In this tutorial, we will look at the DELETE statement in SQL to learn how we can use it to delete an existing row from a table.
DELETE Statement
The following shows the syntax of the DELETE statement in SQL:
FROM
table_name
WHERE
condition;
We start with the DELETE clause to tell the database engine that we wish to remove a row or multiple rows.
We then specify the name of the table from which we wish to remove the rows. Next, we specify the condition in the WHERE clause. This is an important clause as it allows us to narrow down which specific rows we wish to remove.
If we omit the WHERE clause, the statement will remove all the rows from the specified table. Use with caution.
The statement then returns the number of rows that are deleted from the table.
Sample Table
Before we go into the examples on how to use the DELETE statement, let us create a basic table for demonstration purposes.
The CREATE TABLE statement is as follows:
product_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
product_name VARCHAR(255),
category VARCHAR(255),
price DECIMAL(10, 2),
quantity INT,
expiration_date DATE,
barcode BIGINT
);
Once we create the table, we can insert the sample data into the table as shown in the following insert statements:
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Chef Hat 25cm',
'bakery',
24.67,
57,
'2023-09-09',
2854509564204);
insert
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Quail Eggs - Canned',
'pantry',
17.99,
67,
'2023-09-29',
1708039594250);
insert
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Coffee - Egg Nog Capuccino',
'bakery',
92.53,
10,
'2023-09-22',
8704051853058);
insert
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Pear - Prickly',
'bakery',
65.29,
48,
'2023-08-23',
5174927442238);
insert
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Pasta - Angel Hair',
'pantry',
48.38,
59,
'2023-08-05',
8008123704782);
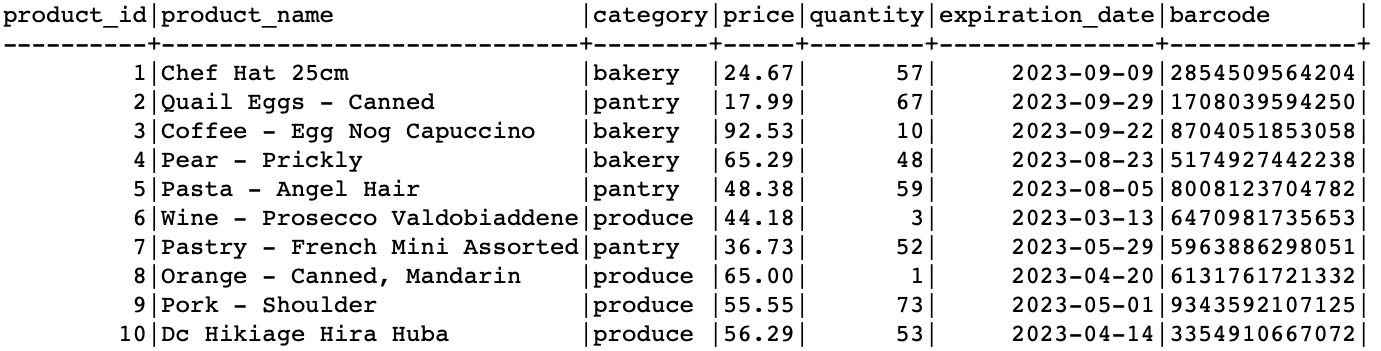
This should provide us with a table as follows:
Example 1: Delete a Single Row
The most basic delete operation is removing a single row from the table. For that, you can use the column with the unique value that identifies the target row.
For example, if we want to remove the “Pork – Shoulder” row which has an ID of 9, we can use the clause as follows:
FROM
products
WHERE
product_id = 9;
This should just remove the row with the ID number of 9. Since the “product_id” column is a primary key, there should be only one row with that value.
Example 2: Delete Multiple Rows
To delete multiple rows, we can set the condition for the target rows using the WHERE clause. We can use the conditional operators such as IN, NOT IN, LIKE, etc.
For example, suppose we wish to remove all the rows of the pantry and produce categories. We can use the query as follows:
FROM
products
WHERE
category IN ('produce', 'bakery');
This should match the “produce” and “bakery” values in the “category” column and remove any rows that match that condition.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned all about the DELETE statement which allows us to remove one or more rows from a given database table.