Open ports are ports that allow traffic from a service or applications to run on it. Opening ports are important if you want a certain service to run on your system. In most systems such as Ubuntu ports are closed by default for security purposes but they can be opened easily.
In this writeup, we have shown how to open ports in Ubuntu.
How Can I Open Some Ports on Ubuntu
To open ports on Ubuntu, we will use an uncomplicated firewall (UFW), which is an Uncomplicated Firewall tool that provides proxy settings in different systems. Many Linux systems come with the pre-installed firewall but in case of Ubuntu it will be required to install.
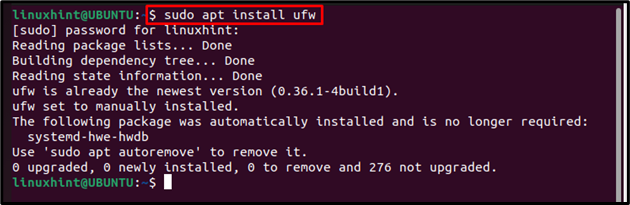
You can install UFW on Ubuntu from the repository using the apt command and for that, it’s mandatory to update/upgrade the repository first using the below-mentioned commands:
$ sudo apt upgrade
Then install UFW by using the below-mentioned command:
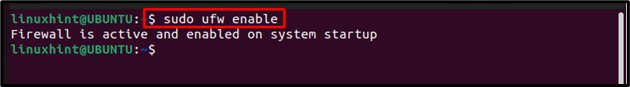
Once the UFW is installed, enable it on your Ubuntu system by using the below-mentioned command:
How to Open Port on Ubuntu
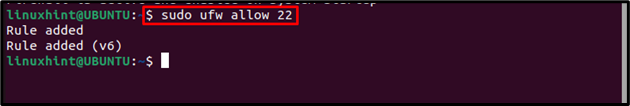
Once the UFW is enabled, you can open ports using the below-mentioned command:
Syntax
For example, to open SSH port which is 22 by default, you can use 22 with the ufw command as shown below:
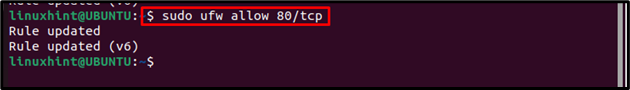
By using UFW, the traffic to the port can also be controlled and for that the user just has to specify the port along with the protocol name they want the traffic:
Syntax
In the stated example, I have allowed the tcp protocol traffic to port 80.
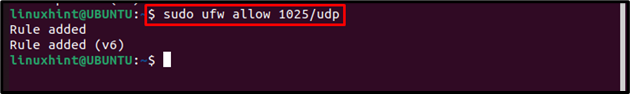
Similarly, the below-written example allows the udp traffic to port 1025:
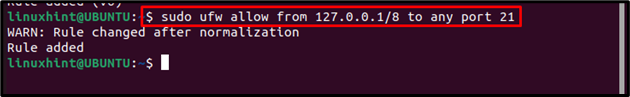
The traffic from a specific IP address can also be allowed to a port by following the below-mentioned command:
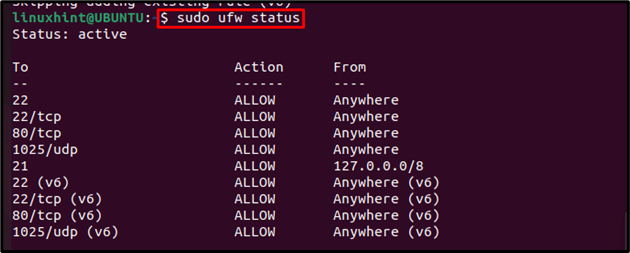
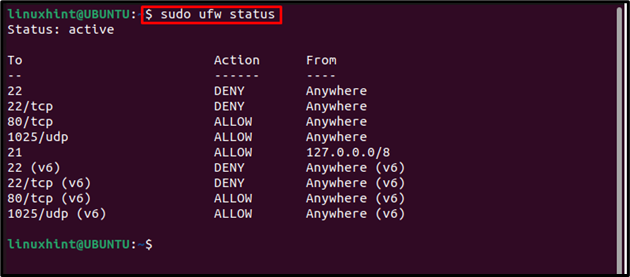
To check the status of the ports, you can follow the below-mentioned command to verify that ports are opened successfully:
How to Close Ports on Ubuntu
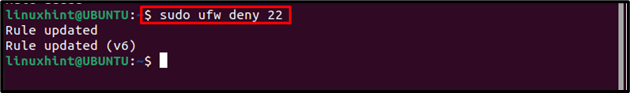
If you have previously opened a port and now you feel the need to block it then you can use the below-mentioned command:
Syntax
Just like opening port command, you can also block the ports with either their name or service name:
Example
Blocking ports by using port number:
Then verify by using the below-mentioned status command:
That’s all for the process, but remember that while using UFW to open ports, ensure that the service you are interested in the opening should be active.
Conclusions
To open ports in Ubuntu, the users have to install UFW from the apt command and then enable its service on the system. After that, they can use the UFW command to open ports with port numbers and allow the desired protocol traffic to it. They can also check the status of opened and blocked ports using the ufw status command.