This post is dedicated to discussing the “date” command, its syntax, and usage in bash. Let’s understand the syntax of the “date” command first:
Let’s have a look at a list of format options for the “date” command:
| Format | Description |
| date +%a | Gives name of the weekday [Mon, Sun, Fri] |
| date +%A | Gives name of the weekday [Monday, Sunday, Friday] |
| date +%b | Gives name of the month [Jan, Feb, Mar] |
| date +%B | Gives name of the month [January, February, March] |
| date +%d | Displays day of the month [05] |
| date +%D | Displays current date MM/DD/YY format [11-01-21] |
| date +%F | Shows date in YYYY-MM-DD format [2021-11-01] |
| date +%H | Shows hour in 24-hour format [22] |
| date +%I | Shows hour in 12-hour format [11] |
| date +%j | Displays the day of the year [001 – 366] |
| date +%m | Displays the number of the month [01-12] |
| date +%M | Displays minutes [00-59] |
| date +%S | Displays seconds [00-59] |
| date +%N | Displays in Nanoseconds |
| date +%T | Displays time as HH:MM:SS [in 24-hour format] |
| date +%u | Day of the week [1-7] 1 is Monday, 6 is Saturday |
| date +%U | Shows week number of the year [00-53] |
| date +%Y | Displays year YYYY [2021] |
| date +%Z | Displays Time zone |
Any of the option mentioned above can be used with the date command; let’s further explore the date command:
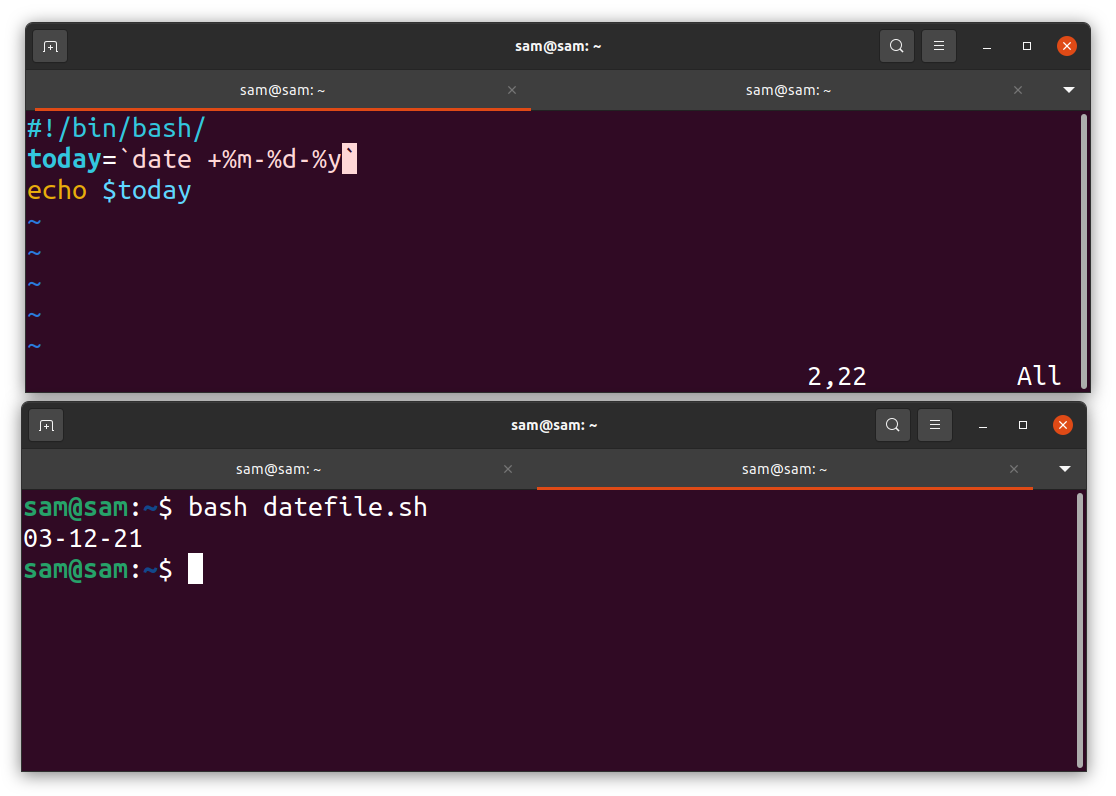
How to print date in MM-DD-YYYY format:
I am writing simple bash scripts to display the date in various formats. To writing the script, I am using the “vim” editor. To getting a versatile editor, use the command mentioned below:
Type “vim” in terminal to launch vim editor:
today = `date +%m-%d-%Y`
echo $today
I have saved the file by the name of “datefile.sh”, to execute it use the command:
Keep in mind the case sensitivity of letters, “M” is for minutes, and “m” is the month.
