In this article, I am going to show you how to install KVM on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS and create a simple KVM virtual machine with it. So, let’s get started.
Enabling Hardware Virtualization:
You must enable hardware virtualization extension from the BIOS of your computer for KVM to work. For Intel processors, you should enable the processor feature VT-x or VT-d from the BIOS. For AMD processors, you should enable the processor feature AMD-v from the BIOS.
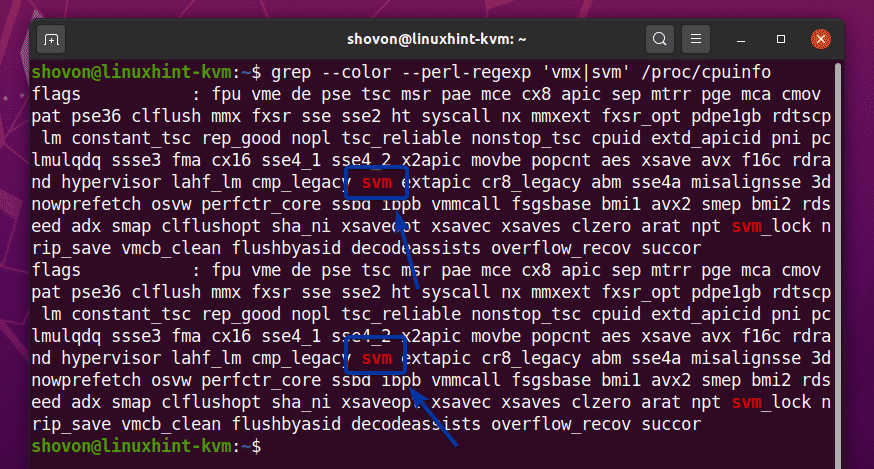
Once you have hardware virtualization enabled in the BIOS, run the following command to verify whether VT-x/VT-d or AMD-v extension is enabled.
You should have either the svm or vmx flag available in the output if you have hardware virtualization enabled in the BIOS.
I am using an AMD processor. So, the svm flag is available in my case. If you’re using an Intel processor, then it will be vmx.
Upgrading the System:
Before installing KVM, you should upgrade the software packages of your Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
First, update the APT package repository cache of Ubuntu 20.04 LTS with the following command:
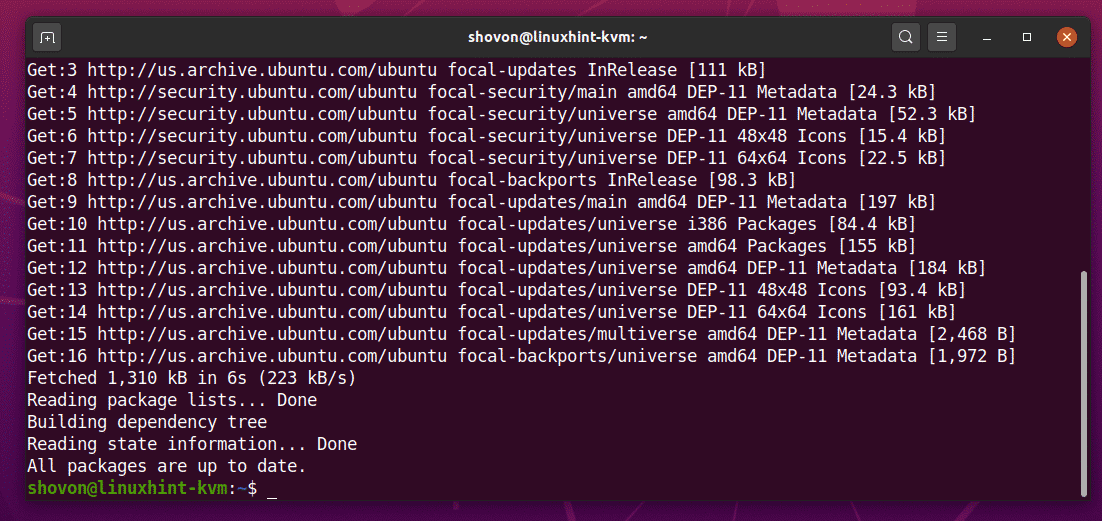
The APT package repository cache of Ubuntu 20.04 LTS should be updated.
