Necessary Methods
The QTableWidget class includes many methods to perform tasks related to table creation. Some of the more commonly used methods of this class are explained below:
| Method Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| setRowCount() | Used to define the number of rows. |
| setColumnCount() | Used to define the number of columns. |
| setHorizontalHeaderLabels() | Used to set the header labels of the table. |
| setItem() | Used to set the cell value of the table. |
| resizeColumnsToContents() | Used to resize the columns of the table based on the content. |
| resizeRowsToContents() | Used to resize the rows of the table based on the content. |
| setMinimumWidth() | Used to set the minimum width of the table. |
| setMinimumHeight() | Used to set the minimum height of the table. |
| show() | Used to display the table. |
QTableWidget Usage
The following sections provide simple examples to explain how to create a table in the PyQt application using static data and list data.
Example 1: Create Simple Table Using Static Data
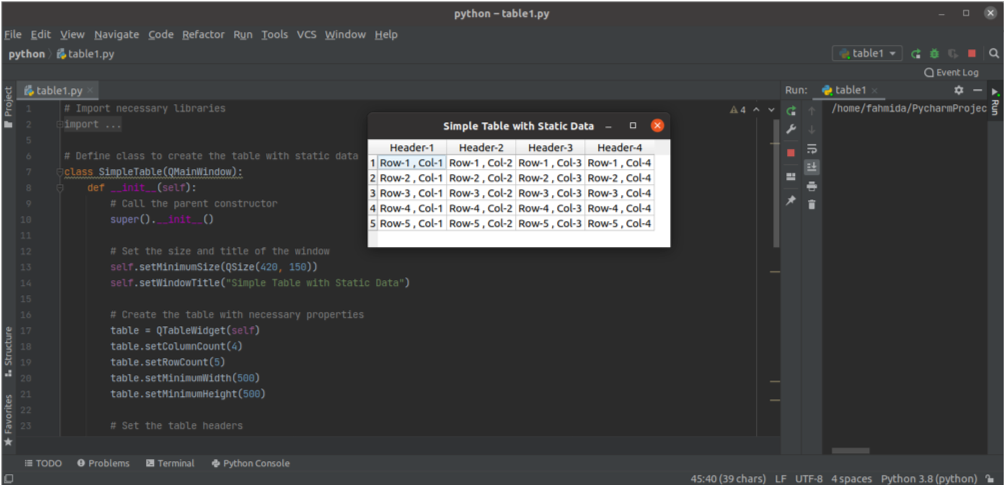
The following script creates a table of static data with five rows and four columns using the QTableWidget class. Two for loops with range values have been used in the script to add the static data into the table cells. The row and column positions of each cell have been added as the content of each cell. The QDesktopWidget is used in the script to display the window with the table in the center of the screen.
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTableWidget, QTableWidgetItem, QDesktopWidget
from PyQt5.QtCore import QSize
# Define class to create the table with static data
class SimpleTable(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
# Call the parent constructor
super().__init__()
# Set the size and title of the window
self.setMinimumSize(QSize(420, 150))
self.setWindowTitle("Simple Table with Static Data")
# Create the table with necessary properties
table = QTableWidget(self)
table.setColumnCount(4)
table.setRowCount(5)
table.setMinimumWidth(500)
table.setMinimumHeight(500)
# Set the table headers
table.setHorizontalHeaderLabels(["Header-1", "Header-2", "Header-3", "Header-4"])
# Set the table values
for i in range(5):
for j in range(4) :
table.setItem(i, j, QTableWidgetItem("Row-" + str(i+1) + " , Col-" + str(j+1)))
# Resize of the rows and columns based on the content
table.resizeColumnsToContents()
table.resizeRowsToContents()
# Display the table
table.show()
# Display the window in the center of the screen
win = self.frameGeometry()
pos = QDesktopWidget().availableGeometry().center()
win.moveCenter(pos)
self.move(win.topLeft())
self.show()
# Create app object and execute the app
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
mw = SimpleTable()
mw.show()
app.exec()
The following window with a table will appear the above script is executed. According to the values of the for loops, the cell value of the first row and the first column is ‘Row-1, Col-1,’ and the cell value of the last row and last column is ‘Row-5, Col-4.’
