The following post will provide details about the attribute “CmdletBinding”.
Learn How PowerShell CmdletBinding Enhances Functions
The attribute “CmdletBinding” is utilized to enhance the function. Particularly, the core function of this attribute is to turn the function into an operable cmdlet.
Examples explaining the stated attribute are given below.
Example 1: Use the “CmdletBinding” Attribute to Transform the String From Upper Case to Lower Case
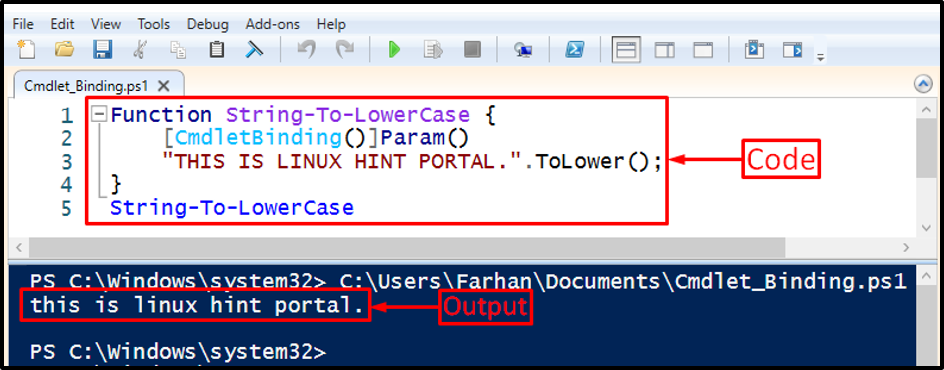
In this example, the “CmdletBinding” attribute will transform the string to lower case:
[CmdletBinding()]Param()
"THIS IS LINUX HINT PORTAL.".ToLower();
}
String-To-LowerCase
In the mentioned code above:
- First, create a function and specify a name for it.
- Then, create a “Param()” and specify the “[CmdletBinding()]” parameter before it.
- After that, write a string within inverted quotes and concatenate it with the “ToLower()” method.
- Lastly, call the function by specifying its name outside the curly braces:
Example 2: Use the “CmdletBinding” Attribute in a Function Along With the “-Verbose” Parameter
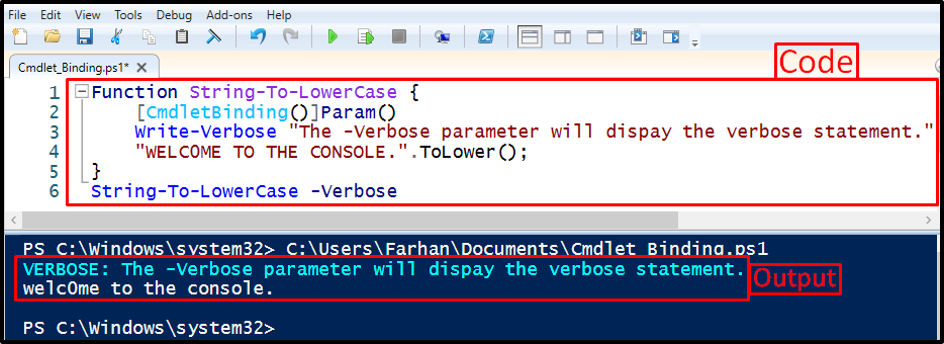
This demonstration will transform the string into lowercase. Moreover, it will display the verbose message with the aid of the “-Verbose” parameter:
[CmdletBinding()]Param()
Write-Verbose "The -verbose parameter will display the verbose statement."
"WELC0ME TO THE CONSOLE.".ToLower();
}
String-To-LowerCase -Verbose
In the above-stated code:
- The verbose statement is given using the “Write-Verbose” cmdlet.
- Then, the function name is specified outside the curly braces along with the “-Verbose” parameter:
Example 3: Use the “CmdletBinding” Attribute Along With the “SupportsShouldProcess” and “PSCmdlet” Object
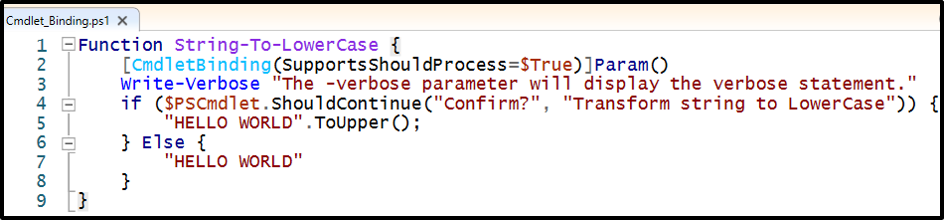
This illustration will create a prompt, which will confirm whether to transform the string to upper case or not:
[CmdletBinding(SupportsShouldProcess=$True)]Param()
Write-Verbose "The -verbose parameter will display the verbose statement."
if ($PSCmdlet.ShouldContinue("Confirm?", "Transform string to LowerCase")) {
"HELLO WORLD".ToLower();
} Else {
"HELLO WORLD"
}
}
In the above-stated code:
- First, create a function and specify a name.
- Inside the function, pass the “SupportsShouldProcess=$True” inside the “CmdletBinding()” attribute.
- After that, create an “if” condition and pass the “$PSCmdlet.ShouldContinue()” parameter inside it.
- Then, add the text inside the above-stated parameter to be displayed at the time of getting affirmation from the user.
- The “if” condition will transform the string to lower-case if the user clicks on the “Yes” button else the string case won’t change:
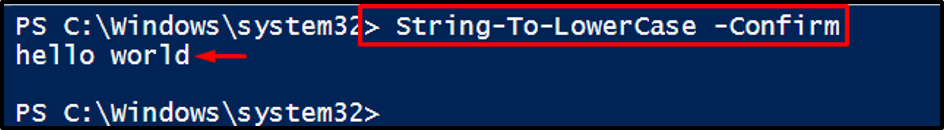
Click on the “Yes” button to transform the string into a lowercase:
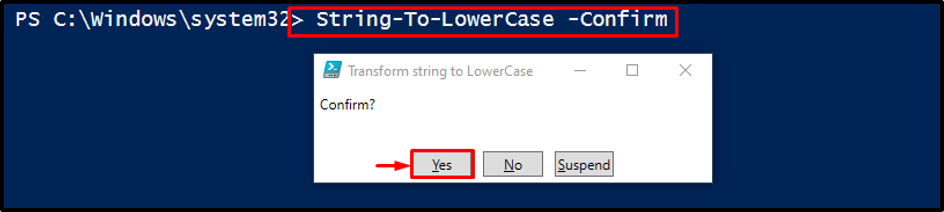
It can be observed that the string has been transformed to lower case.
Conclusion
The “CmdletBinding” attribute in PowerShell is used to convert the function into an operable cmdlet. Doing so will provide access to all cmdlet features to the function turned into a cmdlet. This blog has elaborated on PowerShell’s “CmdletBinding” attribute to enhance the function.