As you can see, all the packages of my Ubuntu 20.04 LTS machine are already up to date. So, I don’t have to do anything.
If you have updates available, you can apply those updates with the following command:
Then, press Y and then press <Enter> to confirm the installation.
Once the updates are installed, reboot your computer with the following command:
Installing KVM:
KVM packages are available in the official package repository of Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
You can install KVM on your Ubuntu 20.04 LTS with the following command:
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press <Enter>.
The APT package manager should download all the required packages from the internet.
Once the packages are downloaded, the APT package manager will install them.
At this point, KVM should be installed.
Installing LibVirt:
LibVirt is a tool for creating and managing KVM virtual machines and configuring KVM. It’s a must-have tool for virtualization with KVM.
LibVirt is available in the official package repository of Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
To install LibVirt, run the following command:
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press <Enter>.
The APT package manager should download and install all the required packages from the internet.
LibVirt should be installed at this point.
Once LibVirt is installed, add your login user to the libvirt group with the following command:
Then, reboot your computer with the following command for the changes to take effect.
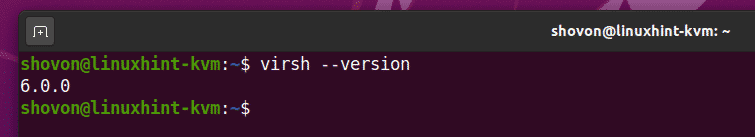
Once your computer boots, run the following command to confirm that LibVirt is working.
The command should return the version number of LibVirt. In my case, it is 6.0.0.
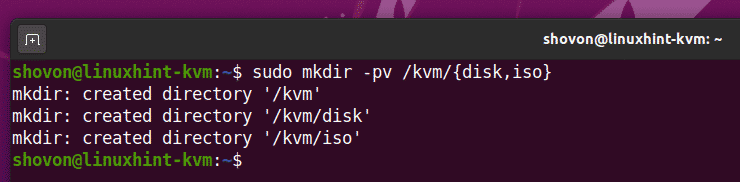
Setting Up Required KVM Directories:
I think it’s a good idea to keep all the virtual machine data organized. I usually keep all the KVM virtual machine data in /kvm/ directory. In the /kvm/ directory, I create 2 subdirectories disk/ and iso/. In the disk/ subdirectory, I keep all the virtual machine (VM) hard disk files. In the iso/ subdirectory, I keep the ISO installation images of different operating systems (i.e. Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, etc.).
You can create the same directory structures with the following command:
Creating a KVM Virtual Machine:
In this section, I am going to show you how to create an Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS KVM virtual machine.
First, you have to download the Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS ISO installation image. To keep all the virtual machine files/data organized, it’s a good idea to store the ISO image in the /kvm/iso/ directory.
So, navigate to the /kvm/iso/ directory with the following command:
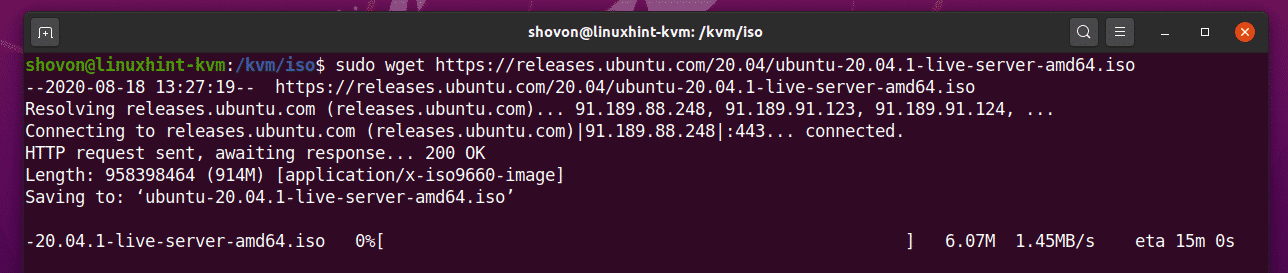
You can download the Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS ISO image from the official website of Ubuntu with the following command:
wget should start downloading the Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS ISO image. It will take a while to complete.