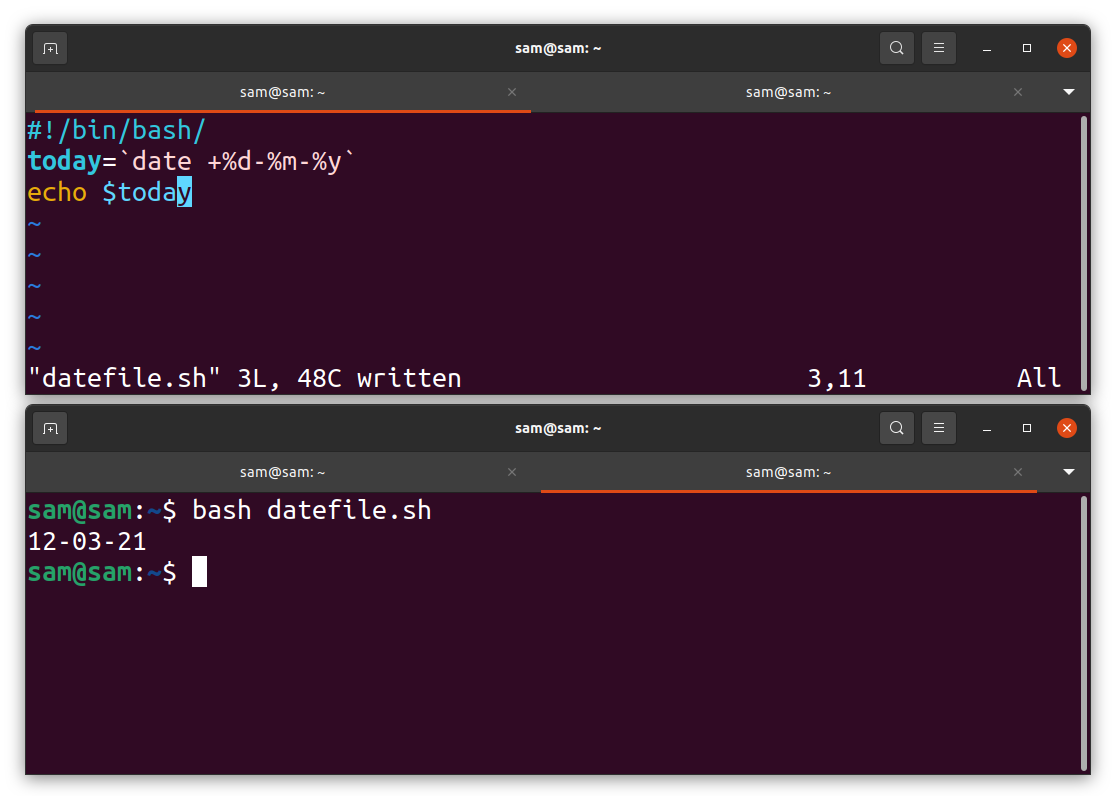
How to print date in MM-YYYY format:
Let’s change the format of the date:
today = `date +%m-%Y`
echo $today
Now the day is displaying before the month.
