To lessen the suffering of typing, developers the command utilities have attempted to eliminate the extraneous typing with abbreviations, for example, “ls” instead of “list”, “cd” instead of “change-directory”, “cat” instead of “catenate” etc. Yet, typing the same command over and over and over is truly boring and unenjoyable.
This is where aliases come handy. Using an alias, it’s possible to assign your shortcut for a specific command. Here, we’ll be talking about how to create Bash aliases and demonstrate some useful aliases that you might enjoy.
Bash alias
When you run a command in the terminal, it’s the job of the shell to process and presents it to the OS to do the target job. Bash (acronym of “Bourne-Again shell) is, by far, one of the most popular UNIX shells out there. Most of the Linux distros come with Bash shell by default.
Now, what’s a Bash alias? We all have an idea of how an alias works, right? Similarly, when you want to use your phrase to denote a certain command, you can create an “alias” for that command. Bash will remember and treat the custom phrase as a command. When run, Bash will automatically translate it into the original command.
There are 2 types of Bash aliases.
- Temporary: This type of alias lasts as long as the shell session is running. Once the shell is terminated, it’ll forget the alias.
- Permanent: Once created, Bash will remember the creation of the alias and its meaning.
I will show next in this tutorial how to create and manage aliases. All these methods described are performed on Ubuntu. However, they’ll work on any Linux distro as long as you’re working with Bash.
Temporary Alias Creation
This is the form of an alias that Bash will forget once the session is closed. That’s why I recommend that you create an alias that’s worthwhile for the session.
For creating a temporary Bash alias, the command structure looks like this.
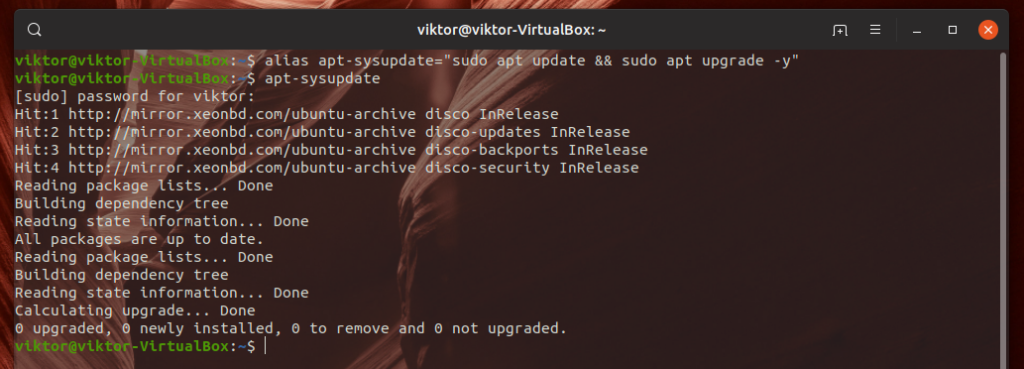
Let’s make it clear with an example. I’m on Ubuntu, so if I want to update all the packages of the system, I have to run the following command.
Now, how about using “apt-sysupdate” as an alternative that’ll do the same job as the aforementioned command? Create the alias by running this command.
Let’s check out if it works!
Voila! It’s working!
Here, whenever Bash sees the command “apt-sysupdate”, it’s going to be translated into the long command that’s going to be executed.
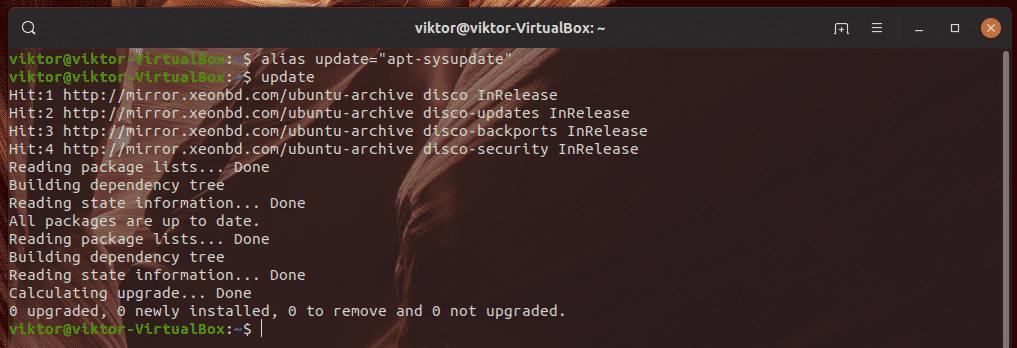
Here’s a fun thing to do. How about we create an alias of an alias? Let’s create the alias “update” for the command “apt-sysupdate”.
Now, let’s see if it works.
Yup, it does!
Permanent Alias Creation
For creating permanent aliases, we need to declare it in the bashrc file. The bashrc is a shell script that’s executed every time a bash session starts. It’s located at “~/.bashrc”. It’s unique to every single user in the system.