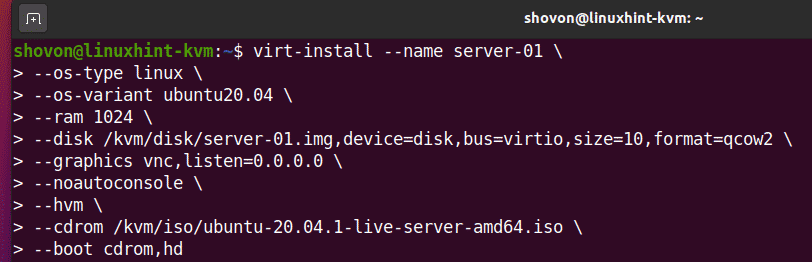
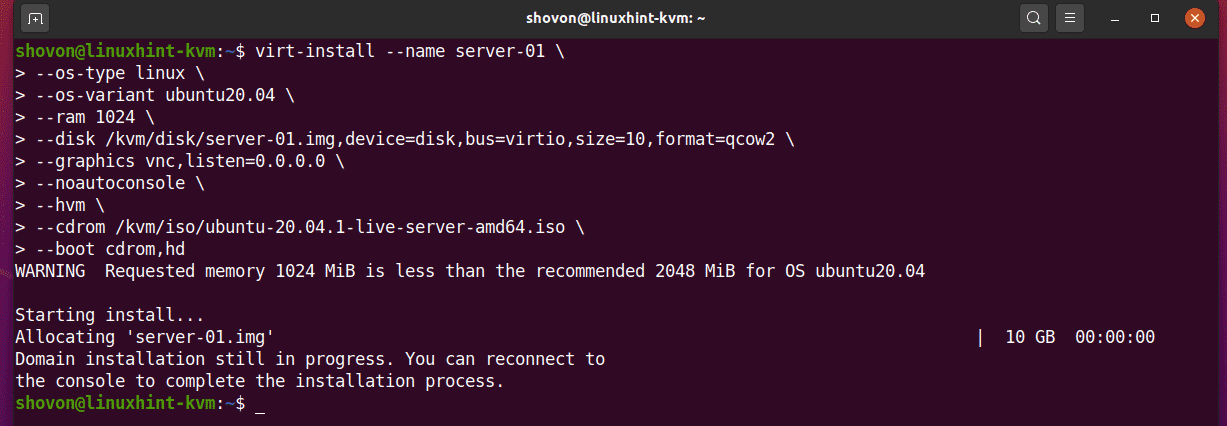
Once the Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS ISO image is downloaded, you can create a KVM virtual machine with the following command:
--os-type linux \
--os-variant ubuntu20.04 \
--ram 1024 \
--disk /kvm/disk/server-01.img,device=disk,bus=virtio,size=10,format=qcow2 \
--graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0 \
--noautoconsole \
--hvm \
--cdrom /kvm/iso/ubuntu-20.04.1-live-server-amd64.iso \
--boot cdrom,hd
Here, the name of the virtual machine will be server-01.
The operating system we will be installing is linux.
The operating system variant is ubuntu20.04 (Ubuntu 20.04 LTS).
