PyTorch is a framework meant for creating models based on machine learning. “Tensors” are used in PyTorch to store individual values of data in an organized manner. Tensors in PyTorch are quite similar to their mathematical counterparts and can have any number of dimensions from unity to infinity. Arithmetic operations can be applied to PyTorch tensors.
In this blog, we will demonstrate how to add tensors in PyTorch.
How to Add Two Tensors in PyTorch?
The addition of two Tensors in PyTorch follows the same mathematical principles. To add the tensors using PyTorch, follow the examples.
Example 1: Add 1D Tensors in PyTorch
Follow the steps below to add two 1D tensors:
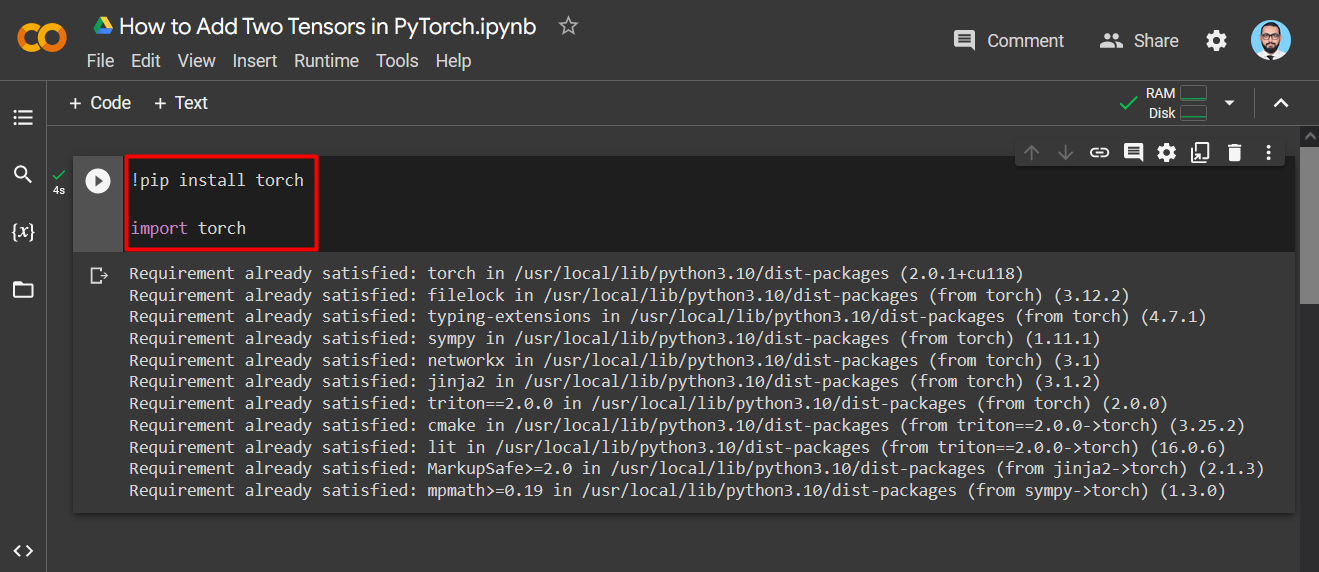
Step 1: Install and Import the Required Libraries
Install the “Torch” library using the “pip” installation package. Then, import “Torch” into the project using the “import” command as shown:
import torch
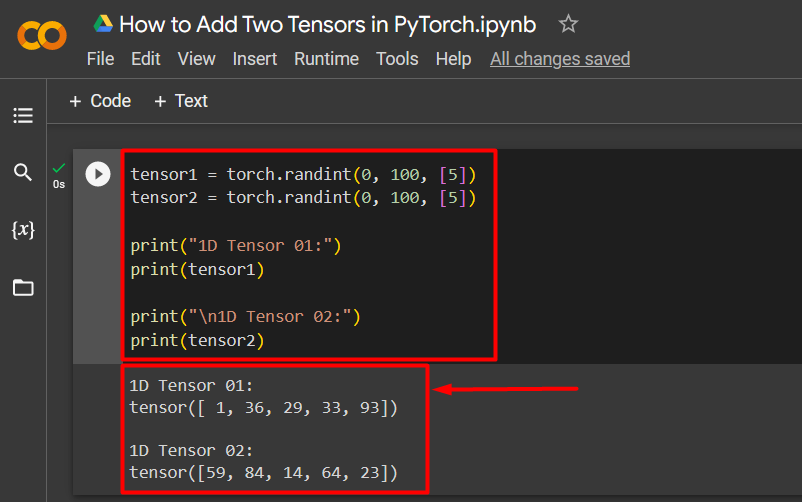
Step 2: Filling Two 1D Tensors with Random Integer Values
Next, use the “torch.randint()” function to fill two 1D Tensors with 5 random integer values each ranging from 0 to 100. Then, we use the “print()” method to show the output as shown below:
tensor2 = torch.randint(0, 100, [5])
print("1D Tensor 01:")
print(tensor1)
print("\n1D Tensor 02:")
print(tensor2)
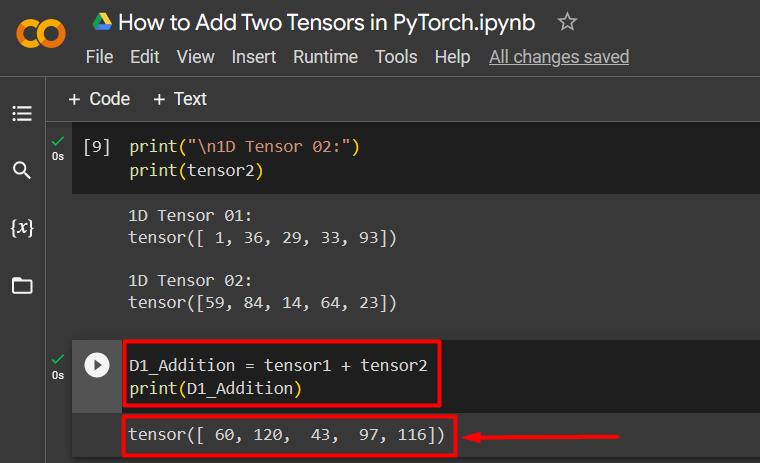
Step 3: Addition of Two 1D Tensors
Next, add the two 1D tensors by defining a simple equation and use the “print()” method to show the result:
print(D1_Addition)
Example 2: Add 2D Tensors of Random Integer Values
To add the 2D tensors of random numbers, go through the below steps.