The bashrc is a popular choice for creating your favorite aliases. Bashrc may or may not be present in your system. Open the bashrc with vim. If not present, vim will open an empty text. Learn more about vim.
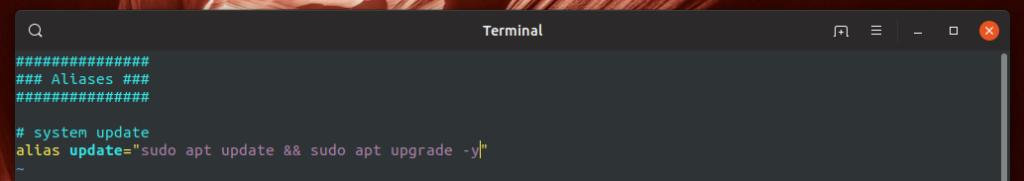
Here’s now the code for an alias looks like.
Let’s create a permanent alias “update” that’ll tell APT to update the repo cache and install all the available updates.
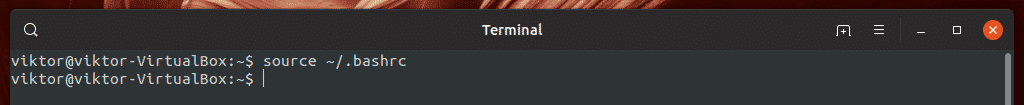
Once the alias is created, save the file. Then, tell bash to reload the file.
It’s time to check if it works. Reboot your system, log in to your account, and run the “update” alias we just created.
Voila! The alias is successfully created!
What’s happening here? Simply put, bash is creating a temporary alias every single time the bashrc is loaded. When bash terminates, it forgets the alias. However, as the bashrc file is the first script that bash executes, the temporary alias is back again. It could be described as “pseudo-permanent” alias.
Overriding alias
Let’s say you’ve set an alias “ls” for the command “ls -lhA” and for some reason, you need to use the main “ls” tool to do something different. In similar cases, bypassing an alias is required.
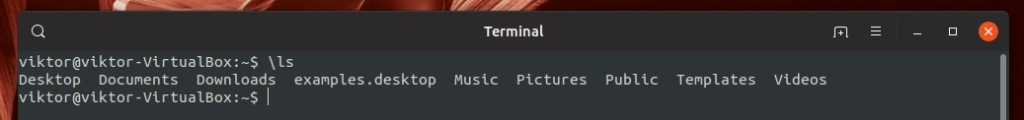
To temporarily bypass an alias, run the command with the following structure.
For example, I’ve created an alias “ls” for the command “ls -lhA”. Whenever I run ls, it’ll be translated into the command. What if I just want to run the “ls” tool without any additional options? Let’s bypass the alias temporarily.
Listing aliases
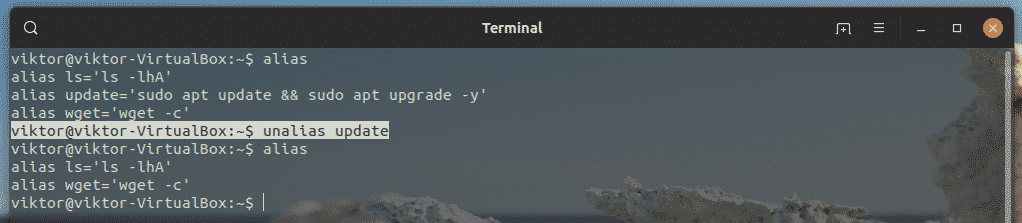
To view all the currently configured aliases, run this command.
Deleting Temporary Aliases
Removing a temporary alias is super simple. Just run this command.
For example, I have 3 aliases in total. To get rid of the “update” alias, the command would be:
Let’s verify the result.
Voila! Alias is gone!
Another way is to lot out of the current bash session or rebooting the system. Bash won’t remember the temporary aliases. Here, I’ve rebooted my computer and there’s no bash alias.
Deleting Permanent aliases
The aliases that are declared in the bashrc file won’t go away. Even if you unalias them, they’re not removed from the bashrc file. Next time the bash session is loaded, the alias is also back. That’s why to get rid of a permanent alias, we have to manually remove them from the bashrc file.
Open the bashrc file in vim.
Remove the bash aliases you don’t need. Alternatively, you can comment them out so that next time you need them, you can simply uncomment.
Save the file and tell bash to reload bashrc.
Some useful bash aliases
Here are some common aliases that many people use. Feel free to experiment with aliases. Remember, anytime you forget an alias, you can just run the “alias” command to see which one to run.
