Quick Outline
This post will show:
How to Add a Custom Memory Type in LangChain
- Installing Frameworks
- Importing Libraries
- Building Custom Memory
- Configuring Prompt Template
- Testing the Model
How to Add a Custom Memory Type in LangChain?
Adding a customized memory type in LangChain allows the user to get the most performance as the memory. The user can configure the memory type according to his requirements. To add a custom memory type in LangChain, simply go through the following steps:
Step 1: Installing Frameworks
First, install the LangChain framework to get started with the process of adding a custom memory type:
Running the above command in the Python Notebook will install the dependencies for the LangChain as displayed in the following snippet:
Install the OpenAI module to get its libraries that can be used to configure the LLMs:
This guide will use the spaCy framework to design the custom memory type in the LangChain and the following code is used to install the module:
The spaCy model uses the hash table to store the information as the observation like previous chat messages. The following code is used to download the Large Language Model or LLM from the spaCy library to build an advanced NLP model:
Importing “os” and “getpass” libraries are for entering the API key from the OpenAI’s account to set up its environment:
import getpass
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("OpenAI API Key:")
Step 2: Importing Libraries
The next step is to import the required libraries for customizing the memory type according to the chat model:
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
from pydantic import BaseModel
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from typing import List, Dict, Any
Importing the “spaCy” library to load the “en_core_web_lg” model and assign it to the “nlp” variable as it is the Natural Language Processing model:
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_lg")
Step 3: Building Custom Memory
After that, simply build the custom memory using BaseMemory and BaseModel arguments in the Memory class. Then, configure entities (collected/stored from the data) that can be stored in the memory as complete information or as a single unit. The memory is configured to contain all the entities from the document to optimize the performance of the memory and model:
""" Memory class for storing information about entities"""
entities: dict = {}
memory_key: str = "entities"
def clear(self):
self.entities = {}
@property
def memory_variables(self) -> List[str]:
""" Initialize the variables provided to the query"""
return [self.memory_key]
#define the memory variables using the arguments
def load_memory_variables(self, inputs: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, str]:
""" Call the variables for memory i.e. entity key"""
doc = nlp(inputs[list(inputs.keys())[0]])
#configure entities to be stored in the memory for an individual unit
entities = [
self.entities[str(ent)] for ent in doc.ents if str(ent) in self.entities
]
return {self.memory_key: "\n".join(entities)}
#define the save_context() to use the memory
def save_context(self, inputs: Dict[str, Any], outputs: Dict[str, str]) -> None:
"""Store observation from this chat to the memory"""
text = inputs[list(inputs.keys())[0]]
doc = nlp(text)
for ent in doc.ents:
ent_str = str(ent)
if ent_str in self.entities:
self.entities[ent_str] += f"\n{text}"
else:
self.entities[ent_str] = text
Step 4: Configuring Prompt Template
After that, simply configure the prompt template that explains the structure of the input provided by the user/human:
template = """The following is an interaction between a machine and a human It says it does not know If the machine does not know the answer The machine (AI) provides details from its context and if it does not understand the answer to any question it simply says sorry
Entity info:
{entities}
Communication:
Human: {input}
AI:"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["entities", "input"], template=template)
Step 5: Testing the Model
Before testing the model, simply configure the LLM using the OpenAI() method and set up the ConversationChain() function with arguments:
conversation = ConversationChain(
llm=llm, prompt=prompt, verbose=True, memory=SpacyEntityMemory()
)
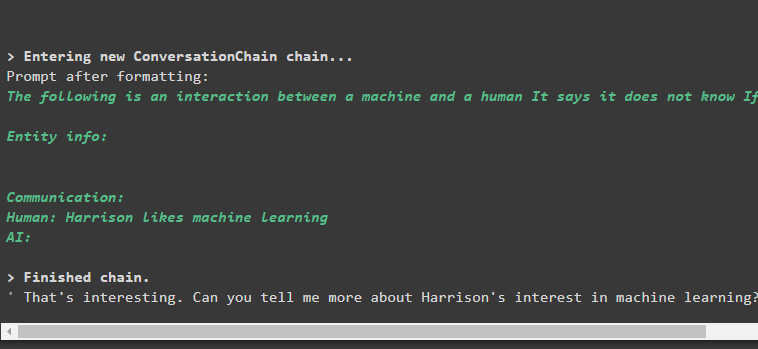
Give information to the model using the input argument while calling the predict() method with the conversation variable:
Output
The model has absorbed the information and stored it in the memory and also posed the question related to the information for getting on with the conversation:
The user can respond to the question from the model to add more information to the memory or test the memory by asking the question about the information:
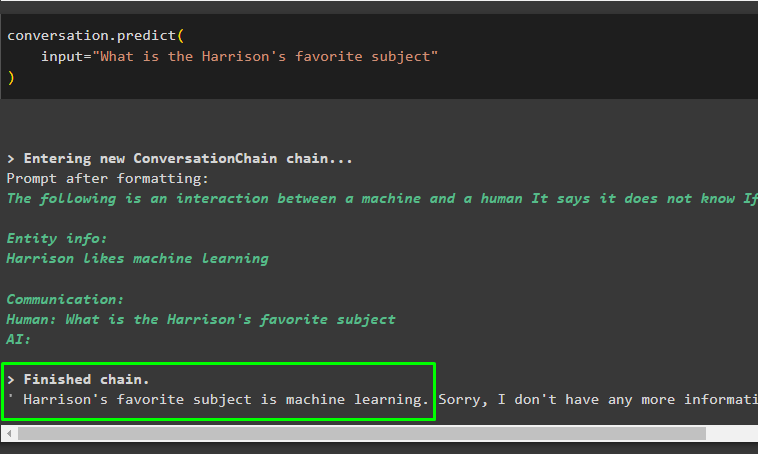
input="What is the Harrison's favorite subject"
)
The model gives the output based on the previous information and displays it on the screen as the following snippet shows:
That’s all about adding a custom memory type in LangChain.
Conclusion
To add a custom memory type in LangChain, simply install the required modules for importing libraries to build the custom memory. The spaCy is the important library that is being used in this guide to add a custom memory using its NLP model. After that, configure the custom memory and prompt template to give the structure of the chat interface. Once the configuration is done, simply test the memory of the model by asking for information related to stored data.