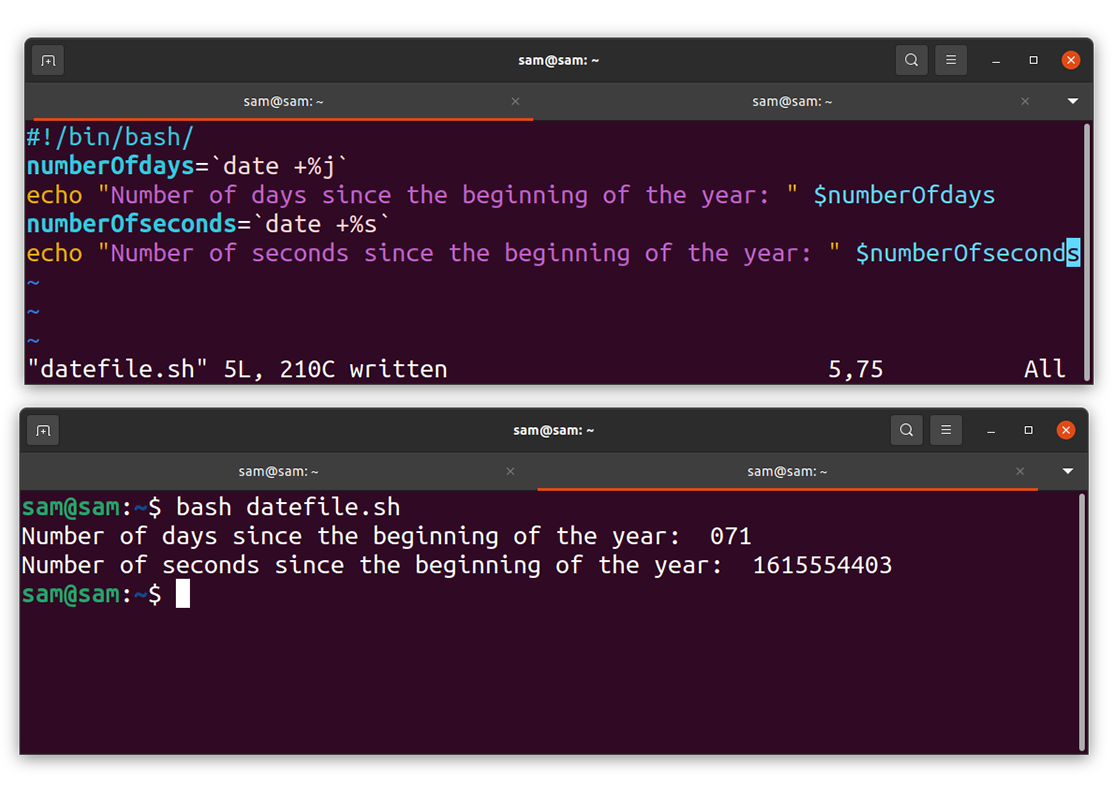
How to display the current day number and seconds passed:
Calculating the number of days and even the number of seconds seem impractical, but thanks to the “date” command, it can easily be printed in terminal:
numberOfdays = `date +%j`
echo “The Current Day Number: “ $numberOfdays
numberOfseconds = `date +%s`
echo “Total seconds passed this year: “ $numberOfseconds
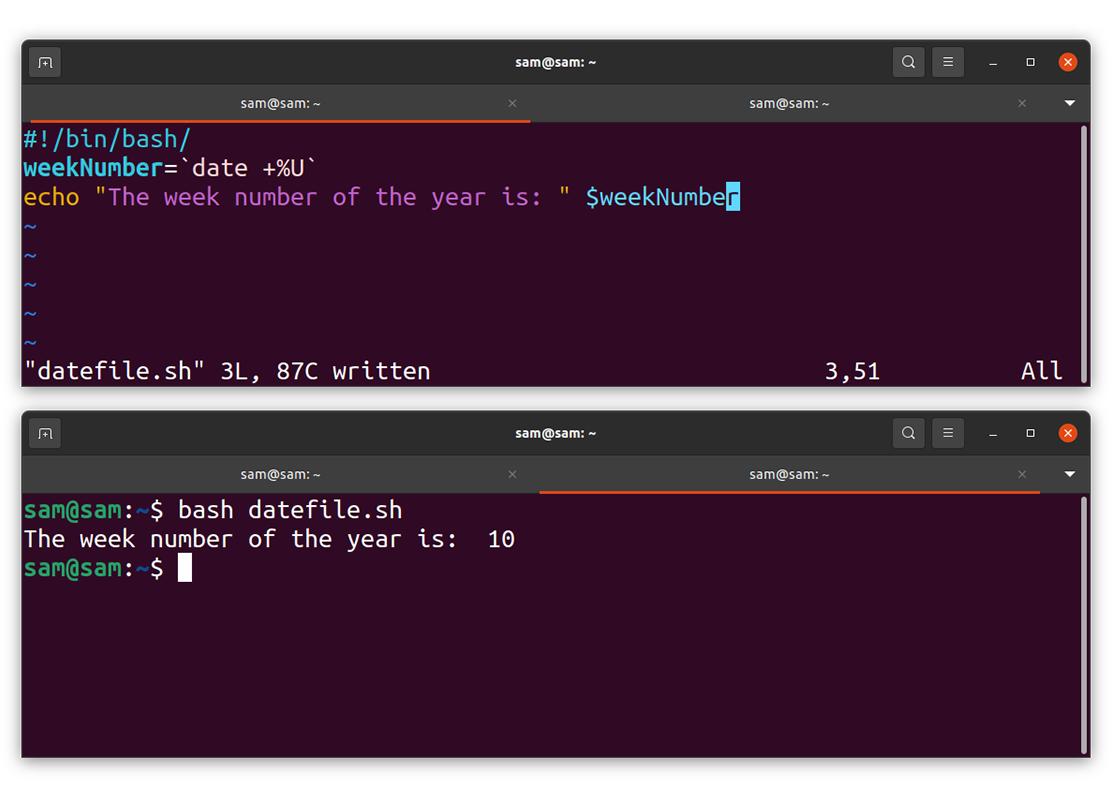
How to display the week number using the date command:
Another exciting feature of the “date” command is that it can quickly tell you the year’s week number. To get the week number, type the following command:
