In C++, the fork() system call duplicates the parent process to produce a new child process. It is employed to produce a child node that is a perfect replica of the parent node, complete with all its attributes, file system descriptors, and storage locations. It is useful in scenarios when a user wants to create an instance of a program already running on the system or he/she wants to start a new program.
Declaration of fork() in C++
The “fork ()” function, which comes from Unix/Linux operating systems isn’t part of the standard C++ library, hence it is accessible via the “unistd.h” header file.
pid_t fork();
Return Values in the fork()
The fork() function returns two values 0 and -1.
- It might provide the child process return value as 0 while giving the parent process, upon successful completion, the child process’s process ID.
- It returns a -1 value when the child process is not created, and it will automatically generate an error.
Significance of fork () in C++
- By using fork (), developers do parallel processing at the same time by creating multiple processes.
- Allows the process to create a clone of itself called a child process.
- It enables us to create complex programs with security and better fault tolerance.
- The parent and child processes run concurrently.
- Used for multitasking applications.
- Helps two different independent processes to communicate with one another.
A Simple Example of fork () in C++
Here is an example of how to utilize C++’s fork () function successfully:
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
pid_t child_id = fork();
if (child_id == -1) {
perror ("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else if (child_id > 0) {
cout << "Message from Parent process My child has process ID: " << child_id << endl;
}
else {
cout << "Message from Child Process: " << child_id ;
}
return 0;
}
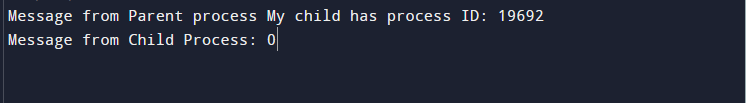
In the above example, the fork() method responds in both processes with no or null arguments. As seen below output, a child process’s process id is the parent processes, and the child process itself returns 0. The parent returns -1 if doesn’t work.
Output
Conclusion
Overall, the fork() system function is a strong feature that lets C++ programmers generate and control numerous processes. The system-call fork() increases the performance of complex programs and enables to do multi processes. It takes zero parameters and returns integer values with corresponding processes.