The Hostname
The hostname is the label assigned to a device on a network – a desktop computer, database server, tablet pc, wifi router, or smartphone. This name is used to distinguish the devices from each another on a specific network or over the internet.
Mostly, the chosen name is human-readable, and has to be unique among the other machines in the local network. Hostnames must not contain a space since they can only contain letters, digits and a hyphen.
In institutions with a large number of users like universities it is quite common to name a computer after fruits, favourite places, greek letters, geographical regions, or musical instruments. For private networks there are no name conventions to be followed, and hostnames like “FamiliyPC”, “dads-tablet”, or “printer” can be found.
The computer’s hostname is set initially during the installation, and stored in the file “/etc/hostname”. The screenshot below is taken from the graphical setup of Debian GNU/Linux 9, and uses the label “debian95” as a hostname referring to the release of Debian GNU/Linux 9.5.
As soon as your computer starts several services are initialized. This also includes the network, and the hostname, which can be used to address the device from then onwards. Using the UNIX command “hostname” reveals its name as follows:
debian95
$
More information can be retrieved using the command hostnamectl as follows:
Static hostname: debian95
Icon name: computer-laptop
Chassis: laptop
Machine ID: 7c61402c22bf4cf2a9fcb28a4210da0b
Boot ID: 6e8ca49158ff4bc4afaa26763f42793b
Operating System: Debian GNU/Linux 8 (jessie)
Kernel: Linux 3.16.0-4-amd64
Architecture: x86-64
$
The hostname plus domain name result in the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) [1] that is needed to identify a computer without fail. In order to get the FQDN of the device use the switch “-f” (short for “–fqdn” or “–long”), instead:
debian95.wunderwerk.net
$
Changing The Hostname
At first sight, changing the hostname (or renaming a computer) is comparably easy and takes a few minutes, only. It can be done in the following ways:
- temporary change (valid until reboot) open a terminal window, change to user root, and invoke the command “hostname” followed by the new hostname:
# hostname cucumber
# hostname
cucumber
# - permanent change open the file “/etc/hostname” with a text editor as user “root”, change the hostname, and save the file
- permanent change for users of systemd open a terminal window, change to user root, and invoke the command “hostnamectl” as follows:
# hostnamectl set-hostname cucumber
The picture below illustrates this step using “hostnamectl”.
Being aware of side-effects
Still, it is half of the story. The file “/etc/hostname” is not the only place in which programs on your computer store the hostname. Using the “grep” command we find out which other files are affected, and need to be adjusted. The command below shows this for the hostname “debian95”:
/boot/grub/grub.cfg
/etc/hostname
/etc/hosts
/etc/wicd/wired-settings.conf
/etc/wicd/wireless-settings.conf
/etc/mailname
/etc/exim4/update-exim4.conf.conf
/etc/initramfs-tools/conf.d/resume
/etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key.pub
/etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key.pub
/etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key.pub
/etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key.pub
/etc/fstab
/home/debian/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
…
#
The file “/etc/hosts” is essential for networking, and needs to be adjusted. Change “debian95” to “cucumber” to have the following result:
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts ::1 localhost ip6-localhost
ip6-loopback ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters $
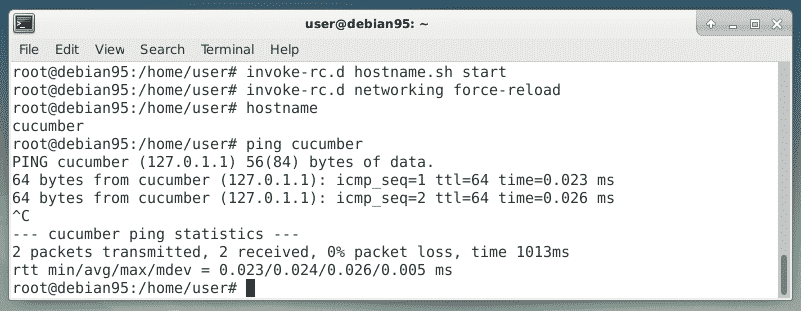
Next, reload the network configuration as follows:
# invoke-rc.d networking force-reload
In order to check your new network configuration you may ping your machine with the new hostname:
Et voila – it worked well. The final step is to check your applications according to the list above. The referring page in the Debian Wiki [2] gives you a good overview what to do with each application, and shall work as a reference guide for you.