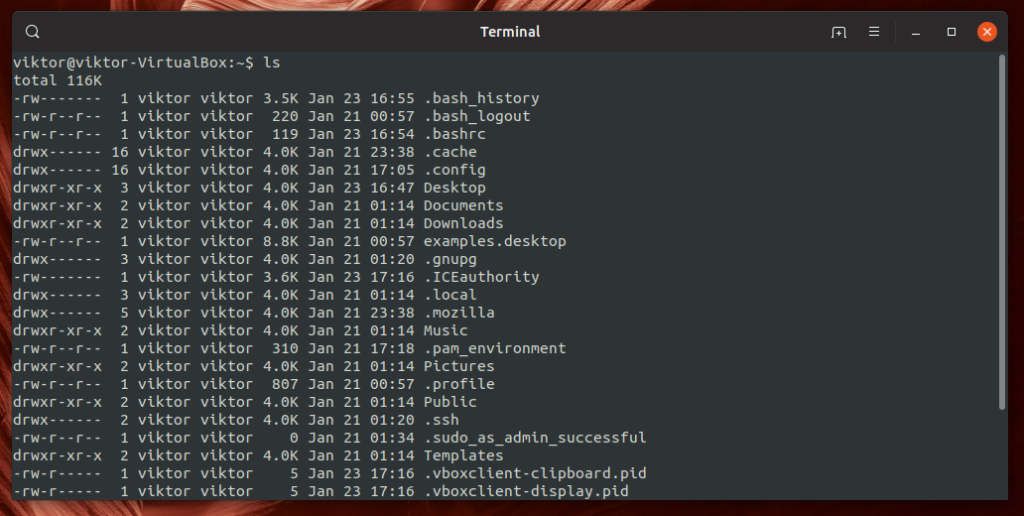
The following command will print the directory content with human-readable information in a “long listing” format.
Let’s make “ls” to display entries in a column with indicators.
We can also make a typo run the intended command.
Sometimes, the ls output will be very long. In such a situation, let’s pipe the output of ls to less.
Next up, it’s the “cd” command. Let’s add an alias to back to the parent directory.
Use the next alias to search for your desired file/folder in the current directory.
Now, let’s check out some system aliases. The “df” tool is used for checking out the disk usage. Set the following alias so that it reports the output in the human-readable unit along with filesystem type and print total at the bottom.
How about reconstructing the “du” tool output?
The “free” tool reports the amount of used/unused memory of the running system. Let’s make the “free” output friendlier.
If you’re constantly working with the process table, there are many aliases we can implement. For example, let’s set out a default output for the command “ps”.
Let’s add a search function to the process table.
How about making a directory/folder a little easier? Often, “mkdir” is followed by the “-p” flag for making any necessary parent directory. Let’s bind it in the following alias.
Want to get notified of every directory creation? Let’s add the “-v” flag with “mkdir”.
Wget is a simple command-line downloader. However, if it faces any problem during download, it’ll cancel automatically. To force wget to continue downloading, the “-c” flag has to be passed. Let’s combine them in this alias.
Need to check out the public IP address? Let’s add it to the alias list!
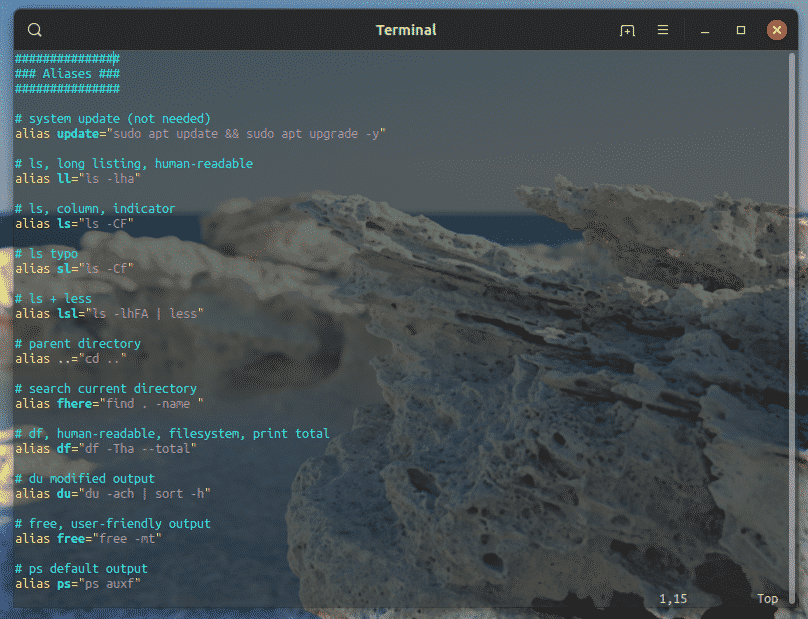
Here’s how my bashrc looks with all these aliases.
Final thoughts
Alias is a wonderful feature that lessens the burden and boredom of typing the same long command. It’s also extremely useful in using bash scripts to lessen the workload while the code remains free from unnecessary clutter.
There’s no fixed set of aliases. The aliases I mentioned before are some common ones that experts always use. However, depending on your day-to-day work, you’ll eventually come up with your own aliases.
If you’re using a lot of aliases, I recommend keeping them together in the bashrc file with necessary commenting.
Enjoy!