So using old version of software packages is good in a way. If you’re looking for bleeding edge software packages in Debian, then one alternative is Debian testing releases. Debian testing has more up to date software packages. But don’t expect it to be like Arch Linux.
Let’s say, you need the stability of Debian stable and still need some specific up to date software packages which is available in the Debian testing releases. Well, that’s when Debian Backports package repository comes in. According to the official website of Debian, the Debian Backports packages are packages from the Debian testing release (or the next version of Debian) adjusted and recompiled for using in Debian stable releases.
The official website of Debian also states that, if you use Debian Backports packages, then upgrade to the next Debian release (when it’s released) will not cause problems at all as the packages are already available there. There is a little bit problem with Debian Backports packages. The packages are not extensively tested as in Debian stable packages. Again, Debian Backports packages may conflict with your Debian stable packages. So you should be careful when using Debian Backports packages.
Debian recommends you use only the packages you need from the Debian Backports package repository. You should not use all the available Backports packages on Debian stable.
In this article, I will show you how to use Debian Backports package repository on your Debian stable release. I will be using Debian 9 Stretch (which is the latest version of Debian stable release at the time of this writing) in this article. So Let’s get started.
Searching for Backports Packages:
Debian Backports package repository contains a lot of Debian packages. You can search to find out whether the package of software version you’re looking for is available in the Debian Backports package repository from your web browser.
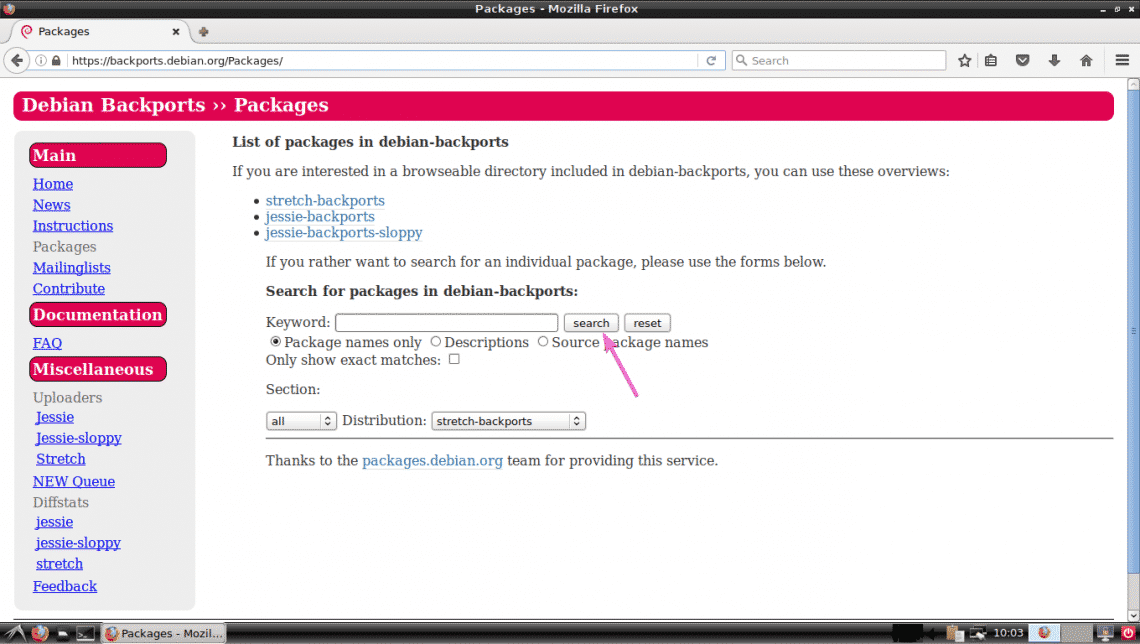
First, go to the official website of Debian Backports package repository at https://backports.debian.org/Packages/
Then, type in the package name and click on search. If the package is available in the backports package repository, it should show up.
Adding Debian Backports Package Repository to Debian 9 Stretch:
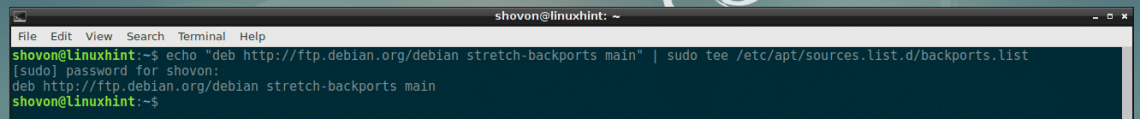
In this section, I will show you how to add the Debian Backports package repository on your Debian 9 Stretch stable release. First, open up a Terminal and run the following command:
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/backports.list
The Debian backports package repository should be added to your Debian 9 Stretch machine.
