Creation of a Crontab file
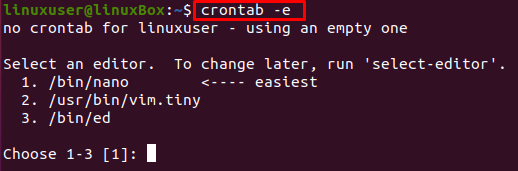
Crontab shortened for Cron table file is used to run the Cron jobs. The user first must create a crontab file because it is not available by default on the system. The crontab file can be created on any Linux-based Operating system using the command given below:
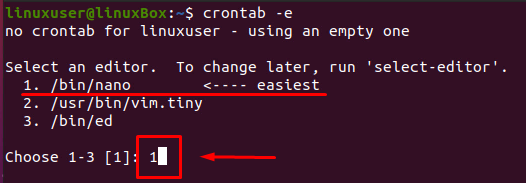
If you are running the above-given command for the first time, it will first ask you to choose the text editor. Select the easiest one, “Nano Editor,” as shown in the screenshot by typing the index number of your desired editor and after selecting the editor, hit Enter:
The new crontab file will be created. Now, in this file, you can write all the Cron jobs of your choice.
Syntax
The syntax for running cronjob is that we first have to mention the time and then specify the command that we want to execute. The syntax for mentioning time is further divided into five fields.
- The first field describes the minute.
- The second field describes the hour.
- The third field describes the day of the Month.
- The fourth field describes the month.
- The fifth field describes the day of the Week.
Alright, once you have understood the right position for describing the time for running the cronjob, there are several ways as well for mentioning time.
➔ The asterisk ‘*’ operator, a.k.a wildcard, is described as all allowed values. For example, 0 0 1 * * will run the command at midnight on the first day of every month.
➔ A comma-separated list of values describes the list of values for repetition. For example, 10,20,30
➔ The dash ‘-’ operator describes the range of values. For example, 5-10.
➔ The slash ‘/’ operator helps in making the conjunction with ranges. For example, */2 * * * * will run the Cron job after every interval of 2 minutes.
Now, you have got enough theoretical knowledge about Cron jobs, let’s perform some practical stuff and see how to run Cron jobs every 10, 20, or 30 minutes.
Run a Cron Job after every 10 minutes
There can be two ways to run a Cron job after a specific interval of time, like after every 10 minutes.
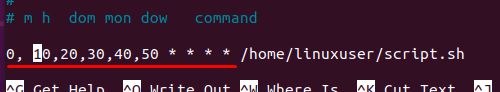
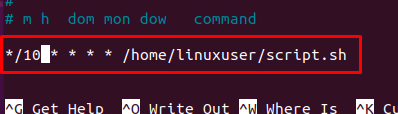
The first way is to use a comma-separated list of minutes; for example, if we want to run a script after every 10 minutes, the syntax for writing such a Cron job is given below:
But isn’t it looking too tedious task to write the whole list of minutes? The slash operator helps in writing the easy syntax for running a Cron job after every 10 minutes.
In this command, */10 will create a list of minutes after every 10 minutes.
Run a Cron Job after every 20 minutes
Just like we wrote the Cron job for running the script after every 10 minutes, we can do the same for running the script after every 20 minutes:
Run a Cron Job after every 30 minutes
Similarly, the syntax for running a Cron job after every 30 minutes will be like:
Conclusion
Cron jobs are used to run the commands after a specific interval of time to manage the system updates or backing up the system’s data and we have learned how to run Cron jobs every 10, 20, or 30 minutes post. We hope this post helps in understanding and running Cron jobs.