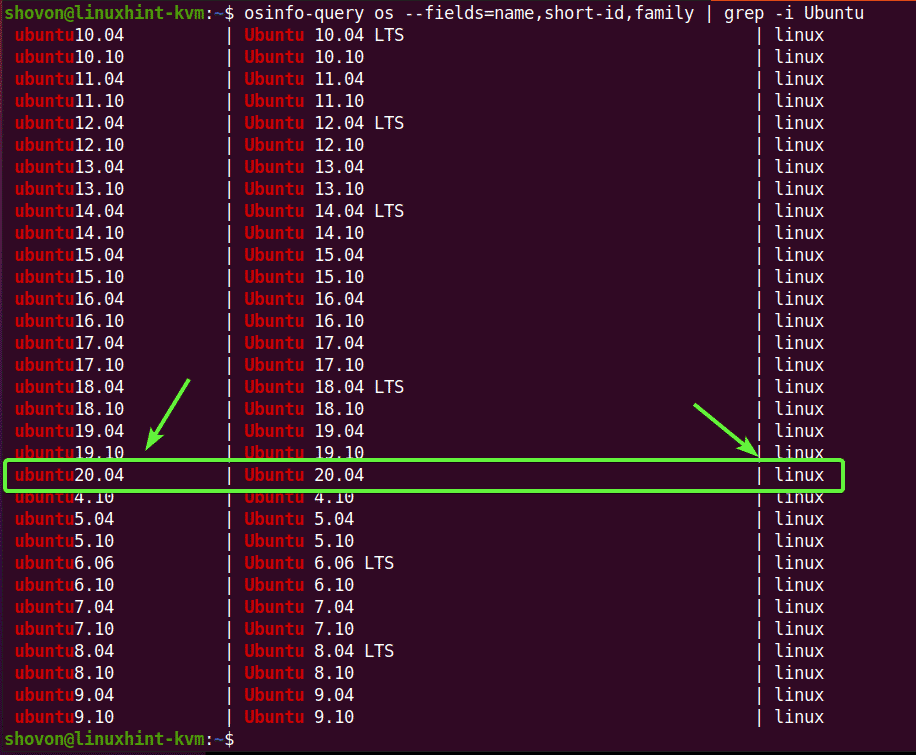
The OS type and OS variant values are not random. You can find the OS type and OS variant for your desired Linux distribution with the osinfo-query command. As you can see, for Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, the OS type in linux and OS variant is ubuntu20.04.
If you don’t have osinfo-query command available in your computer, you can install it with the following command:
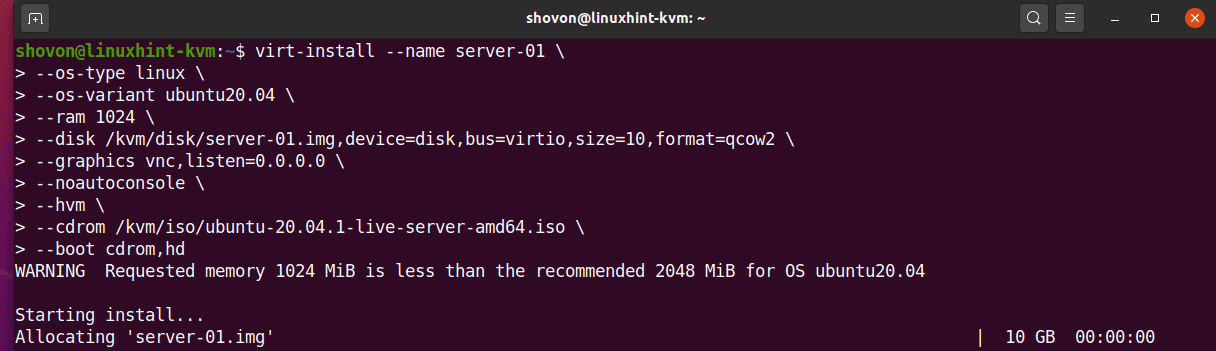
The RAM (Random Access Memory) of the VM will be 1024 MB (Megabytes).
