Different Uses of the Perl Data::Dumper
The uses of the Dumper function to print the scalar variables, array variables, hash variables, and file content are shown in this part of the tutorial.
Example 1: Using the Data::Dumper for Scalar Variables
Create a Perl file with the following script that prints the values of the “string” variable and the “number” variable using the Dumper function:
use strict;
use warnings;
use 5.34.0;
use Data::Dumper;
#Declare a string variable
my $name = "Md. Ali";
#Declare a number variable
my $age = 35;
#Print the scalar variables
print Dumper $name."\n";
print Dumper $age."\n";
Output:
The following output appears after executing the script. The string value of “Md. Ali” and the number of “35” are printed by the $VAR1 variable of the Dumper function. The number value is printed as a string value in the output:
Example 2: Using the Data::Dumper for the Array Variable
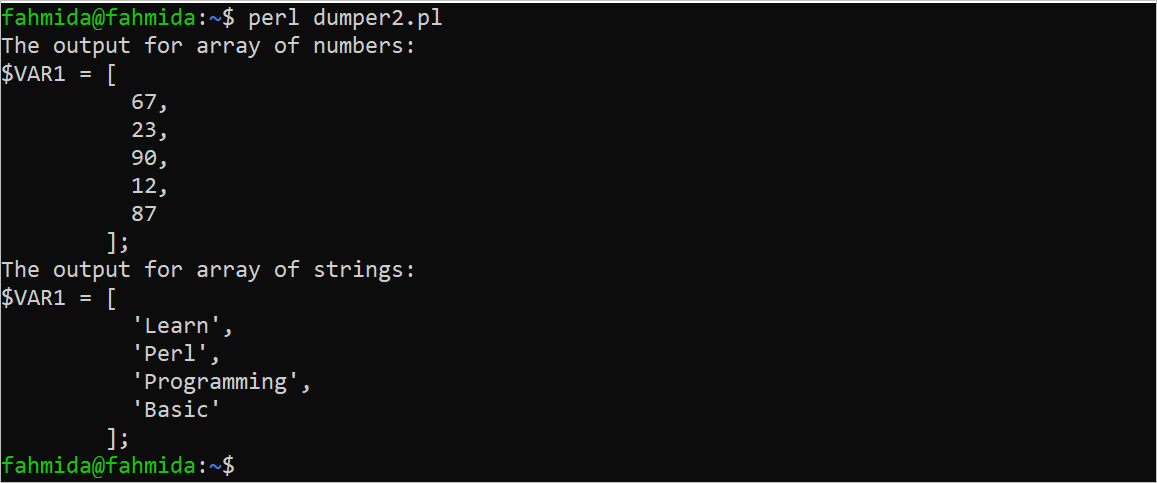
Create a Perl file with the following script that prints the values of an array of numbers and an array of strings using the Dumper function. An array of five numbers and an array of four string values have been define in the script. The values of these arrays have been printed later.
use strict;
use warnings;
use 5.34.0;
use Data::Dumper;
#Declare an array of numbers
my @arrnum = (67, 23, 90, 12, 87);
#Declare an array of string
my @arrstr = ('Learn', 'Perl', 'Programming', 'Basic');
#Print the array variables
print "The output for an array of numbers:\n".Dumper \@arrnum;
print "The output for an array of strings:\n".Dumper \@arrstr;
Output:
The following output appears after executing the script. According to the output, the values of the array of numbers are printed as number values, and the values of the array of strings are printed as string values:
Example 3: Using the Data::Dumper for the Hash Variable
Create a Perl file with the following script that prints the values of a hash variable using the Dumper function. A hash variable of four key-value pairs is declared in the script. The keys and values of this hash variable are printed later:
use strict;
use warnings;
use 5.34.0;
use Data::Dumper;
#Declare a hash variable
my %hashvar = ('HDD' => 6000, 'Monitor' => 7000, 'Mouse' => 1000, 'Printer' => 4000);
#Print the hash variable
print Dumper \%hashvar;
Output:
The following output appears after executing the script. According to the output, four key-value pairs of the hash variable are printed by the $VAR1 Dumper variable:
Example 4: Using the Data::Dumper to Read the File
Create a text file named “test.txt” with some content to check the script of this example. Here, the following content is added to the “test.txt” file:
test.txt
This file is created for testing purposes.
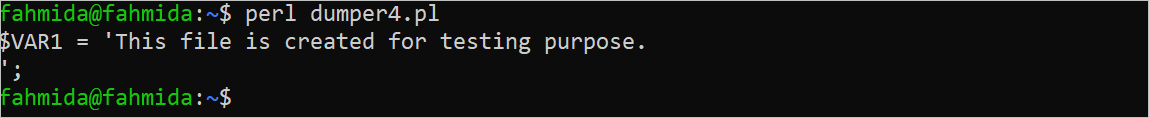
Create a Perl file with the following script that opens the “test.txt” file for reading, read the first line of the file into a variable, and print the variable using the Dumper function. Here, the “<” operator is used to open the file for reading. The first line of the file is read using the file handler named “f_handler” and stored into the $data variable. The content of this variable is printed by the Dumper function.
use strict;
use warnings;
use 5.34.0;
use Data::Dumper;
#Open a file for reading
open(f_handler, "< test.txt") or die "Unable to open the file.\n";
#Read the first line of the file
my $data = <f_handler>;
#Print the first line using Dumper
print Dumper $data;
#Close the file handler
close f_handler;
Output:
The following output appears after executing the script. According to the output, the first line of the “test.txt” file is printed as a string value using the $VAR1 variable:
Conclusion
Some basic uses of the Dumper function are shown in the examples of this tutorial. The Perl Data::Dumper has many functionalities that can be used for various purposes which are not explained in this short tutorial. The Perl users will be able to print all the values of different types of Perl variables and it is helpful for debugging purposes.