Installing GParted on Ubuntu:
GParted is not installed on Ubuntu by default. But it is available in the official package repository of Ubuntu. So, it is easy to install. First, update the APT package repository cache with the following command:
Now, install GParted with the following command:
Now, press y and then press <Enter> to continue.
GParted should be installed.
Starting GParted:
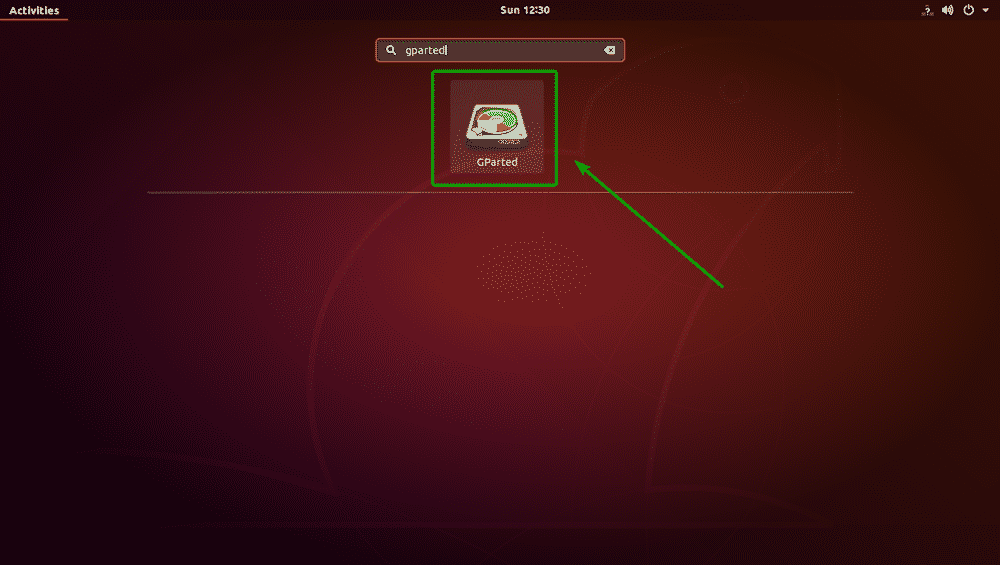
Now that GParted is installed, you can start GParted from the Application Menu of Ubuntu as you can see in the screenshot below.
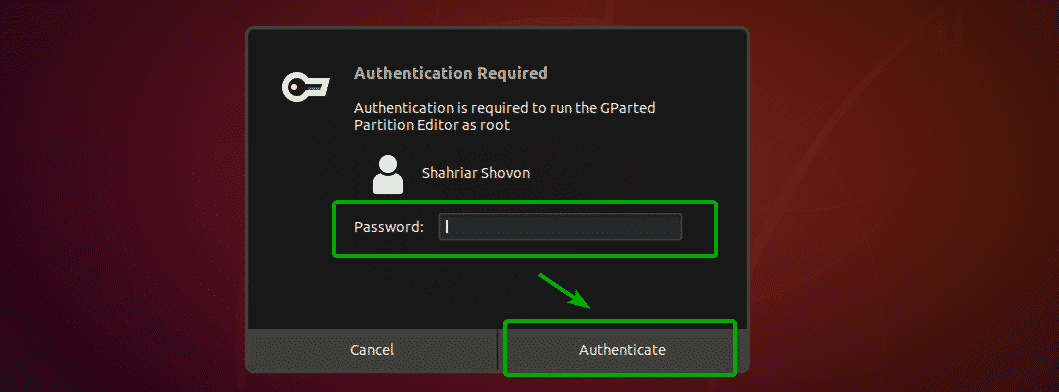
GParted requires root privileges. To allow root privileges to GParted, type in your login password and click on Authenticate.
GParted should start.
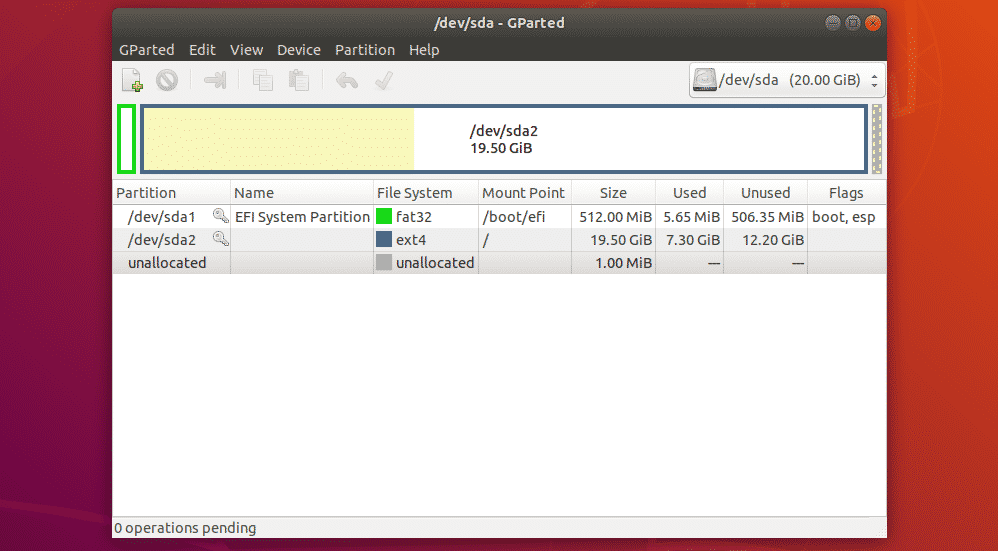
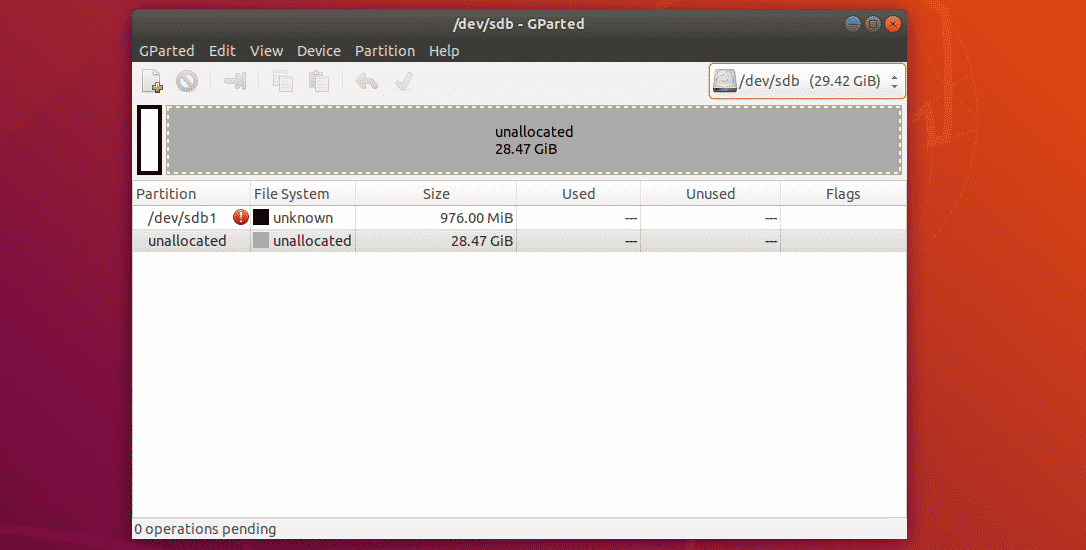
Selecting Storage Device:
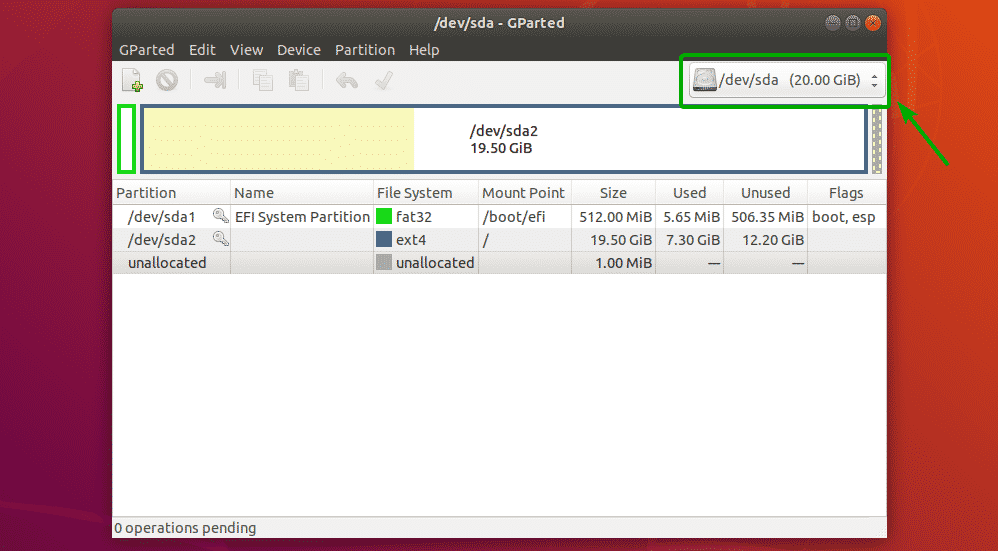
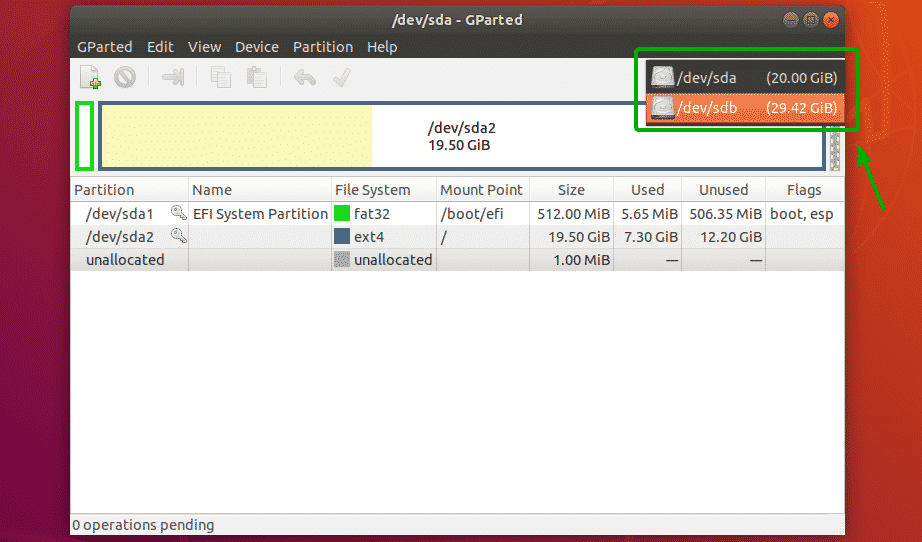
The first thing to do in GParted is to select the storage device that you want to work with. To do that, click on the drop down menu on the top right corner of GParted.
