This write-up will discuss:
- Can We Use Subquery in WHERE Clause in MySQL?
- How to Use Subquery in MySQL WHERE Clause?
- How to Use MySQL Subquery with Comparison Operators in WHERE Clause?
- How to Use MySQL Subquery in WHERE Clause With “IN” or “NOT IN” Operators?
Can We Use Subquery in WHERE Clause in MySQL?
Yes, we can use the subquery in the “WHERE” clause in MySQL. The “WHERE” clause can extract records that meet the specified conditions.
Syntax
The general syntax of the WHERE clause subquery is listed below:
Now, let’s use the subquery in the “WHERE” clause for better understanding!
Step 1: Access MySQL
First, connect with the MySQL server by running the “mysql” query with username and default password:
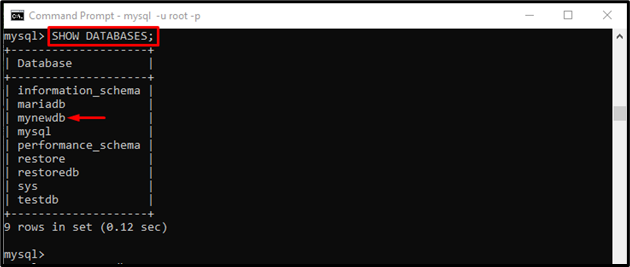
Step 2: View Databases
Then, use the “SHOW” command to list all databases:
We have selected the “mynewdb” database for further process:
Step 3: Change Database
Run the “USE” statement to change the database:
Step 4: View Database Table
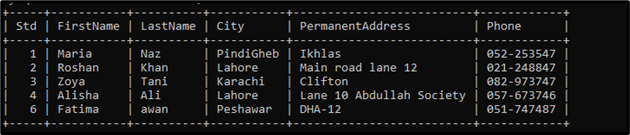
Now, execute the “SELECT” statement to list the content of the table:
Here, we have listed the “student” table:
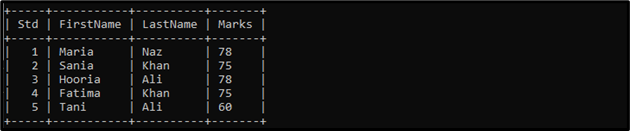
Similarly, list the content of the “student_marks” table:
Now, we will apply the “WHERE” clause with subqueries on the above-listed table to get desired records.
How to Use Subquery in MySQL WHERE Clause?
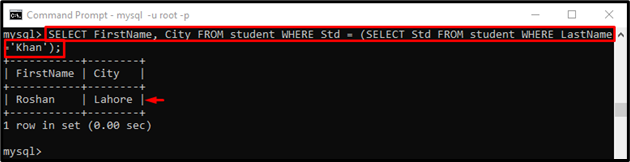
Execute the “SELECT” statement with a “WHERE” clause and “SELECT” statement as a subquery:
Here:
- “SELECT” statement is used to select data from databases.
- “FirstName, City” are the table columns.
- “FROM” clause is used to extract some rows from the table.
- “student” is our table name.
- “WHERE” clause is utilized for filtering records that fulfill specified conditions.
- “Std” is the column name that contains the student ids.
- “LastName=’Khan’” is also our table column.
In the above-stated command, first, the subquery will be executed. After that, the outer query will execute. According to the provided output, only one record fulfills the specified condition:
How to Use MySQL Subquery with Comparison Operators in WHERE Clause?
We can also use different comparison operators to compare a single result returned by the subquery and the expression in the “WHERE” clause. These comparison operators are “>” greater than, “=” equal, and “<” less than.
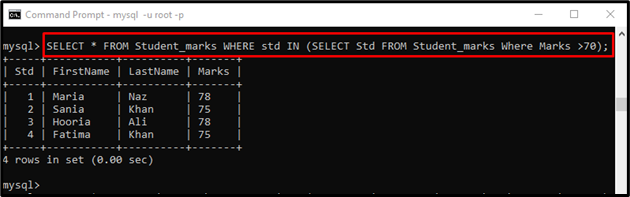
Example 1: Using “>” Greater than Comparison Operator in “WHERE” Clause with Subquery
The below-stated command returns the records of those students whose marks are higher than “70” using the subquery:
In this query:
- First, it will determine the record of those students whose marks are above “70” using the subquery.
