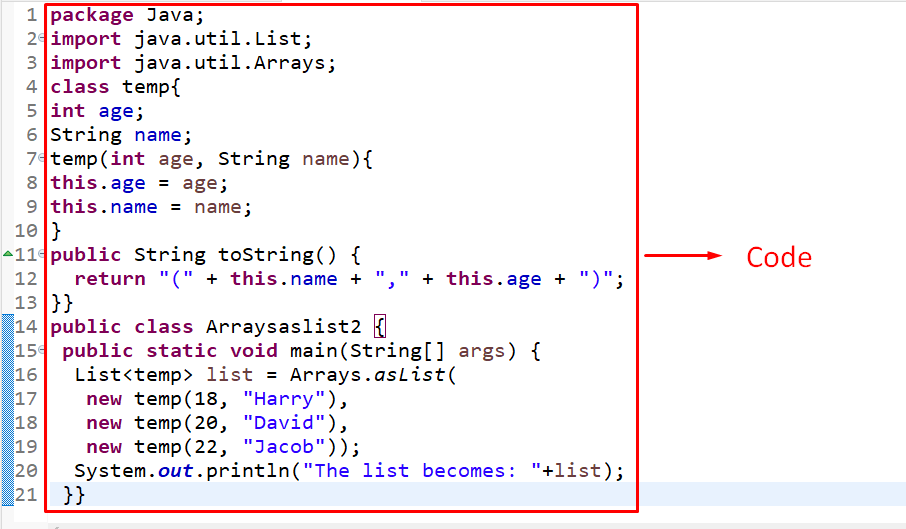
This example can be utilized to append the set class objects into a list.
Firstly, include the below-stated libraries to work with “Arrays” and the “List”:
import java.util.Arrays;
Now, head to the following lines of code:
int age;
String name;
temp(int age, String name){
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() {
return "(" + this.name + "," + this.age + ")";
}}
public class Arraysaslist2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<temp> list = Arrays.asList(
new temp(18, "Harry"),
new temp(20, "David"),
new temp(22, "Jacob"));
System.out.println("The list becomes: "+list);
}}
In these lines of code, apply the following steps:
- First, create a class named “temp”. Within the class, specify the stated variables.
- In the next step, include the class constructor accumulating the parameters identical to the specified variables.
- In the constructor definition, refer to the specified variables via “this” and allocate them the values contained as function parameters.
- After that, override the “toString()” method of the Object class to return the set object’s values.
- In the “main”, create a list and contain the specified values based on the constructor’s parameters by creating a class object via the “new” keyword and the “temp()” constructor.
- Lastly, return the corresponding values in the form of a list.
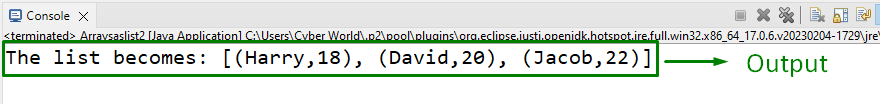
Output
This output implies that the set object values are appended in a list accordingly.
Conclusion
The “Arrays.asList()” method gives a fixed-size list corresponding to the array. This method can transform an array of strings, integers, or class objects, respectively, into a list. This write-up elaborated on using and implementing the “Arrays.asList()” method in Java.