Symbolic links (symlinks) is the most reliable tool for file management that offers an easy way to create a reference to a directory inside other directories. You must know symlinks because it lets you maintain a flexible file-data structure, facilitate an easier file access, cross-partition directory referencing, etc.
Furthermore, symlinks are often used (but not limited to) in organizations that offer website hosting services. However, beginners face issues while linking a directory to another and end up getting errors. So, this quick blog is all about the simple ways to link a directory in Linux with no hassle.
How to Link a Directory in Linux
Symlinks, or soft links, act merely as a pointer to the original file/directory. Thus, if you make any changes to the original directory, they are directly reflected in the linked directory. You can also create a linked directory using a simple “ln” command.
Here, the “ln” command with the “-s” option is used to generate a symbolic link. Furthermore, replace the “/source/path” with the directory path that you want to link and replace “/target/path” with the directory’s path where you want your link to be.
Upon a successful link creation, it does not display anything. However, you must verify it using the following command:
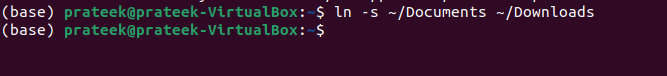
Upon execution, this command displays the list of linked directories at the specified path. For example, let’s link the “Documents” directory inside the “Downloads” directory.
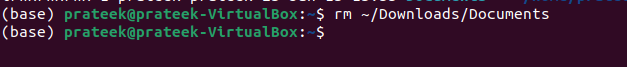
Moreover, in case you accidentally link a wrong directory, delete it using the “rm” command.
Conclusion
Knowing the directory linking in Linux is essential for efficient file management and streamlining your workflows. Hence, this quick blog explains how to link a directory in Linux. We discussed what symbolic links are and why you should create them. Furthermore, we explained it using an example. Lastly, we learned how to remove a linked directory if you mistakenly created the wrong one.