Then, select the storage device that you want to work with.
As you can see, I selected my 32GB USB thumb drive.
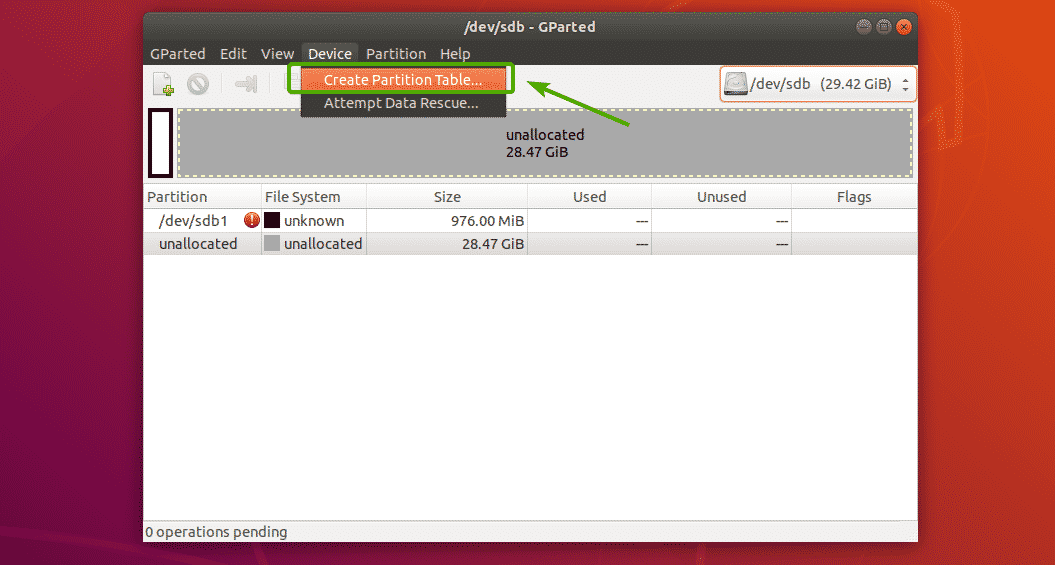
Creating a New Partition Table:
To create a new partition table using GParted, click on Device > Create Partition Table… as marked in the screenshot below.
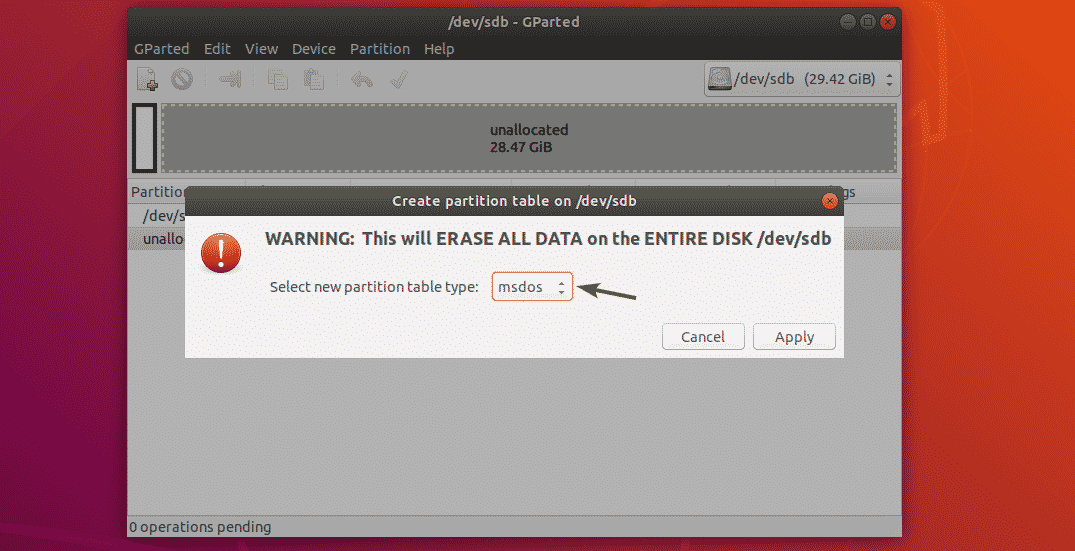
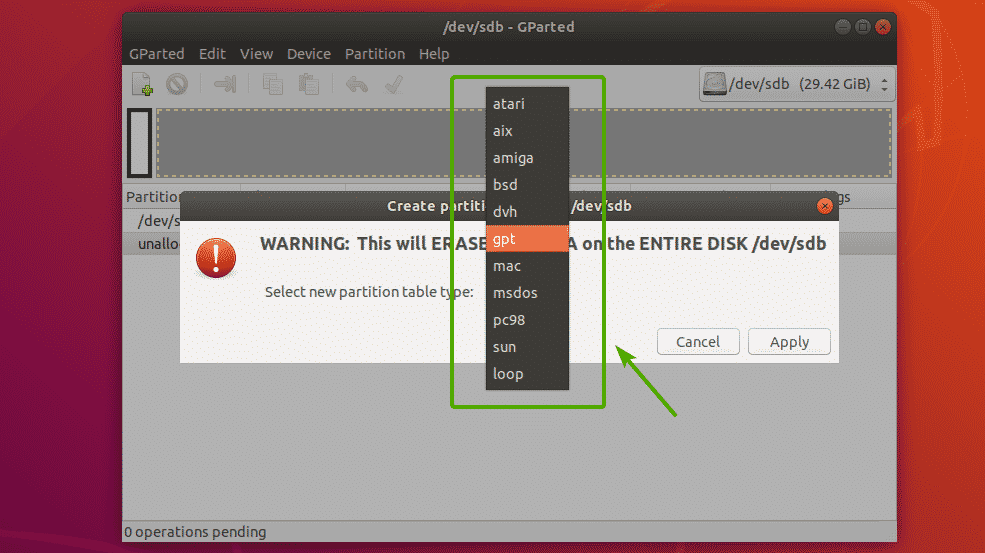
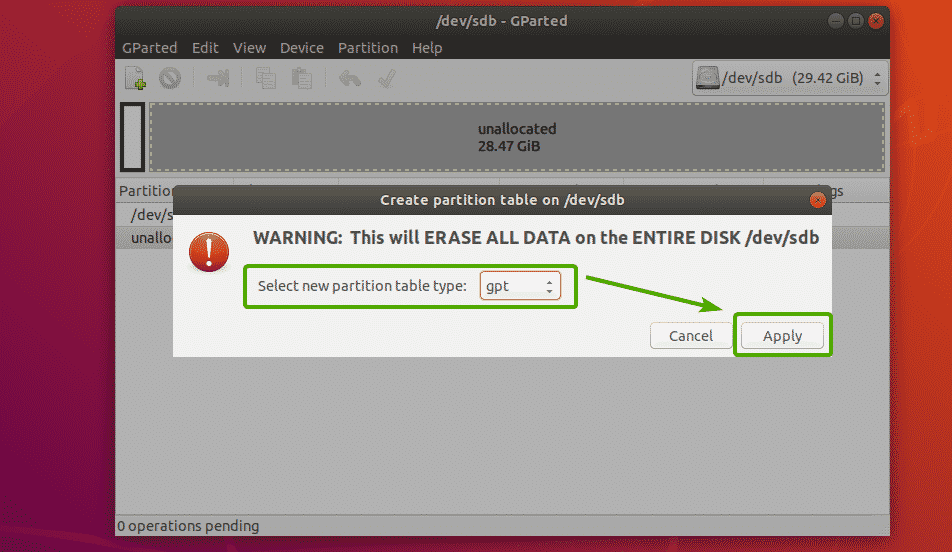
You will see the following dialog box. From here, you can select your desired partition table type. The most widely known partition table types are msdos and gpt. By default, msdos is selected. But you can click on the dropdown menu to change it.
