Different Uses of the Array Reference
The uses of the array reference variables for different purposes are shown in the following:
| Array variable | Array reference variable | Purpose |
| @array | @{ $ref_array } | It is used to refer to all array values. |
| scalar @array | scalar @ref_array | It is used to count the total number of arrays. |
| $#array | $#ref_array | It is used to define the largest index. |
| $array[index] | $tef_array->[index] | It is used to refer to the particular element of the array. |
Uses of the Perl Array References
Different uses of the Perl array reference variables are shown in this part of the tutorial.
Example 1: Create an Array Reference
Create a Perl file with the following script that declares an array of four string values and the reference variable of this array. The reference variable stores the memory location of the main array and both variables share the same location. The content of the reference variable and the main array is printed later.
use strict;
use warnings;
use 5.34.0;
use Data::Dumper;
#Declare an array of string
my @strarr = ('Perl', 'Java', 'Bash', 'Python');
#Create a reference of the array variable
my $ref_array = \@strarr;
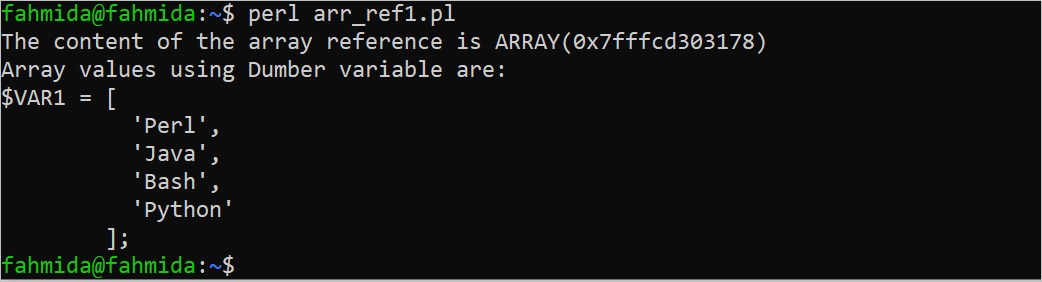
say "The content of the array reference is $ref_array";
say "Array values using Dumber variable are: ";
#Print the reference variable with the Dumper variable
print Dumper $ref_array;
Output:
The following output appears when executing the script:
Example 2: Update the Array after Creating the Reference
Create a Perl file with the following script which shows that if any element of the main array is changed, the corresponding value of the reference array variable is changed at the same time. All values of the main array are printed before updating any value of the array and all values of the array of reference are printed after updating the second element using the “dump” variable.
use strict;
use warnings;
use 5.34.0;
use Data::Dumper;
#Declare an array of string
my @strarr = ('Perl', 'Java', 'Bash', 'Python');
say "Main array values are: ";
#Print the reference variable with the Dumper variable
print Dumper \@strarr;
#Create a reference of the array variable
my $ref_array = \@strarr;
#Update the 2nd element of the array
$strarr[1] = 'C++';
say "Reference Array values (after updating the main array) are: ";
#Print the reference variable with the Dumper variable
print Dumper $ref_array;
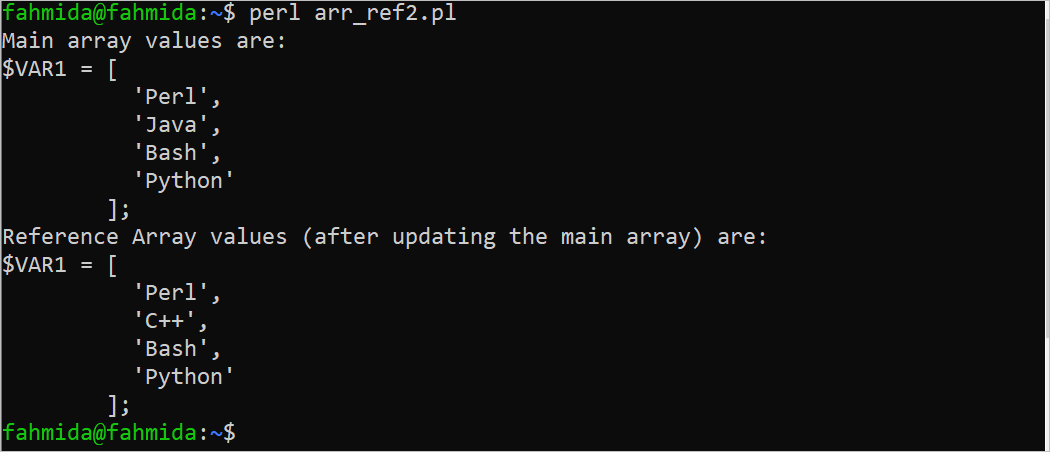
Output:
The following output appears after executing the script. According to the output, the second element is changed to “C++” in the reference array because the second element of the main array is updated by the “C++” value:
Example 3: Pass the Array Reference into a Subroutine
Create a Perl file with the following script where the reference variable of the array is sent as the argument of the subroutine. The value of the third index of the array is updated using the reference variable inside the subroutine. The values of the main array are printed before and after updating the third index of the reference variable using the “dump” variable.