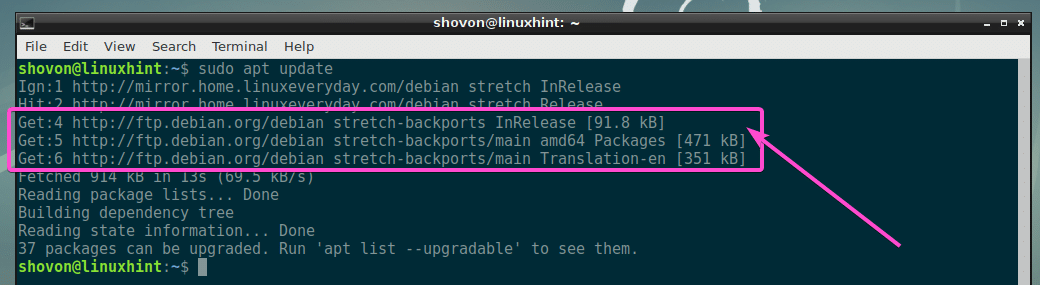
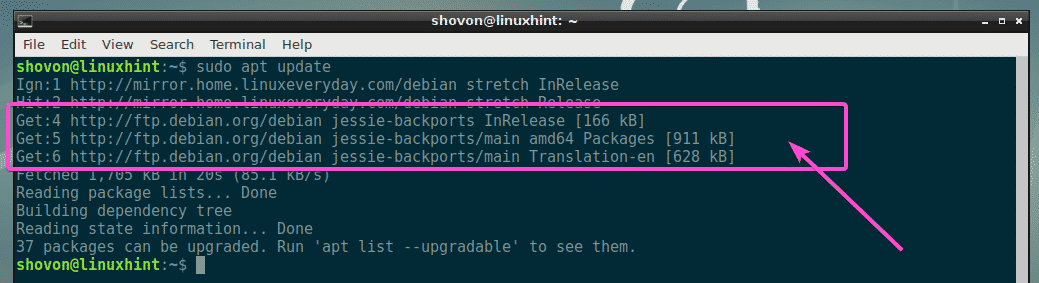
Now, update the APT package repository cache with the following command:
As you can see, the APT package repository cache is updated and it included the Debian backports package repository as well.
Adding Debian Backports Package Repository to Debian 8 Jessie:
In this section, I will show you how to add the Debian Backports package repository on your Debian 8 Jessie stable release.
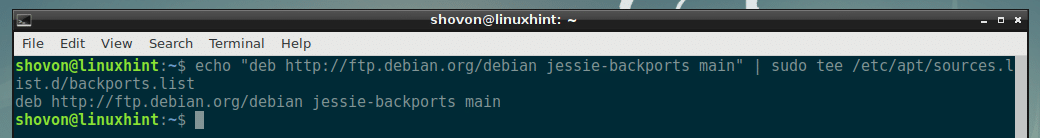
First, open up a Terminal and run the following command to add the Debian Jessie Backports package repository to your Debian 8 Jessie machine:
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/backports.list
Debian Backports package repository should be added to your Debian 8 Jessie machine.
Now update the APT package repository cache of your Debian 8 Jessie machine with the following command:
As you can see, the APT package repository cache is updated and it also includes the Debian Backports package repository.
Installing Packages from Debian Backports Package Repository:
By default, all backports package repositories are disabled on Debian. If you want to install a package from Debian backports package repository, you have to tell the APT package manager that you really do want to install a package from Debian backports package repository specifically. That’s a great safeguard.