As you can see, there are so many partition table types to choose from.
Once you’ve selected a partition table type, click on Apply.
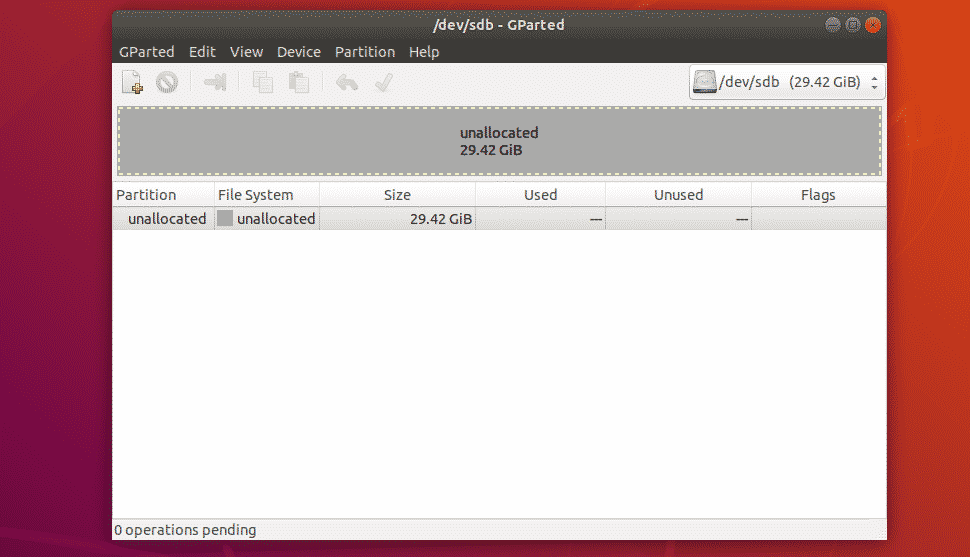
An empty partition table should be created as you can see in the screenshot below.
Creating New Partitions:
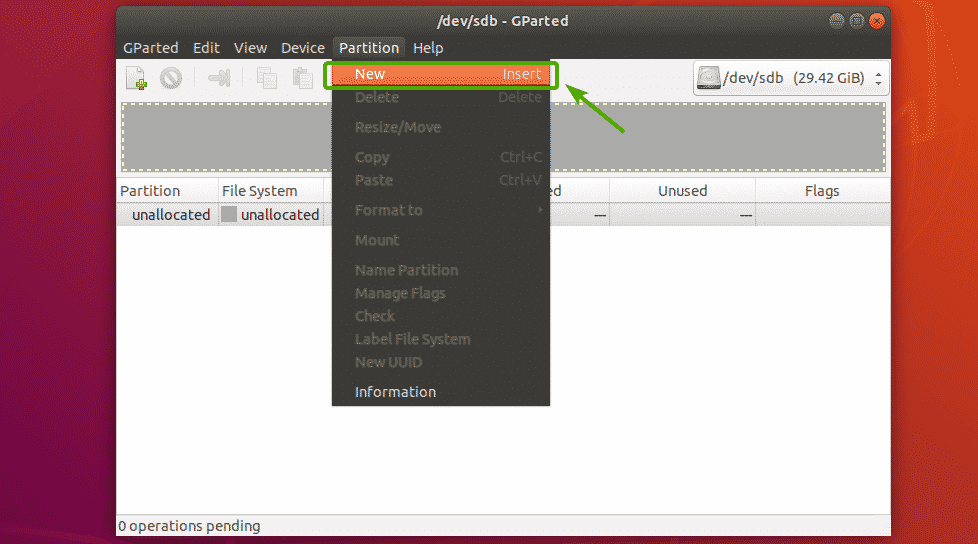
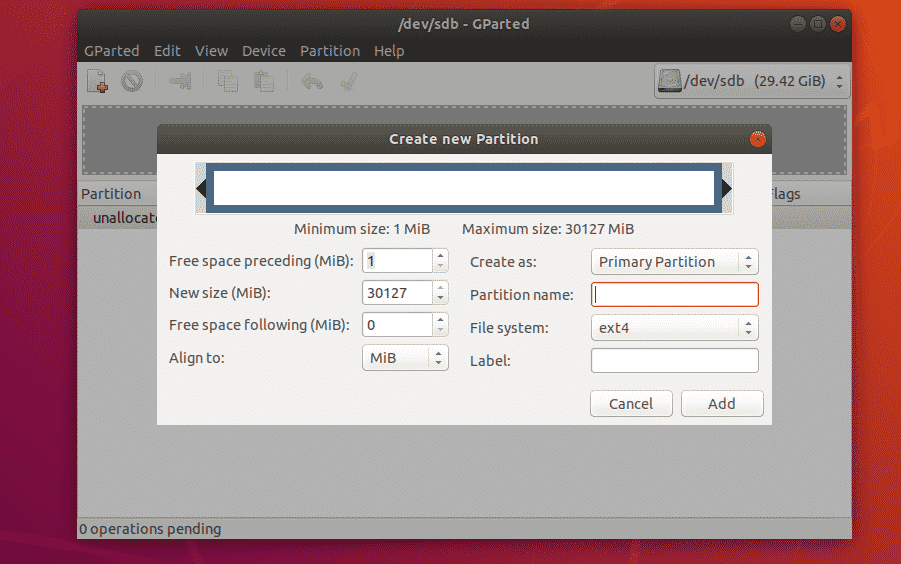
Before you create a new partition, make sure you have enough unallocated free spaces. Now, to create a new partition with GParted, select the unallocated space and click on Partition > New.
A new window should appear.
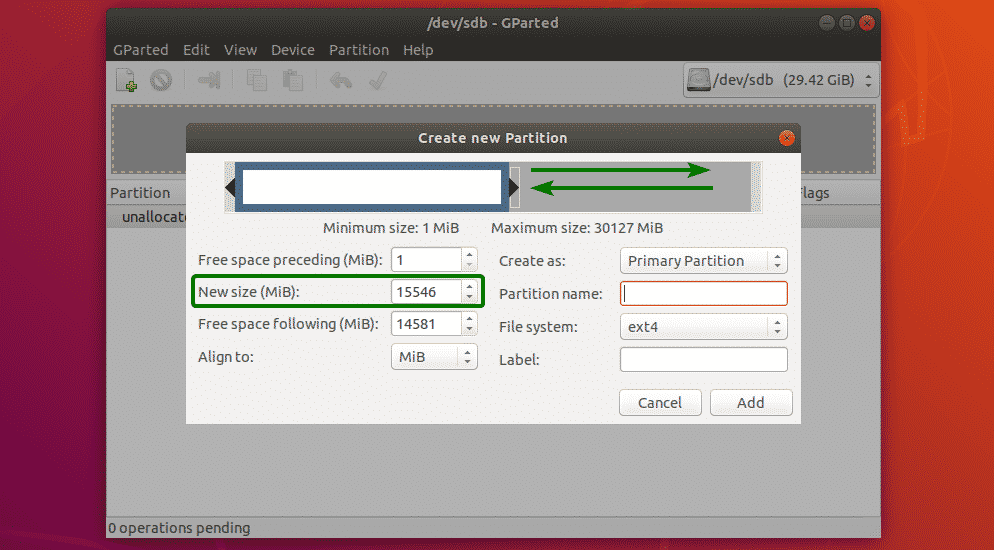
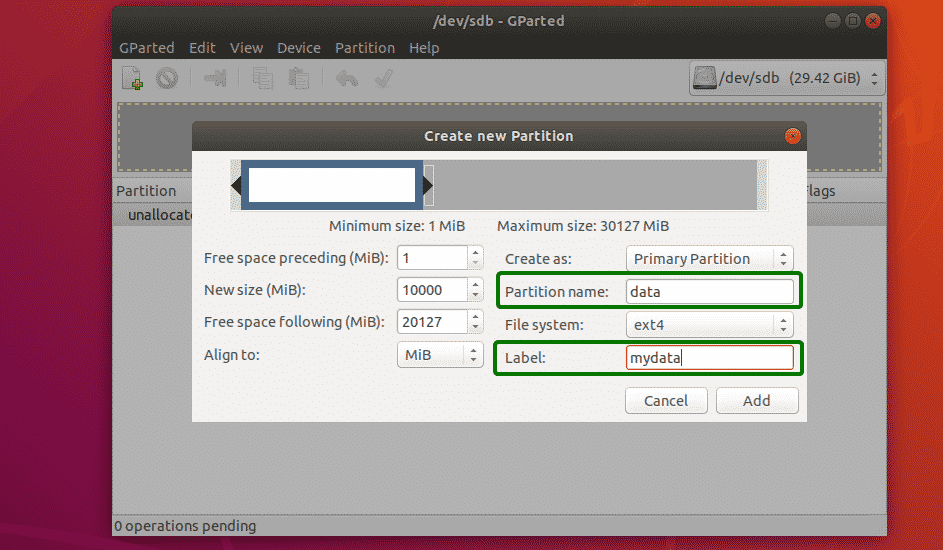
You can move the slider back and forth to change the size of the partition. You can also type in the size of the new partition directly in the New size (MiB) textbox as marked in the screenshot below.