The virtual disk of the VM will be saved in the /kvm/disk/server-01.img file. The virtual disk is about 10 GB in size, and the format is QCOW2 (QEMU Copy-On-Write v2)
The virtual machine will be accessible via VNC (Virtual Network Computing) remote desktop protocol, and the VNC server will be listening on all available network interfaces configured on your Ubuntu 20.04 LTS KVM host.
Ubuntu 20.04 LTS KVM host won’t automatically try to connect to the virtual machine once the virtual machine is created. The virtual machine will keep running in the background.
Use full virtualization for the virtual machine. This will make virtual machines perform better.
Use the Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS ISO image we have just downloaded as the virtual CD/DVD ROM of the virtual machine and used for installing Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS on the virtual machine.
Set’s the boot order of the virtual machine. The first boot entry is the virtual CD/DVD ROM and then the virtual hard drive. So, the virtual machine will be able to boot from the Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS ISO image and install Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS on the hard drive.
That’s basically all the options you need to create a KVM virtual machine.
Once you run the virt-install command, KVM should start creating the virtual machine. It may take a while depending on your virtual machine configuration.
At this point, the KVM virtual machine should be created.
Listing KVM Virtual Machines:
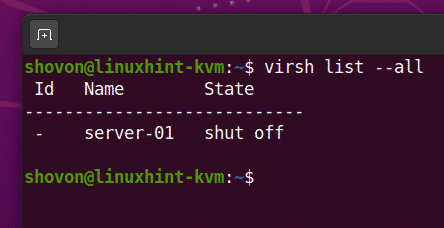
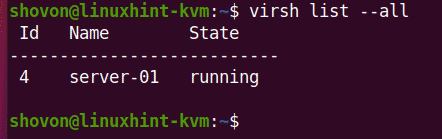
Once the KVM virtual machine is created, you can list it with the following command:
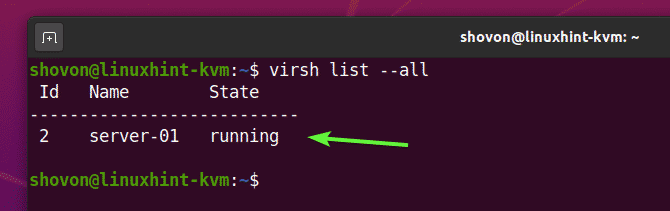
The command should show you all the KVM virtual machines you have. Right now, I have only 1 virtual machine server-01. This is the one I have just created. As you can see, the virtual machine server-01 is running. You should be able to connect to it using any VNC client.
Connecting to KVM Virtual Machines Remotely with VNC:
In this section, I am going to show you how to connect to your KVM virtual machine remotely with VNC.
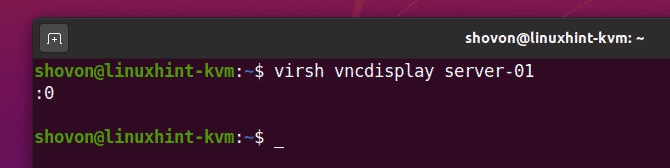
You can find the VNC port number of KVM virtual machine server-01 with the following command:
As you can see, the VNC port number of the server-01 virtual machine is 0.
Here, port 0 means port 5900. The same way, port 1 means port 5901 and so on.