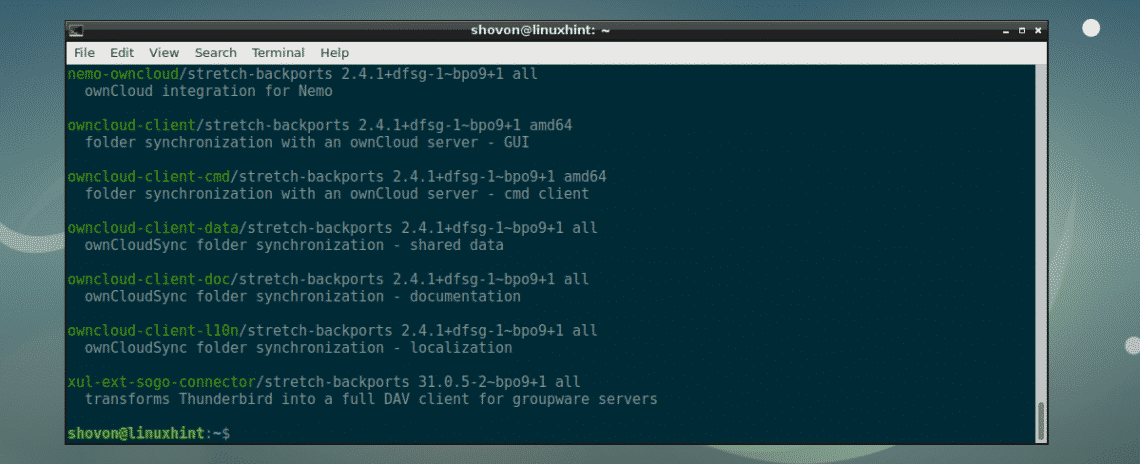
To search for a package (let’s say owncloud) in the Debian backports package repository, run the following command:
On Debian 9 Stretch:
On Debian 8 Jessie:
As you can see, the backports repository packages are listed.
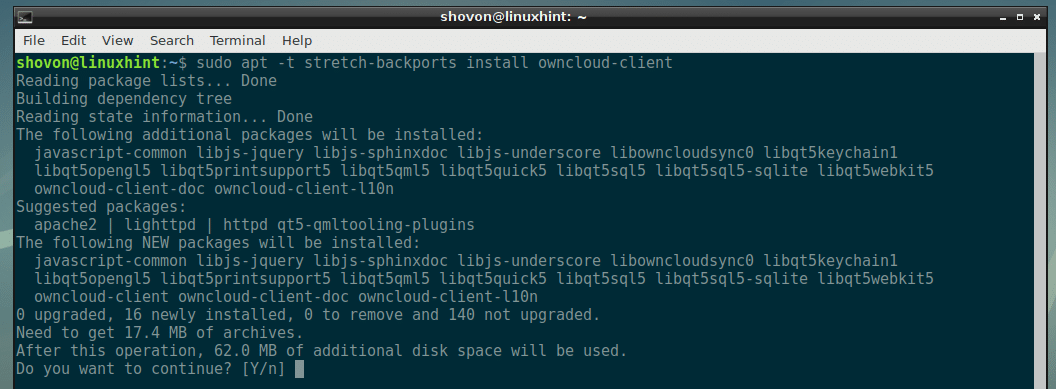
To install a package (let’s say owncloud-client) from Debian backports package repository, run the following command:
On Debian 9 Stretch:
On Debian 8 Jessie:
Now, press y and then press <Enter>.
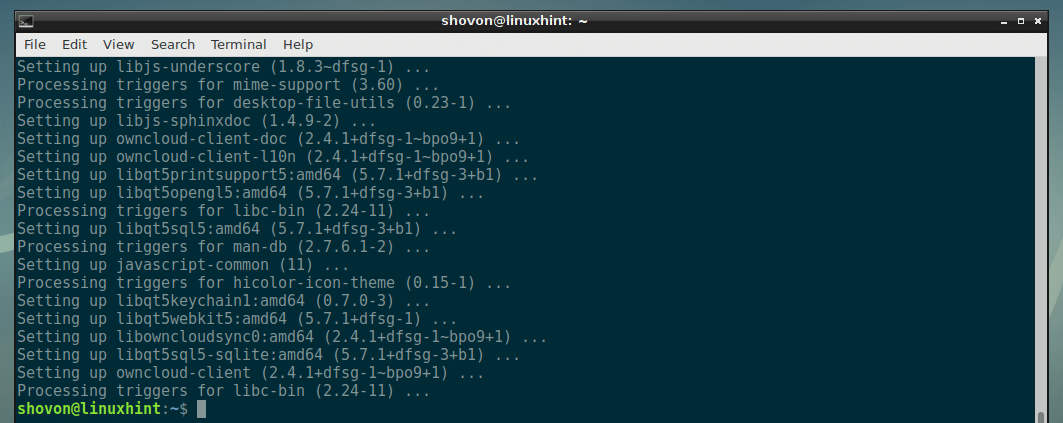
As you can see, the packages are being downloaded from the Debian Backports package repository.