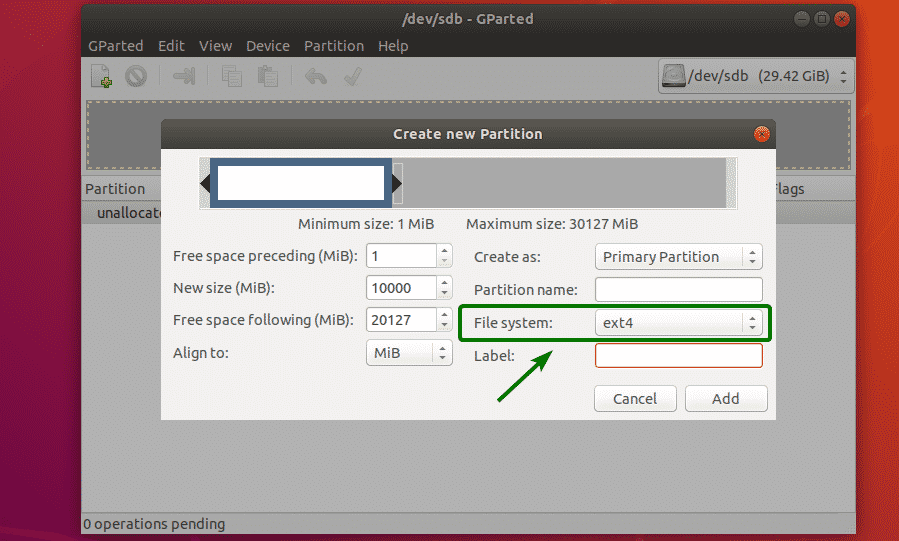
You can also select a file system for your new partition using the File system dropdown menu. By default, ext4 is selected. This is one of the thing I like about GParted. It formats the partition to your desired file system when you create a new partition.
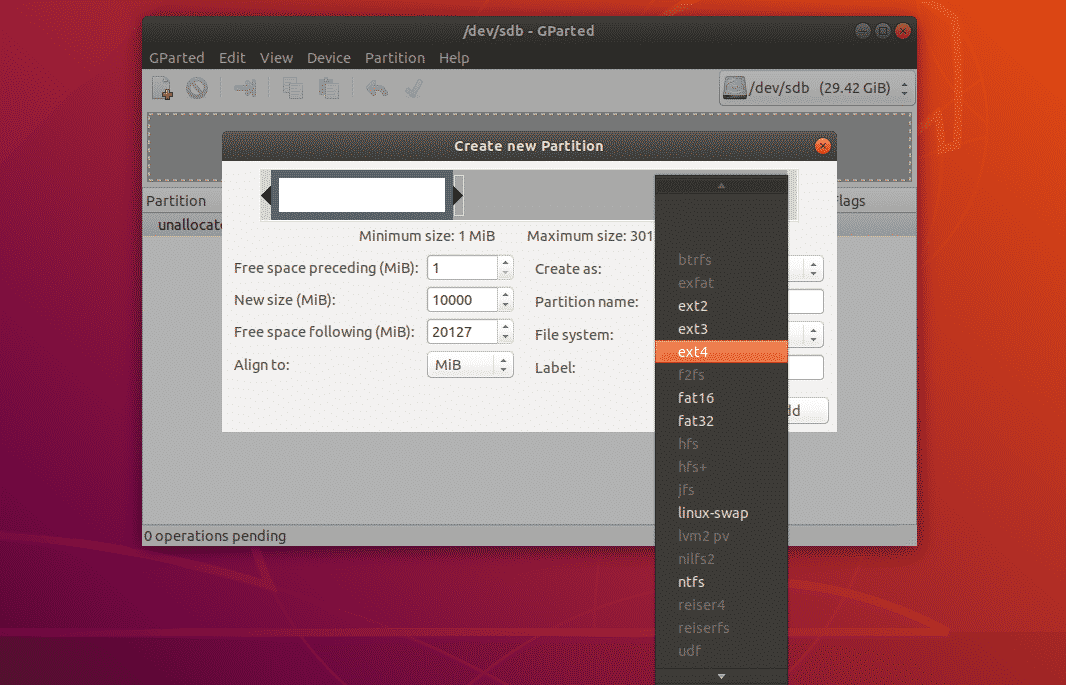
As you can see, GParted supports a lot of file systems. The file systems that are installed on your computer should be enabled here. The ones that are not installed are disabled at the moment. To enable the disabled ones here, you will have to install the file systems on your computer.
You can also type in a Partition name and a Label for your new partition. These are used to make it easy for yourself to identify the partition, nothing else. You can also leave them empty if you want. These are completely optional.
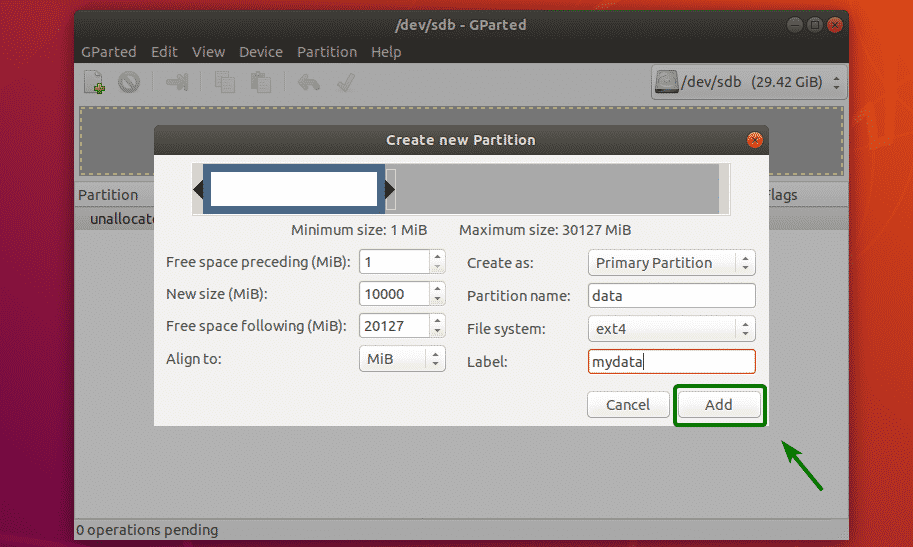
As you can see, a partition is created. But the changes are not saved permanently. To save the changes, click on the tick icon as marked in the screenshot below.
Now, click on Apply.
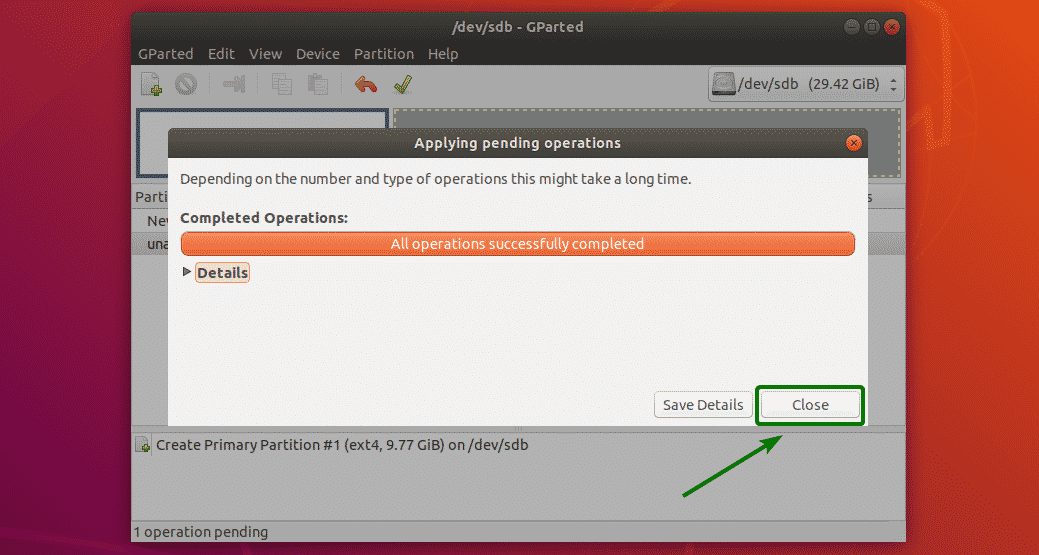
The new partition is being formatted.