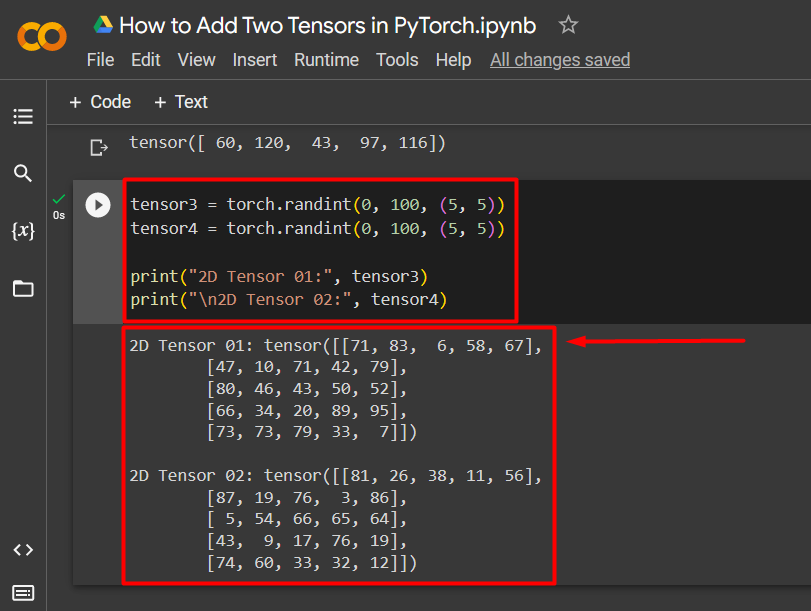
Step 1: Create 2D Random Integer Value Tensor
The addition of two 2D Tensors is similar to that of 1D Tensors. Use the “torch.randint()” function to add random integer values to the two 2D Tensors ranging from 0 to 100. Then, use the “print()” method to show the output as seen below:
tensor4 = torch.randint(0, 100, (5, 5))
print("2D Tensor 01:", tensor3)
print("\n2D Tensor 02:", tensor4)
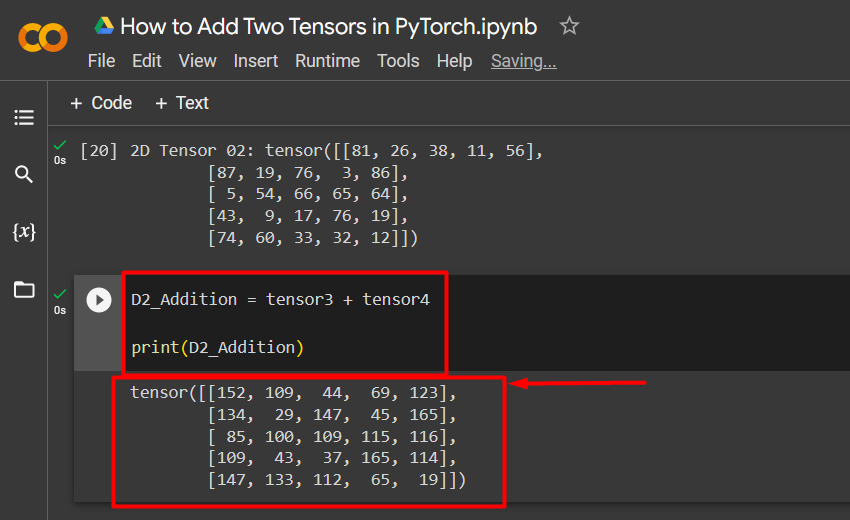
Step 2: Add Tensors and Print Resultant Tensor
In the last step, the two 2D Tensors are added together by using a simple arithmetic equation and their value will be saved in “D2_Addition”. After that, pass the resultant tensor “D2_Addition” to the “print()” method to show the result as seen below:
print(D2_Addition)
Note: You can access our Google Collaboratory Notebook to check the Addition of Two Tensors for yourself at this link.
Pro-Tip
You can establish any limit on the range of random integer values that are used to fill the tensors before addition. This range always depends on your choice. In our case, we used the range from 0 to 100.
Success! In this blog, we have demonstrated how to fill tensors with random integer values and how to add 1D and 2D tensors.
Conclusion
The addition of Two Tensors in PyTorch is done by using a simple arithmetic equation after filling the tensors with random integer values using the “torch.randint()” function. The output is then displayed on the console using the “print()” method. This post illustrates how to add two tensors.