In a programming language, the data is stored in the main memory through variables so that we can retrieve, access, and perform some operations on data. C++ has data types that are utilized to allocate data in memory using variables. These data types tell the type of data, and they are predefined in the C++ compiler. We can also make the reference of one data with another data in memory by using & operator in C++. This article will put some light on the following points.
Let’s demonstrate the above queries one by one.
What is int in C++?
In C++ an int is a data type that refers to only integer-type data. The int is a reserved keyword in C++ that only has an integer value so that we can save it in memory and perform some operations. In C++ we use int datatype to declare any positive, negative, and zero value in our program.
An integer-type variable takes 4 bytes in memory. In C++ the declaration of the integer type variable is mentioned below:
Above, an integer-type variable is created with the name of a and a place in the main memory that has a stored value of 10.
What is int& in C++?
The int& means reference to an integer type variable. It means it will point to an integer-type variable that already exists in the storage. A reference variable must be initialized to link to a real item of the same type when it is declared. The following is the initialization of int&:
int& ref_var= a;
In this case, the ref_var is a reference to a. Any operation on ref_var represents an action on a variable. For example, if we type ref_var= 25; the value of a will be changed to 25 because the ref_var variable is just an alias for a variable.
Examples: Difference Between int and int& in C++
To understand the difference between int and int&, see the examples below:
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a = 2; // create an integer variable a and assign it the value 2
int b = a; // create a copy of a and assign it to b
a = 4; // change the value of a to 4
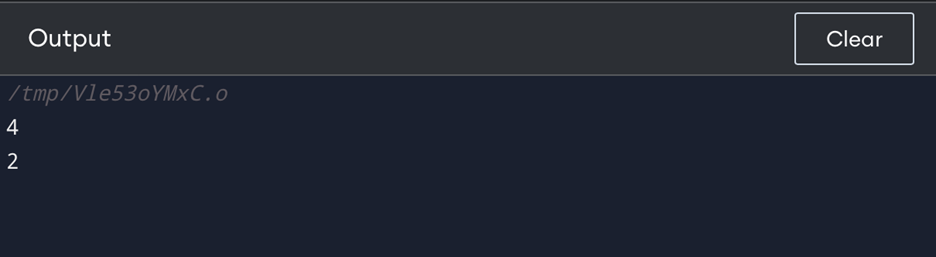
cout << a << endl; // output: 4
cout << b << endl; // output: 2
return 0;
}
Output
In this above code, changing the value of a does not change the value of b, because b is just a copy of a which is defined at the beginning of the main function.
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a = 2; // create an integer variable a and assign it the value 2
int& ref_var = a; // create a reference to a
a = 4; // change the value of a to 4
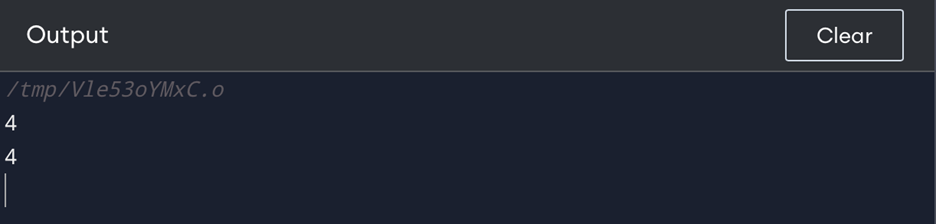
cout << a << endl; // output: 4
cout << ref_var << endl; // output: 4
return 0;
}
Output
In this example, ref_var is a reference to a. When the value of a is changed, the value of ref_var is also changed, because they both refer to the same value.
Key Distinctions of int and int& in C++ Language
The following table will explain some general differences between the int and int&:
| int | int& |
| A data type that is primitive and that holds a numerical value is int. | int& is an access point to a numerical variable that serves as an alias for the actual variable. |
| Employing int interacts with the variable’s real value. | Int& is an alias for an integer that can be applied to change the actual variable. |
| An int-type variable takes a new memory allocation. | An int& does not allocate new memory, as it uses the existing variable memory. |
| The scope and duration of integer variables are independent. | The scope and duration of int& are not specified. They take place only while the int reference variable which they refer to occurs. |
Conclusion
Like other programming languages, C++ also gives many functionalities that are already defined in the C++ interpreter. One of the popular data types is the int data type which accepts integer data, and int& is an int variable reference that makes direct changes to int variables. The main difference between int and int& is int declares a new variable, while int& is a reference variable that makes changes to the declared variables of the int type.