Once it’s done, click on Close.
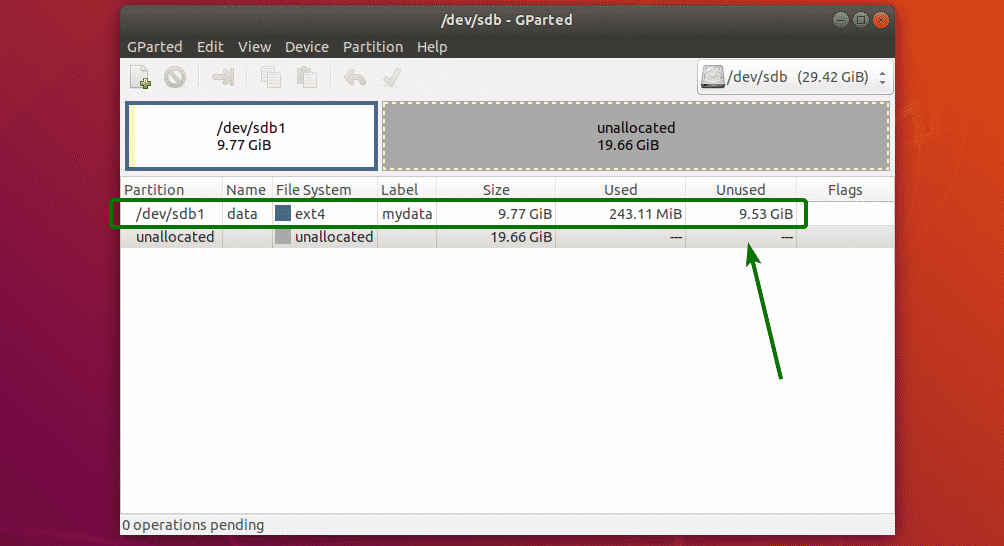
As you can see, a new partition is created.
Resizing Partitions:
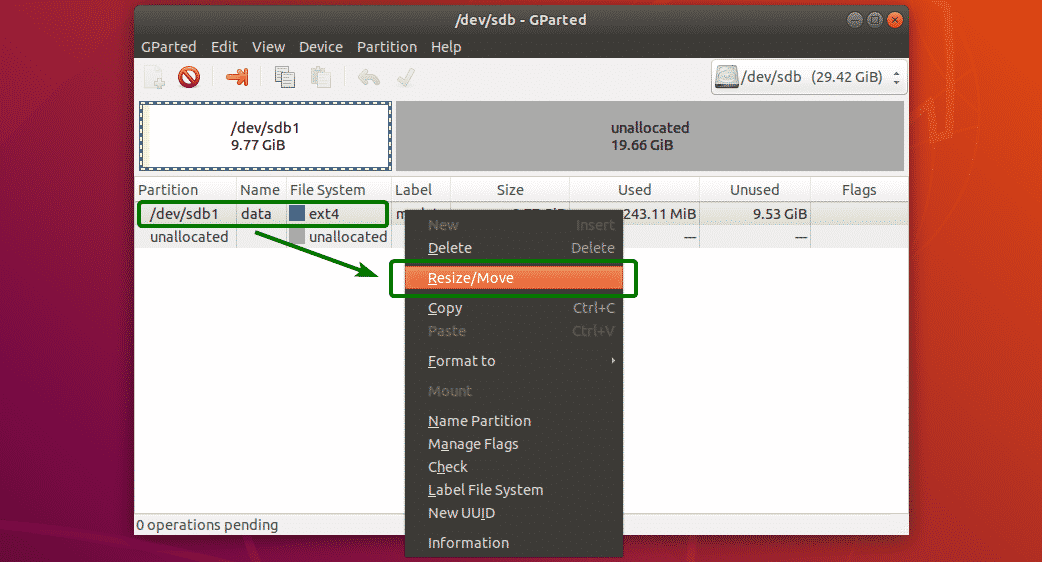
There are 2 resize operations that you can perform on a partition, Extend and Shrink. In order to extend a partition, you must have unallocated free spaces after that partition. To resize a partition, right click on the partition and click on Resize/Move.
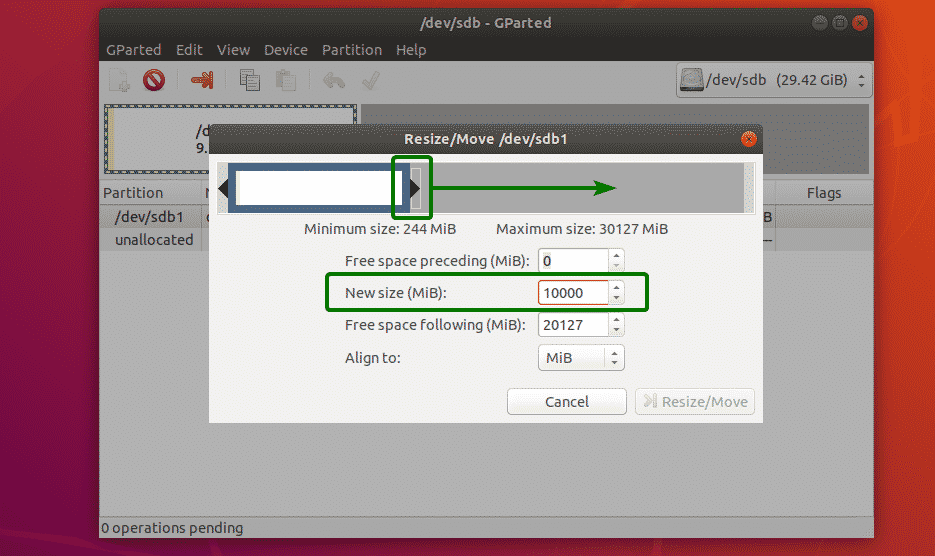
Now, you can use the handle to extend or shrink the partition. You can also type in the new size of the partition directly on the New size (MiB) textbox.
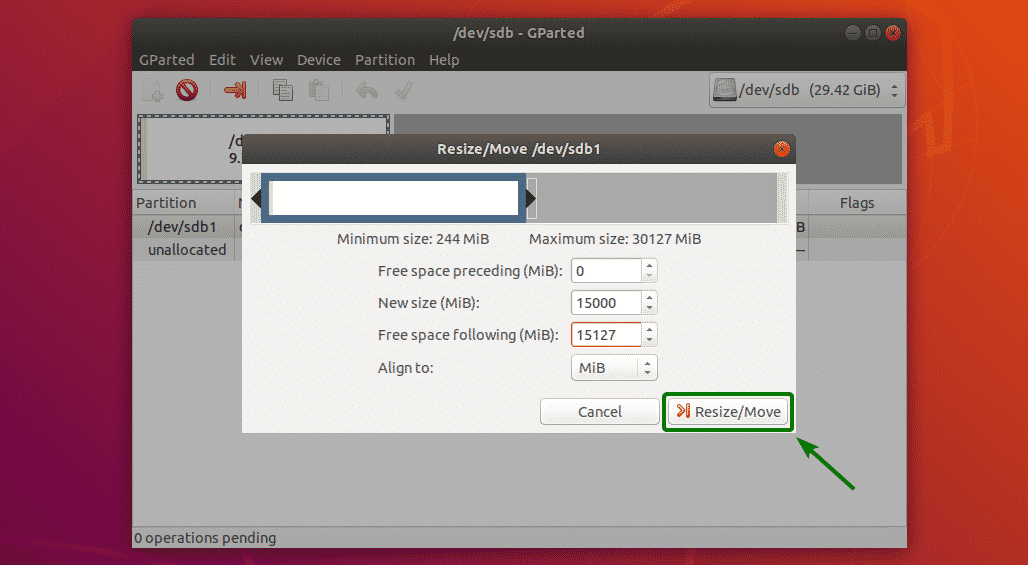
Once you’re done, click on Resize/Move.