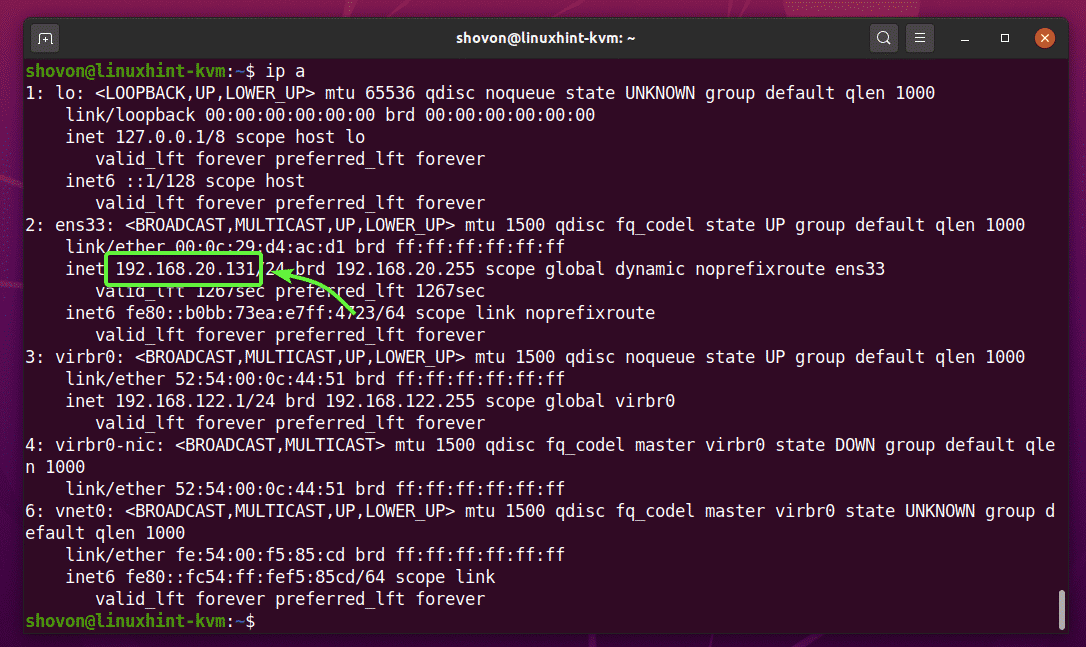
Now, find the IP address of your Ubuntu 20.04 LTS KVM host with the following command:
In my case, the IP address is 192.168.20.131. It will be different for you. So, make sure to replace it with yours from now on.
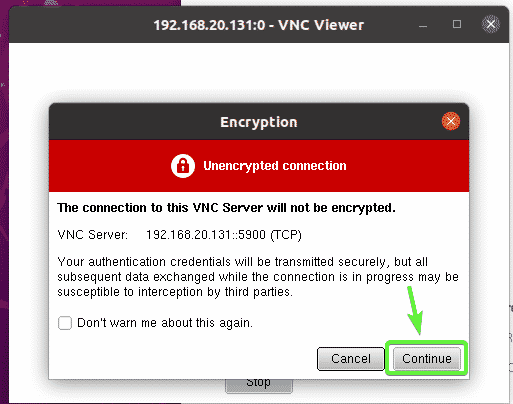
Open any VNC client and connect to the address 192.168.20.131:0.
Click on Continue.
You should be connected to the display of the server-01 KVM virtual machine, as you can see in the screenshot below.
Now, you can install your desired operating system on the virtual machine.
In my case, I will install the Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS operating system on the virtual machine.
Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS is installed on the virtual machine at this point. Let’s reboot the virtual machine.
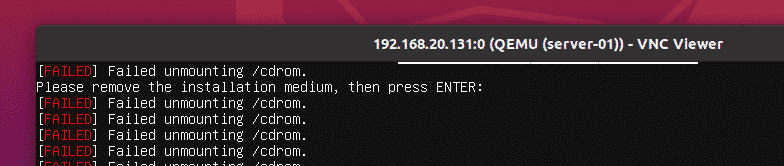
Press <Enter> when you see this message.
The server-01 KVM virtual machine should be powered off automatically, as you can see in the screenshot below.
Start the server-01 KVM virtual machine with the following command:
The virtual machine server-01 should be started.
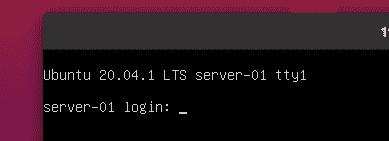
Now, you can connect to the server-01 virtual machine from a VNC client as before. As you can see, the Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS login screen is displayed.