- After that, the outer query will return the marks with details whose student ids are in the result set returned by the executed subquery:
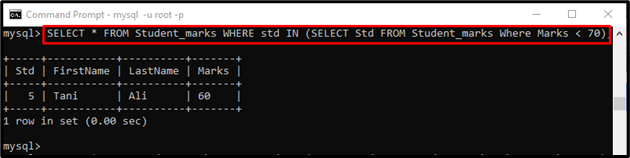
Example 2: Using “<” Less than Comparison Operator in “WHERE” Clause with Subquery
The following command will return the details of those students whose marks are less than “70” using the subquery in the “WHERE” clause:
According to the executed statement, only one student has less than “70” marks:
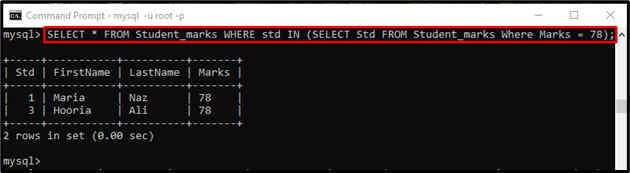
Example 3: Using “=” Equal Comparison Operator in “WHERE” Clause with Subquery
Similarly, the below-stated command will get the details of those students whose marks are equal to the “78” using the “SELECT” statement as a subquery:
How to Use MySQL Subquery in WHERE Clause With “IN” or “NOT IN” Operators?
If the specified subquery returns multiple values, we are required to use the “WHERE” clause with the “IN” or “NOT IN” operator.
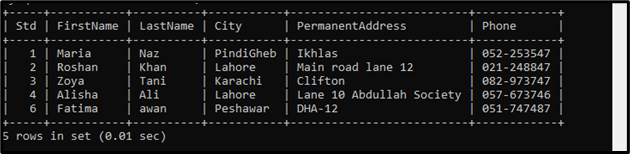
Suppose we have a table named “student” that contains the following data:
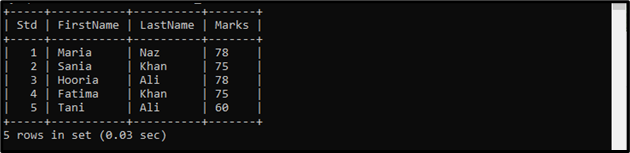
The “student_marks” table contains the below-listed records:
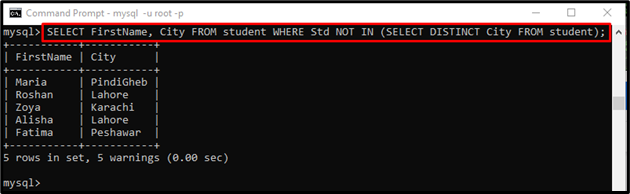
Example 1: Using “NOT IN” Operator in “WHERE” Clause With Subquery
Suppose we have a table named “student” that contains the student’s data, such as “FirstName”, “LastName”, “City”, “PermanentAddress”, and more details. We want to get the “FirstName” and “City” from the “student” table where student ids do not exist in the subquery. In a subquery, we get the record of students with different city names:
Here, the “DISTINCT” statement is used to return only different values:
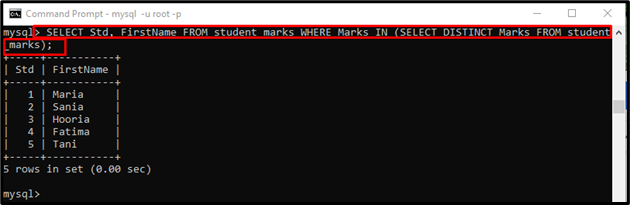
Example 2: Using “IN” Operator in “WHERE” Clause with Subquery
We have a table named “student_marks” that contains the student’s data, such as “Std”, “FirstName”, “LastName”, and “Marks”. We need to get the “FirstName” from the “student_marks” table where student marks exist in the subquery. In a subquery, we are getting the marks of those students who differ from each other.
To do so, execute the below-listed statement:
That’s all about using a subquery in the WHERE clause in MySQL.
Conclusion
Yes, you can use the subquery in MySQL’s “WHERE” clause. We can use comparison operators, such as less than, equal, and greater than, in the “WHERE” clause subquery. Additionally, the “IN” and “NOT IN” operators can be used in the subquery. This write-up demonstrated the about subquery in the “WHERE” clause in MySQL.