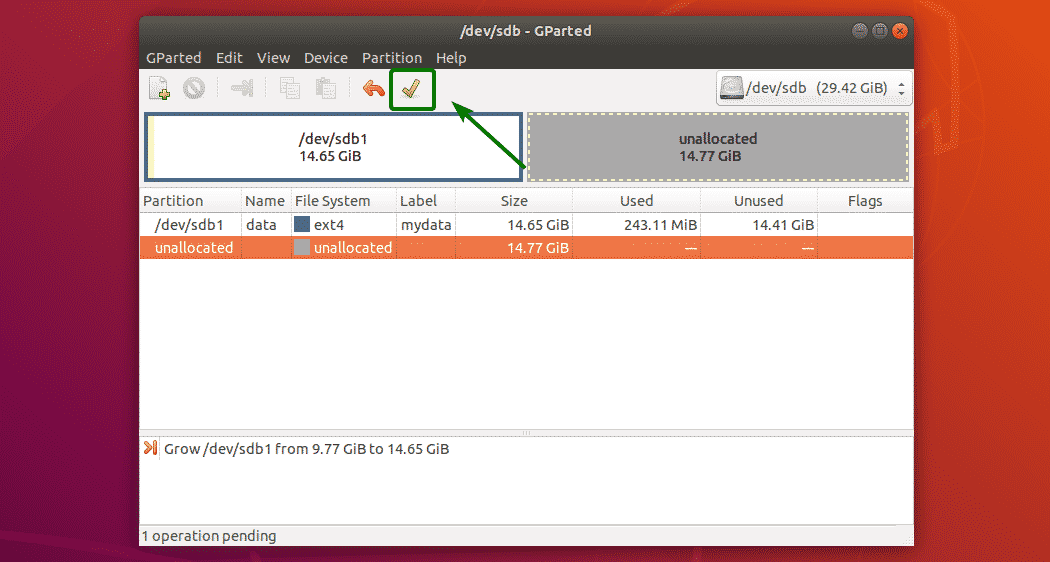
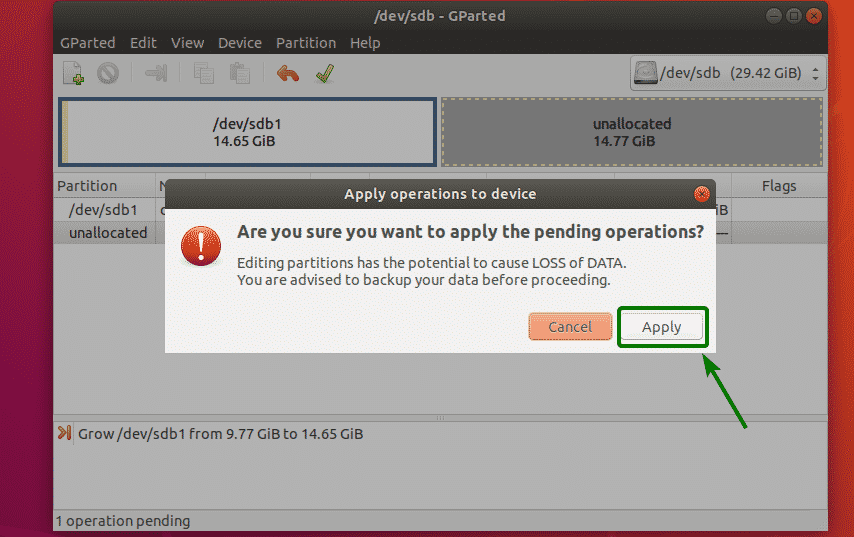
If everything is alright, then click on the tick icon to save the changes permanently.
Now, click on Apply to confirm the operation.
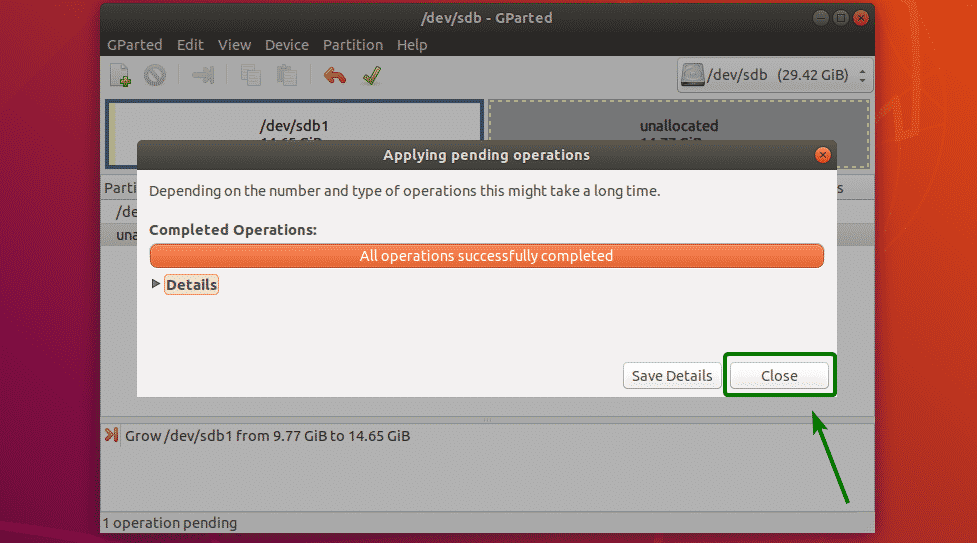
The changes should be applied. Now, click on Close.
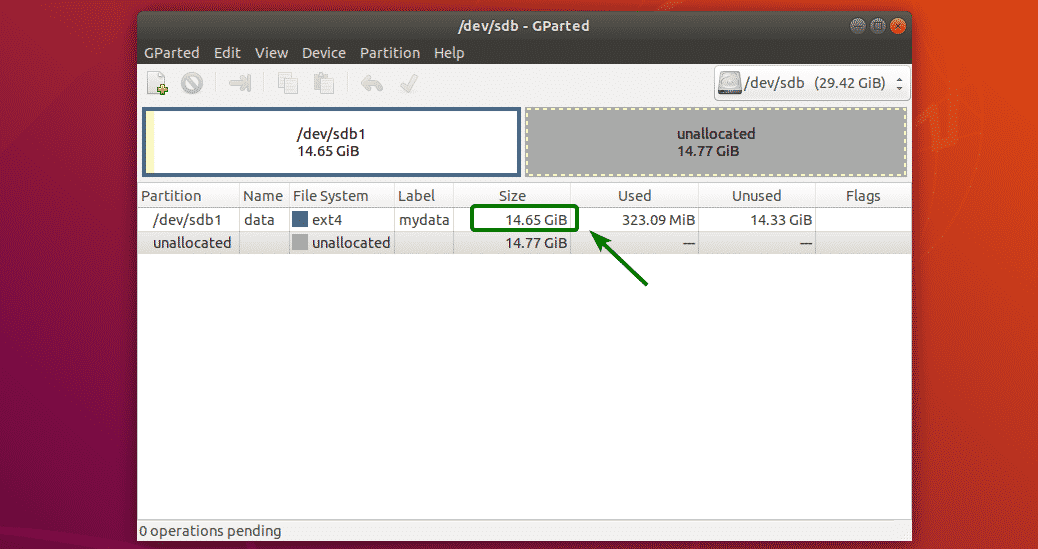
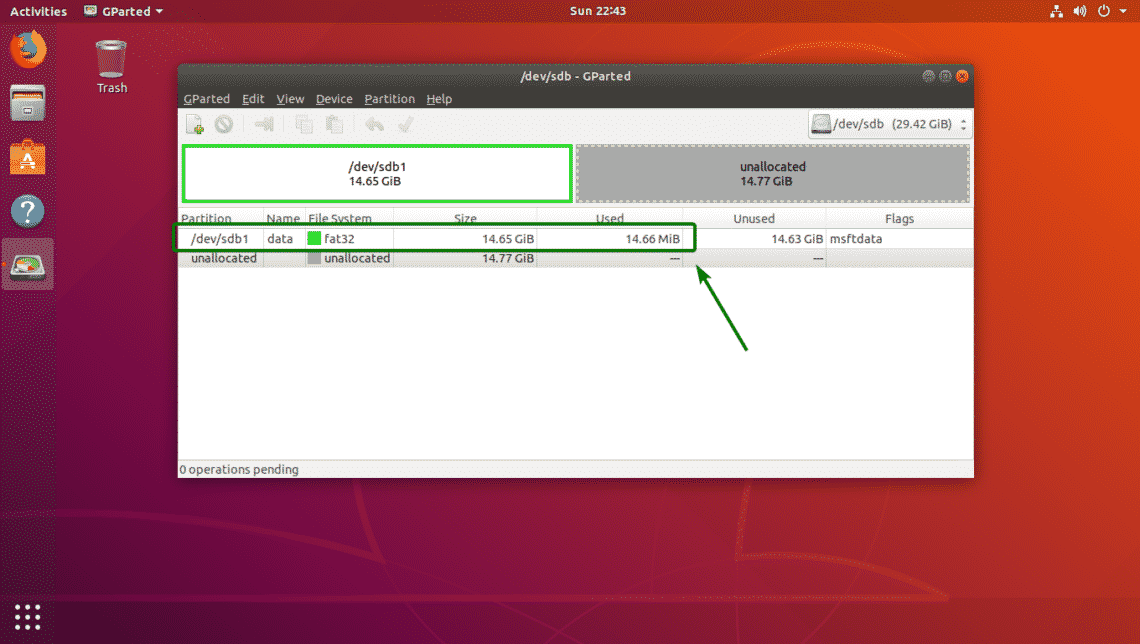
As you can see, the partition has been resized.
