Method 1: Using wc Command
One of the simplest ways to count the number of lines in terminal output is by using the “wc” command. The “wc” command is a powerful tool that can be used to count words, lines, and characters in a file or output stream. The output from the terminal can be piped to the “wc” command and the “-l” option can be used to instruct “wc” to count the number of lines in the output. For instance, the following code can be used to count the number of lines in the output of the “ls” command:
ls
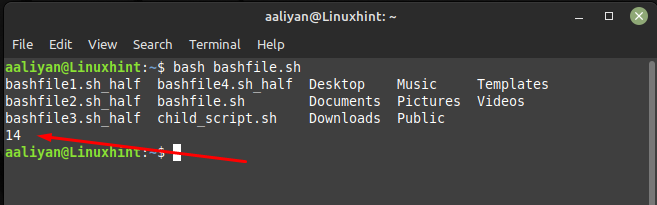
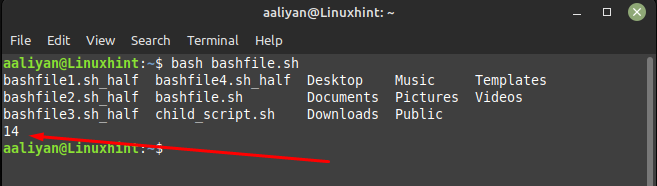
ls | wc -l
This will return the number of lines in the output of the “ls” command along with the files and folders in the current directory:
Method 2: Using grep Command
The “grep” command is a powerful tool that can be used to search for specific patterns or strings in a file or output stream. To count the number of lines in terminal output using “grep”, we can pipe the output to “grep” and specify a pattern that matches every line.
For example, if we want to count the number of lines in the output of the “ls” command using “grep,” we can use the following command:
ls
ls | grep -c '^'
This will return the number of lines in the output command along with the files and folders in the current directory:
Method 3: Using awk Command
The “awk” command is a powerful tool that can also be used to manipulate and process text files or output streams. To count the number of lines in terminal output using “awk”, we can pipe the output to “awk” and use the “END” pattern to perform an action at the end of the input stream. We can then print the value of a counter variable that increments for each line.
For example, if we want to count the number of lines in the output using “awk,” we can run the following bash code:
ls
ls | awk 'END { print NR }'
This will return the number of lines in the output of the “ls” command along with the files and folders in the current directory:
Conclusion
Counting the number of lines in terminal output is a simple yet useful task that can be accomplished using various commands line tools such as “wc”, “grep”, and “awk”. Depending on the situation and the type of output, one method may be more suitable than the others. By mastering these techniques, we can efficiently count the number of lines in terminal output and improve our productivity as developers or system administrators.