In this tutorial, we will look at how to print boolean values as 0 or 1 in C Programming.
What is Boolean in C?
In C, a boolean data type can only store two values: true or false. It is denoted by the keyword bool and defined in the header file stdbool.h. Since they allow conditional statements to be evaluated based on a true/false value, boolean variables are useful in programming. In C, true is represented by the value 1 and false is represented by the value 0.
Print Boolean Values as 0 and 1 in C Programming
There are two ways to print boolean values as 0 and 1 in C programming:
Method 1: Using printf() Function with Format Specifier
A straightforward approach to print a boolean in C Programming is by using the printf() function with a format specifier. The format specifier %d is used to print integer values, but since a boolean value is stored as either 0 or 1, we can use the %d format specifier to print the boolean value as an integer.
The following C program example code uses the printf() function to print a boolean value.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x, y;
printf("Enter first integer: ");
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("Enter second integer: ");
scanf("%d", &y);
if (x < y) {
printf("x is smaller than y\n");
}
else {
printf("y is greater than x\n");
}
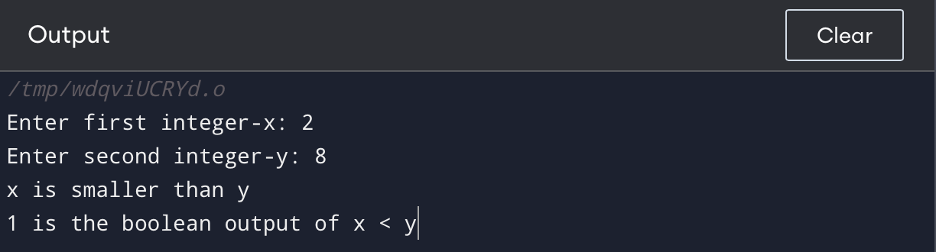
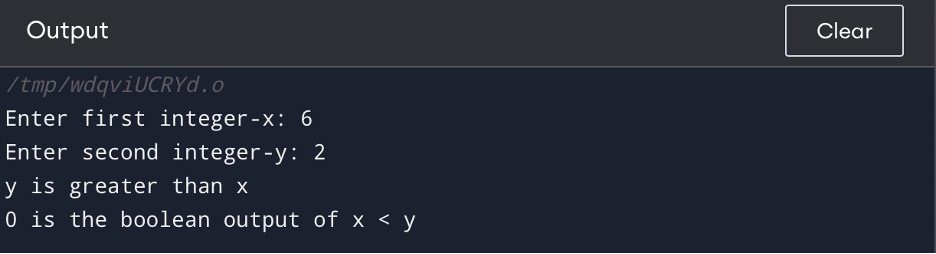
printf("%d is the boolean output of x < y", x < y);
return 0;
}
The above program user enters two integer values to variables x, and y. The program then moves to the if-else statement to test the condition if x is less than y and prints the corresponding message. Finally, the program uses the printf() function with %d format specifier to print the boolean result of x and y.
Output
And:
Method 2: Using puts() Function with Ternary Operator
In C programming, the puts() function can also be used with the ternary operator to print boolean values as 0 or 1. A ternary operator is a simplified form of the if-else statement that allows us to verify a condition and return one of two values depending on the condition using a single line of code.
Here’s an example that illustrates printing a boolean in C programming using puts() function and ternary operator.
#include <stdbool.h>
int main() {
bool flag = true;
puts(flag ? "1" : "0");
return 0;
}
The above program initializes a boolean variable flag to true and then uses the ternary operator to print the corresponding value “1”.
Output
Bottom Line
In C programming, you can print boolean values using several ways such as the printf() function with a format specifier and the puts() function with a ternary operator. Understanding boolean data types and their representation in C is essential for programmers to effectively use them in conditional statements and logical operations.