Deleting Partitions:
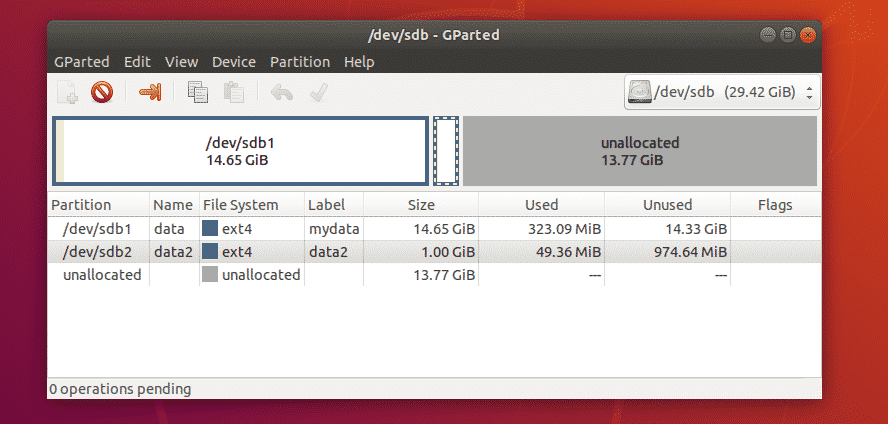
I created a new partition to demonstrate how partitions are deleted with GParted. Right now, the partition table looks as follows:
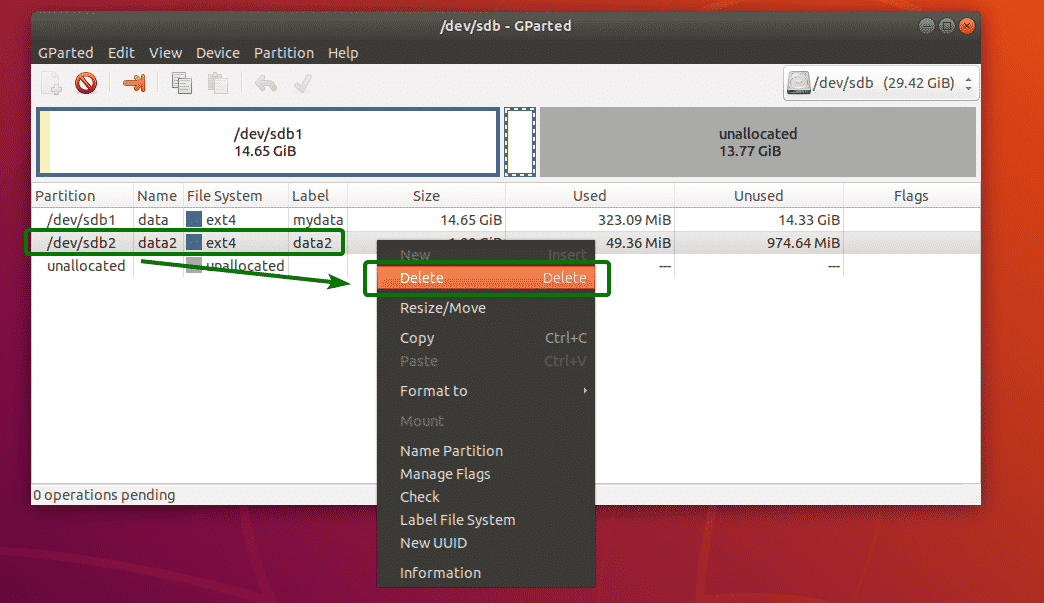
To delete a partition, right click on the partition and click on Delete.
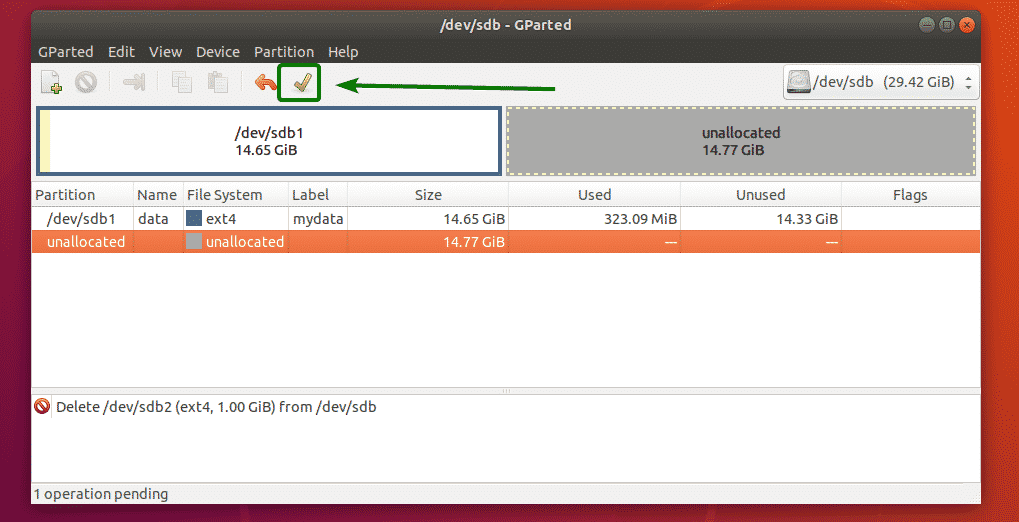
Now, to save the changes permanently, click on the tick icon as marked in the screenshot below.
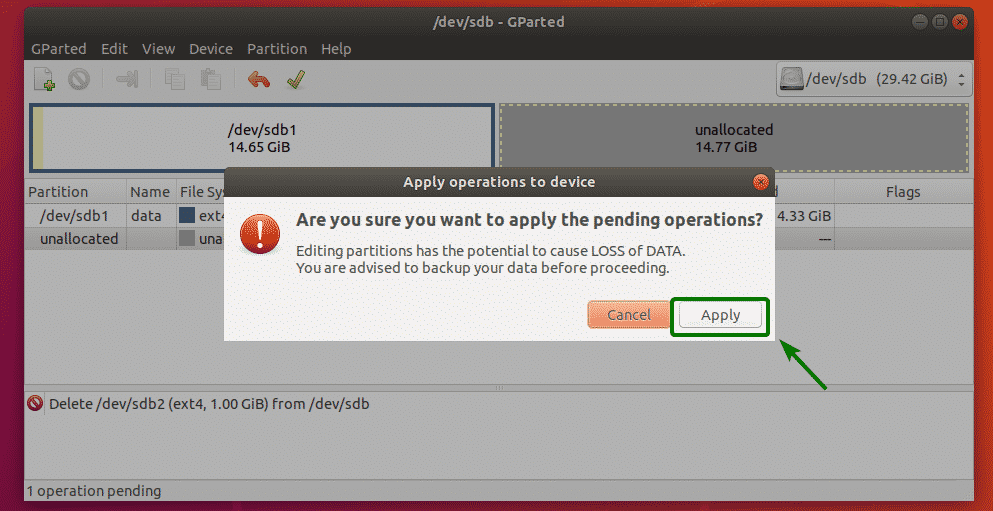
Now, to confirm the operation, click on Apply.
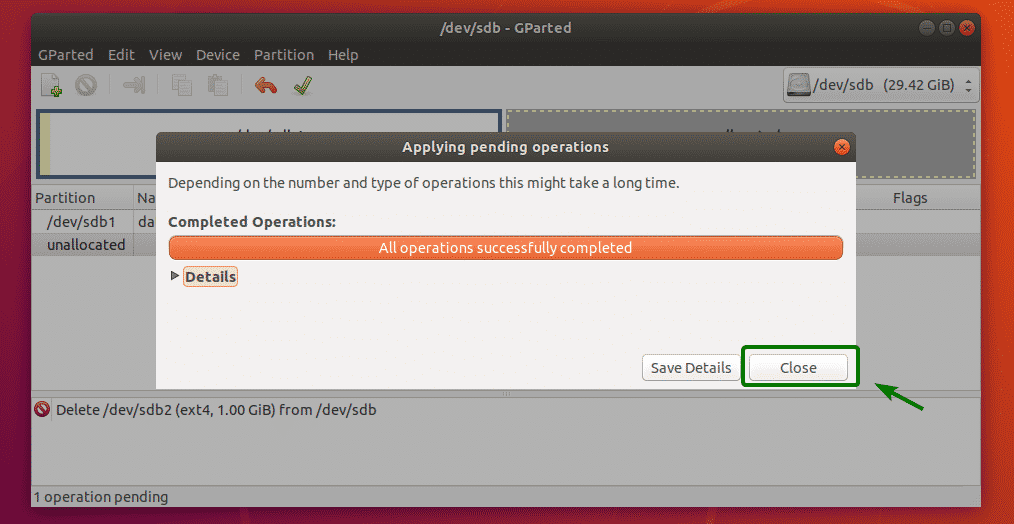
Once the operation is complete, click on Close.