Example 2: Create Table with Tool-Tip Using Dictionary and List Data
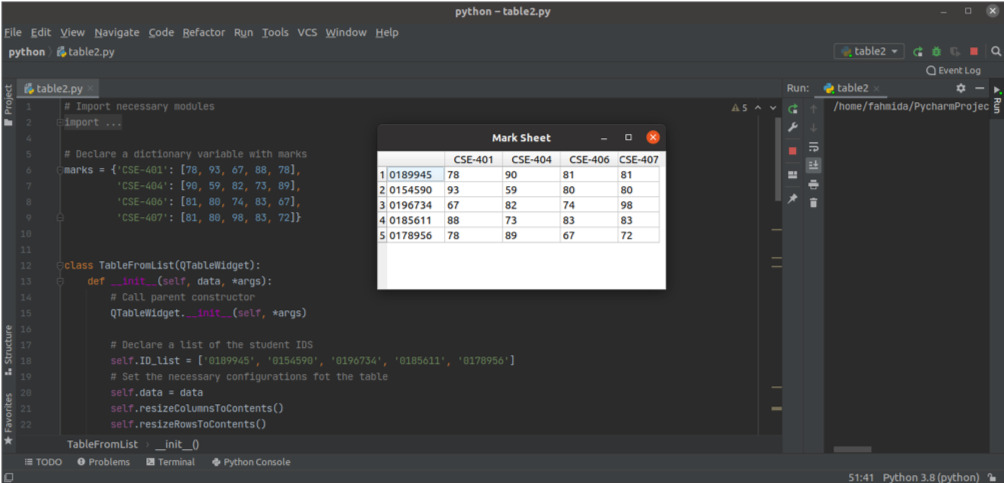
The following script creates a table with the content of a Python dictionary and list using the QTableWidget class. The script also adds a tool-tip text for the table header. A Python dictionary named marks is also declared in the script. The course codes are used as the key values of the dictionary. A Python list is declared to define the student IDs. The key values of the dictionary are added to the header of the table, the values of the list are added to the first column of the table, and the values of the dictionary are added to the other columns of the table.
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QTableWidget, QTableWidgetItem, QDesktopWidget
# Declare a dictionary variable with marks
marks = {'CSE-401': [78, 93, 67, 88, 78],
'CSE-404': [90, 59, 82, 73, 89],
'CSE-406': [81, 80, 74, 83, 67],
'CSE-407': [81, 80, 98, 83, 72]}
class TableFromList(QTableWidget):
def __init__(self, data, *args):
# Call parent constructor
QTableWidget.__init__(self, *args)
# Declare a list of the student IDS
self.ID_list = ['0189945', '0154590', '0196734', '0185611', '0178956']
# Set the necessary configurations fot the table
self.data = data
self.resizeColumnsToContents()
self.resizeRowsToContents()
self.setColumnWidth(0, 100)
for i in range(4):
self.setColumnWidth(i, 80)
self.setMinimumWidth(400)
self.setWindowTitle("Mark Sheet")
# Declare the variable to set the header content
headers = []
headers.append('')
# for loop to read the keys of the dictionary
for n, key in enumerate(sorted(self.data.keys())):
headers.append(key)
# for loop to read the values of the dictionary
for m, item in enumerate(self.data[key]):
ID = QTableWidgetItem(self.ID_list[m])
self.setItem(m, 0, ID)
newVal = QTableWidgetItem(str(item))
self.setItem(m, n+1, newVal)
# Set the header label of the table
self.setHorizontalHeaderLabels(headers)
# Set the tooltips for the headers
self.horizontalHeaderItem(1).setToolTip("Multimedia ")
self.horizontalHeaderItem(2).setToolTip("Artificial Intelligent")
self.horizontalHeaderItem(3).setToolTip("Advanced Database")
self.horizontalHeaderItem(4).setToolTip("Unix Programming")
# Read the particular cell value
self.clicked.connect(self.on_click)
# Display the window in the center of the screen
win = self.frameGeometry()
pos = QDesktopWidget().availableGeometry().center()
win.moveCenter(pos)
self.move(win.topLeft())
self.show()
def on_click(self):
for ItemVal in self.selectedItems():
# Read the header value based on the selected cell
subject = self.horizontalHeaderItem(ItemVal.column()).text()
# Print the detail information of the mark
print("\n", self.ID_list[ItemVal.row()], " got ", ItemVal.text(), " in ", subject)
# Create app object and execute the app
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
table = TableFromList(marks, 5, 5)
table.show()
app.exec()
The following window with the table will appear after the above script is executed.
Conclusion
This tutorial showed you how to create tables with fixed data, dictionary data, and list data using two examples. Tables can also be created with dynamic data using database tables or other data sources.