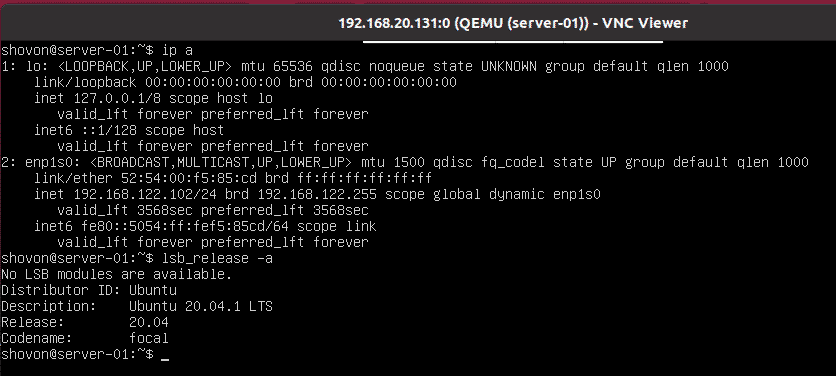
You can login and run any command you want.
Removing KVM Virtual Machines:
You can also remove a KVM virtual machine very easily using LibVirt.
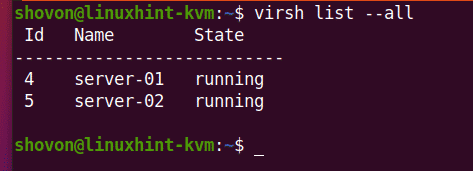
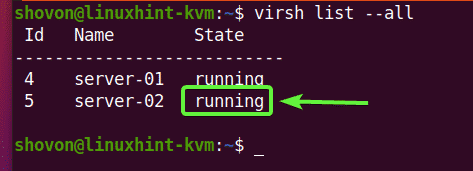
As you can see, I have 2 KVM virtual machines (server-01 and server-02) running on my Ubuntu 20.04 LTS KVM host. Let’s remove server-02 KVM virtual machine.
As you can see, the server-02 KVM virtual machine is running. You must stop it before you remove it.
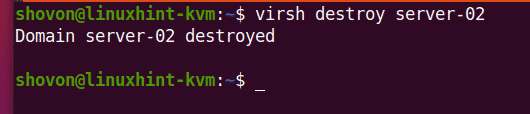
To force stop the server-02 KVM virtual machine, run the following command:
As you can see, the server-02 virtual machine is powered off.
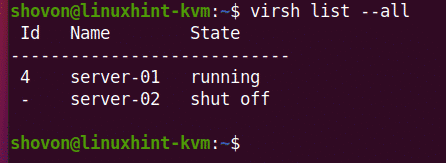
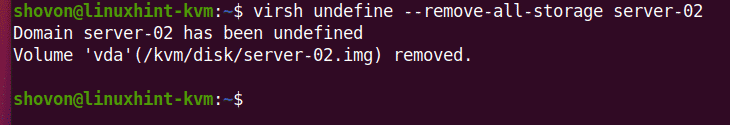
You can permanently remove the server-02 virtual machine and all of its attached virtual hard disks with the following command:
As you can see, the server-02 virtual machine is no longer available.