use strict;
use warnings;
use 5.34.0;
use Data::Dumper;
#Declare an array of numbers
my @numarr = ( 67, 34, 90, 12, 39);
say "The values of the main array before update:";
print Dumper \@numarr;
#Pass the array as a reference into the subroutine
read_array(\@numarr);
#Declare subroutine to modify the array value
sub read_array
{
#Define the array reference variable
my $arr_ref = $_[0];
#Update the third element of the array
$arr_ref->[2] = 99;
}
say "The values of the main array after update:";
print Dumper \@numarr;
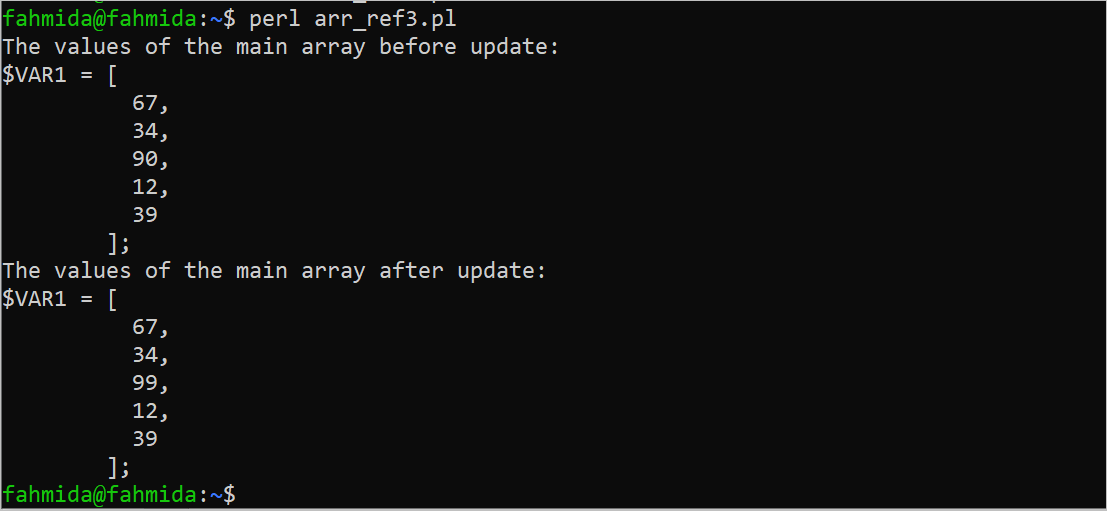
Output:
The following output appears after executing the script. The third element of the array was 90 and this value is changed to 99 using the reference variable of the array. The third element of the original array is also updated by 99 because both variables share the same location:
Conclusion
The methods of accessing or updating the array values by creating the reference variable of the array are shown in this tutorial. Perl users will get a clear concept of using the reference variables of the Perl array after reading this tutorial.