Or if you are working with bash scripting, then try the following program using any editor:
weekNumber = `date +%U`
echo “The week number of the year is:” $weekNumber
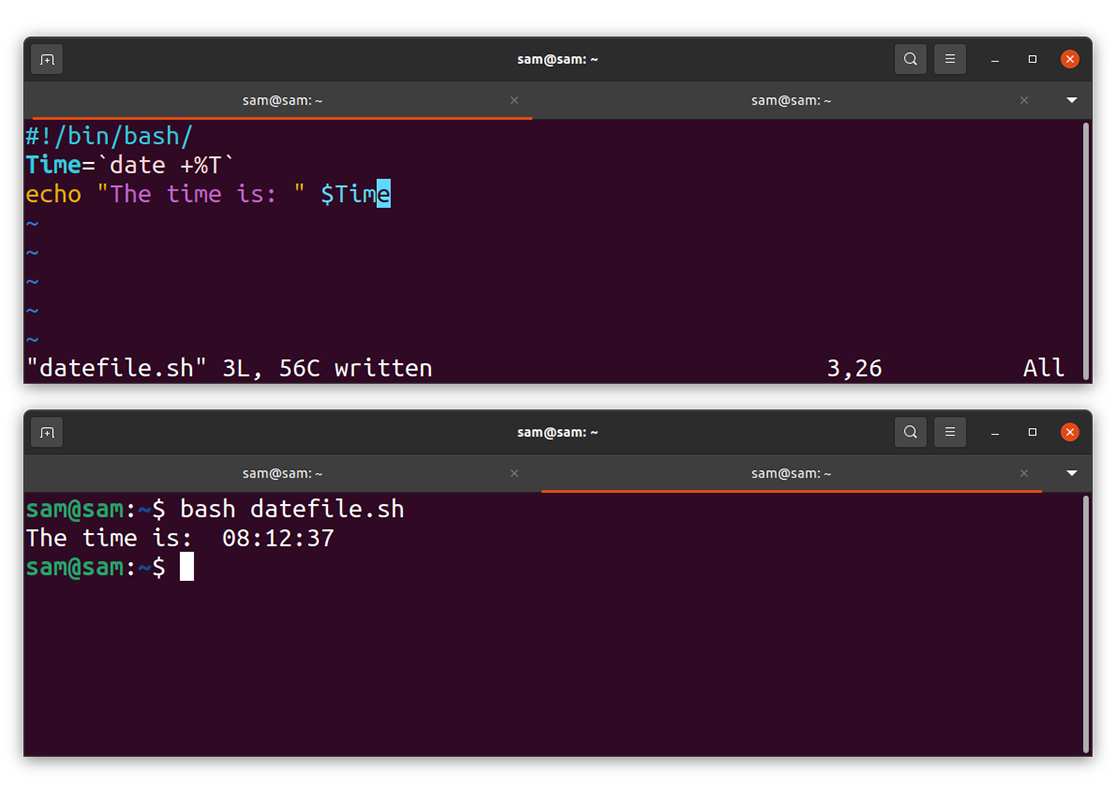
How to display time using the date command:
Let’s write a program to display time using the date command:
Time = `date +%T`
echo “The time is: ” $Time
Conclusion:
The “date” command is a built-in command of Unix-like operating systems that, apart from displaying date can be used with other commands as well. In this guide, we understood the syntax and usage of the “date” command in bash scripting to display it in various formats.