Finding a package that provides a file is important on Linux systems including Ubuntu. The reason is it helps users solve package dependency problems that occur when you install a package on the system and if a file is missing, you won’t be able to perform the installation until the file is found. Further, it also helps users debug server-related issues on the system that may fail to start if a required library is missing.
If you want to find a package that provides a file on Ubuntu, you should follow this article’s guidelines.
Find a Package that Provides a File on Ubuntu
There are two ways to find a package that provides a file in Ubuntu and those are:
Method 1: apt-file
The first method to find a package that provides a file is by using an apt-file package. The apt-file marks the indexes for all installed packages which are present in the repository. By using apt-file, the users can search for a file provided by any of the packages present inside the repository, and this all searching process completes within a few seconds. This method is divided into two parts which are:
i: Installing apt-file
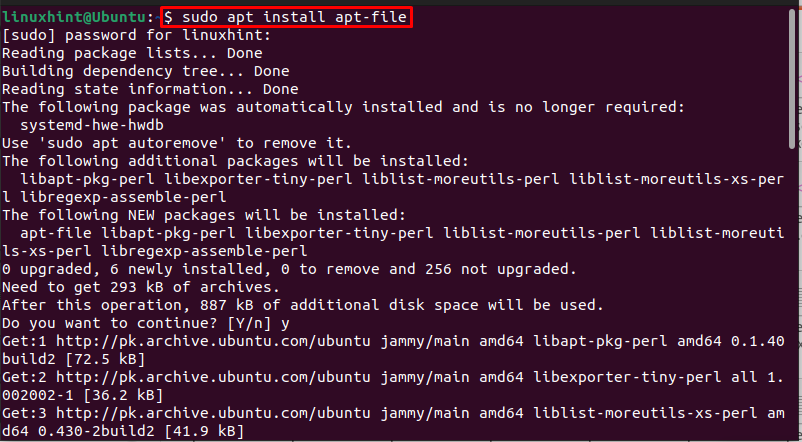
To install “apt-file” on your Ubuntu system, firstly update and upgrade the repository:
sudo apt upgrade
Then install apt-file by using the below-mentioned command:
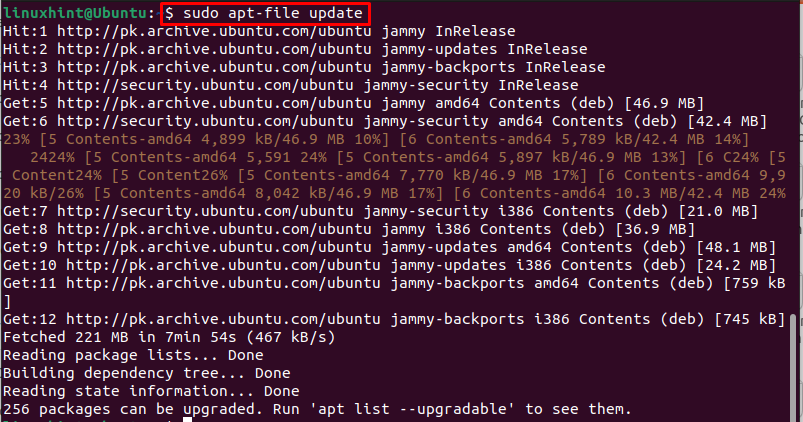
The apt-file access database to find the packages belonging to a package and for that reason, it is important to update apt-file through the following command before searching for a file on Ubuntu:
ii: Searching File Using apt-file
To search the file using apt-file, run the below-mentioned command along with the name of the file:
For example:
Or you can also use the file path to directly navigate the file, and its associated package:
For example;
Method 2: By Using dpkg
The other method to find a package that provides a file is by using the dpkg command, which is used to find the packages that were installed without a repository that is what makes it unique from apt-file. But dpkg can only list the files of packages which are installed in the system, whereas apt-file can even list the packages which are not installed in the system but are present in the repository.
Use the below-written dpkg file along with -S identifier for search, to find the package associated with the desired file:
For example:
Just like apt-file, you can also use a file path instead of just file name with the dpkg command to property navigate the file from its directory:
For example;
Bonus Tip
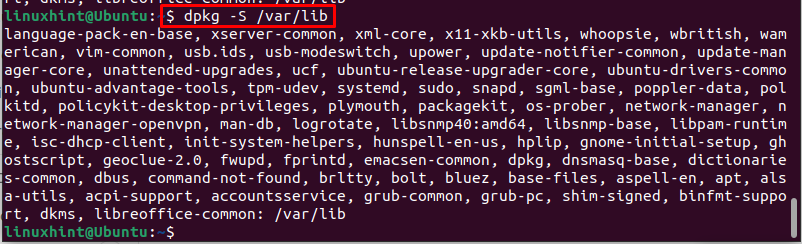
The dpkg command can also be used to search all the packages present inside a directory or library by using the below-mentioned command:
For instance, here I have displayed all the packages present inside the /var/lib:
Conclusion
To find a package that provides a file on Ubuntu, there are two ways: One is by using the “apt-file” tool which uses the database to search the file from the list of packages present inside the repository. The other method is by using the dpkg -S command to search the file from the list of installed packages. The apt-file tool needs to be installed, whereas “dpkg” is already present by default in Ubuntu.