As you can see, the owncloud-client is installed from the Debian backports package repository.
As you can see, the ownCloud GUI client I just installed from the Debian backports package repository runs just fine.
Removing Packages from Debian Backports Package Repository:
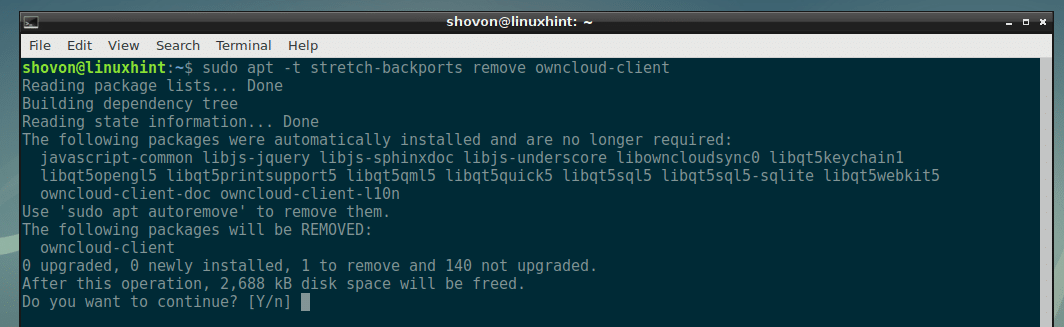
If you want to remove a package that you installed from the Debian backports package repository, then this section is for you. To remove a package (let’s say owncloud-client) that you installed from the Debian backports package repository, run the following command:
On Debian 9 Stretch:
On Debian 8 Jessie:
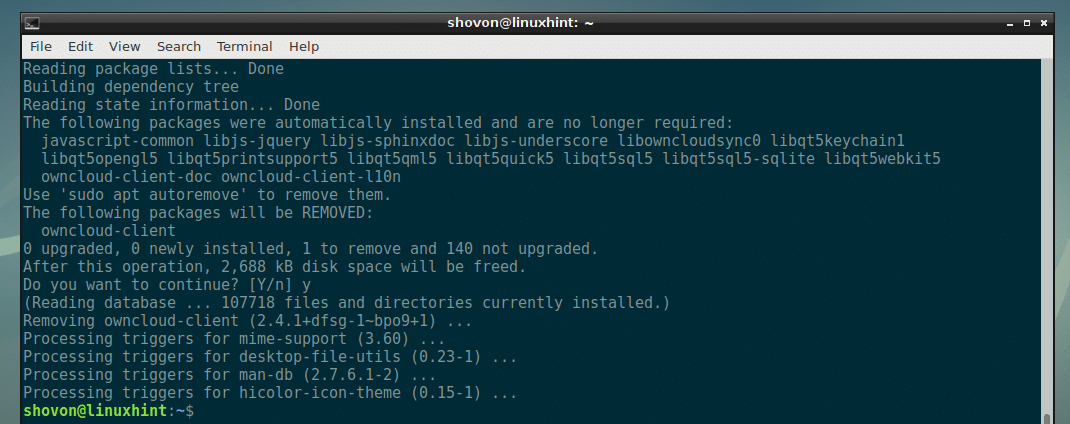
Now, press y and then press <Enter>.
The owncloud-client package should be removed.
Removing Debian Backports Package Repository:
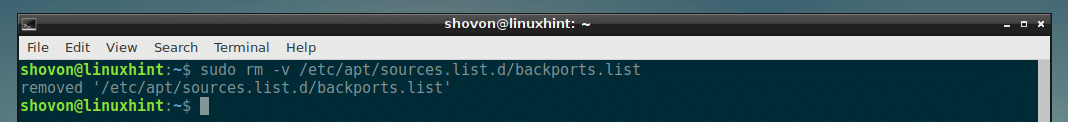
If you’ve followed this article to add Debian backports package repository on your Debian 9 Stretch or Debian 8 Jessie machine, then you can remove it very easily with the following command:
Debian Backports package repository should be removed.
Now, update the APT package repository cache with the following command:
The APT package repository cache should be updated.
So, that’s how you use Debian backports package repository on Debian. Thanks for reading this article.