As you can see, the partition is deleted.
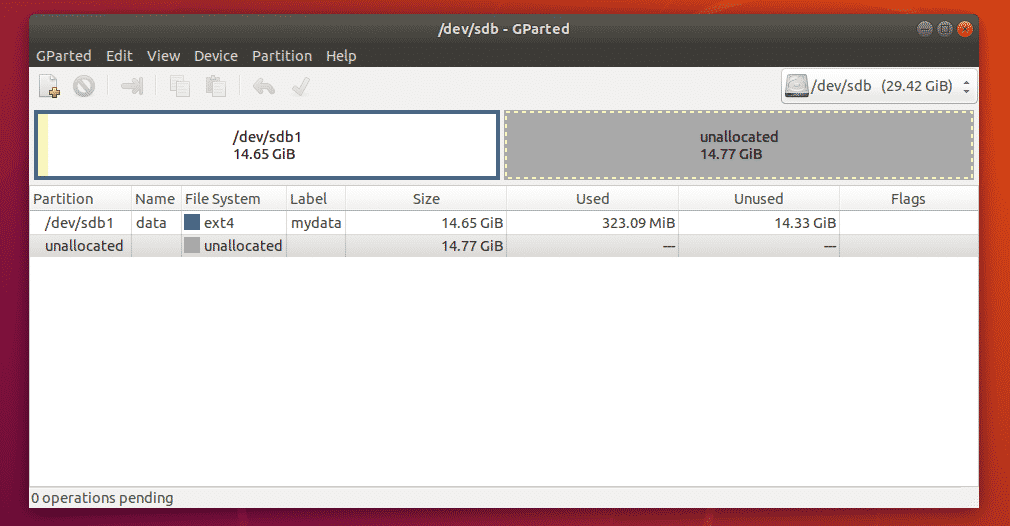
Formatting a Partition with GParted:
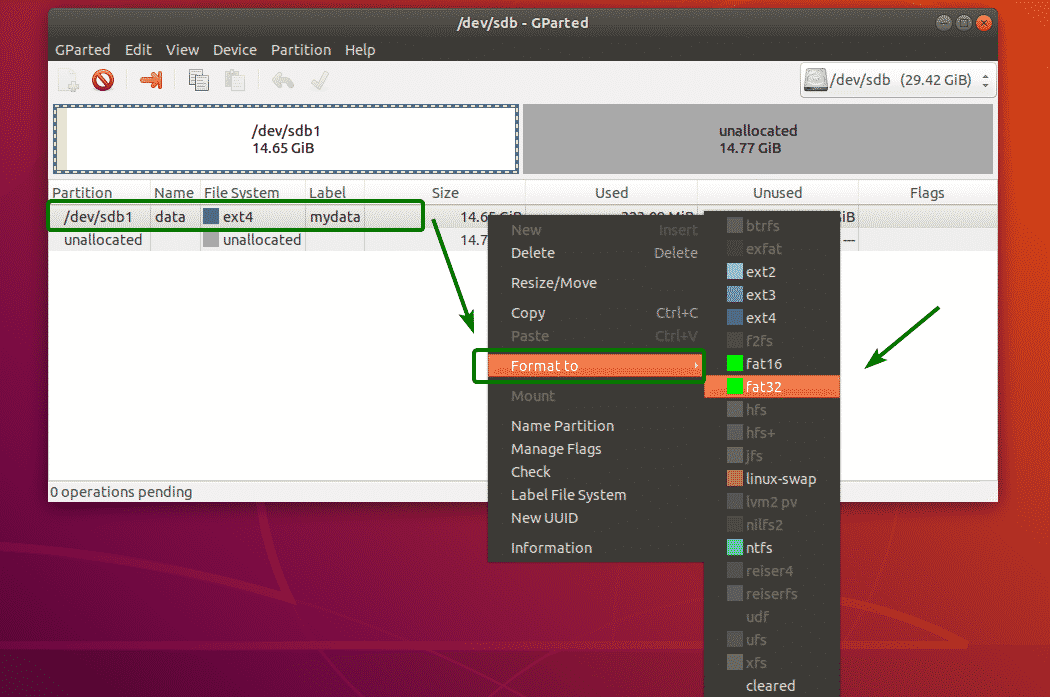
To format a partition with GParted, right click on the partition and click on Format to and select the filesystem type which you want the partition to be formatted to.
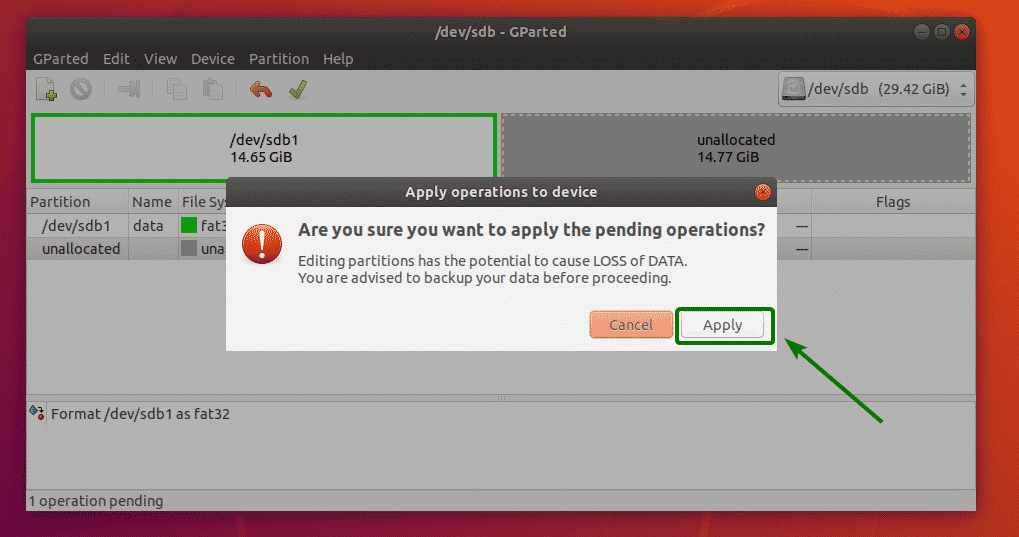
Now, to save the changes permanently, click on the tick icon as marked in the screenshot below.
Now, click on Apply.
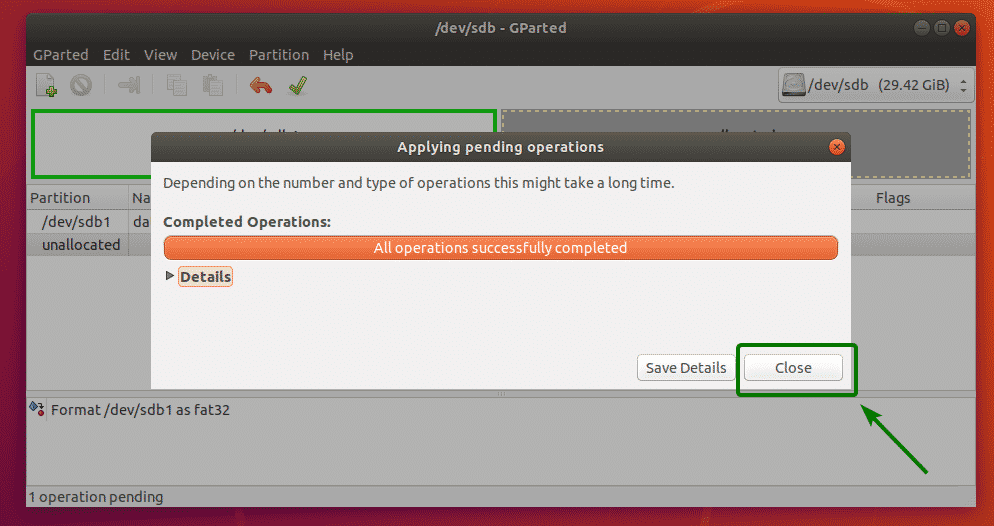
Once the operation is complete, click on Close.
As you can see, the partition is formatted to the newly selected filesystem type.
So, that’s how you use GParted on Ubuntu to do basic partitioning and disk management. Thank you for reading this article.