This guide will demonstrate the method to roll back/reset a Git repository to a specific commit.
How to Roll Back/Reset a Git Repository to a Specific Commit?
To reset a Git repository to the desired commit, follow the provided steps:
- Redirect to the local repository.
- View commits history.
- Choose a particular commit and its copy SHA-hash.
- Run the “git reset –hard <commit-id>” command.
- Verify changes.
Step 1: Switch to Git Directory
First, type out the below-provided command to redirect to a desired local directory:
Step 2: Check Git Commit History
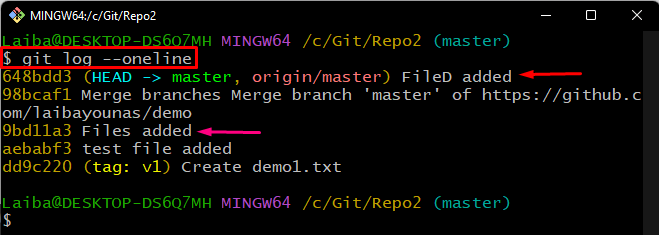
Then, view the current position of HEAD by checking the log history using the “git log” command:
The below screenshot indicates that the HEAD is pointing to the “FileD added” commit. Now, choose and copy the SHA-hash value of the commit that is required to reset. For instance, we have selected the “Files added” commit, whose hash value is “9bd11a3”:
Step 3: Reset to Particular Commit
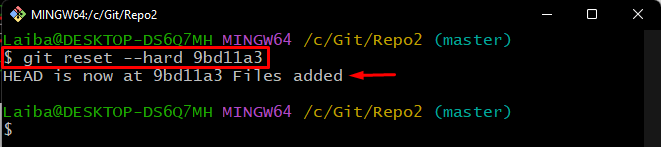
Now, execute the “git reset –hard” command along with the copied commit hash and move the HEAD pointer to it:
Here, the “–hard” option is used to roll back to the desired commit:
Step 4: Verify Git Log
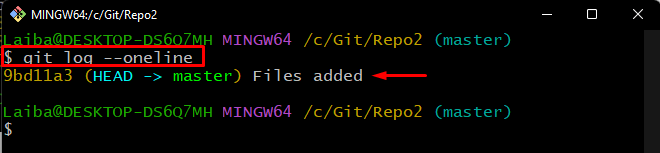
Lastly, view the commit history to check the current position of HEAD:
In the below-given screenshot, it can be observed that the HEAD is now pointing to the specified “9bd11a3” commit:
We have explained the procedure of rolling back a Git repository to a desired Git commit.
Conclusion
To roll back/reset a Git repository to the specific commit, first, move to the local Git directory. Then, view the commit history and select the desired commit. Lastly, run the “git reset –hard <commit-id>” command to roll back the Git repository to the desired commit. This guide demonstrated the easiest way to reset a Git repository to a particular commit.