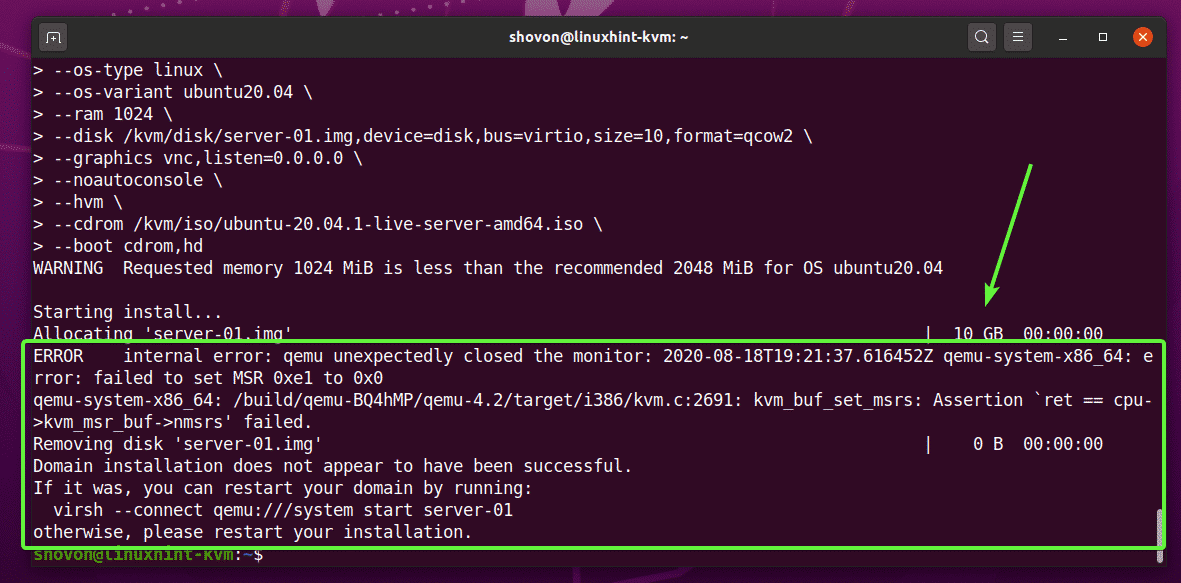
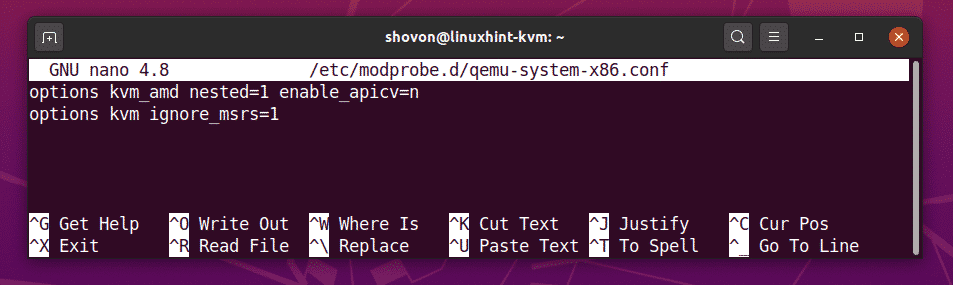
Issue#1: Fixing cpu->kvm_msr_buf->nmsrs Assertion Error
While creating a KVM virtual machine on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, you may see the following error message. It’s a kernel bug. Usually, this happens when you run KVM inside another virtual machine. I am running KVM inside a VMware virtual machine. This is why I got this error, I believe. It is easy to fix.
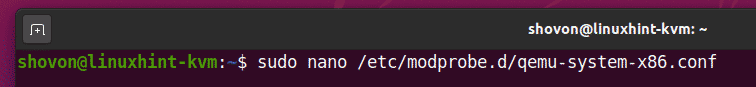
Create a new file /etc/modprobe.d/qemu-system-x86.conf with the following command:
Add the following lines in the file if you’re using an AMD processor.
options kvm ignore_msrs=1
Add the following lines in the file if you’re using an Intel processor.
options kvm ignore_msrs=1
Once you’re done, press <Ctrl> + X followed by Y and <Enter> to save the /etc/modprobe.d/qemu-system-x86.conf file.
Then, reboot your computer with the following command for the changes to take effect.
Your problem should be solved.
Conclusion:
In this article, I have shown you how to install KVM on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS and create KVM virtual machines using LibVirt. I have also shown you how to remove KVM virtual machines. This should help you get started with Linux KVM virtualization.