If you want to know the XFS mount options, read this tutorial completely. Here, we will give you a brief walkthrough on the mount options and methods to use them.
What Are XFS Mount Options (Explained)
There are some parameters of the mount command which you can use to mount the XFS file system. Here is the basic syntax of the mount:
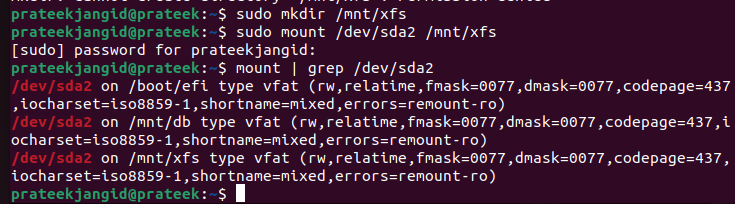
Let’s take an example of mounting the XFS filesystem in Linux. First, we need to create a directory using the following command:
The mkdir command creates the /mnt/xfs. Now, it is time to mount the XFS partition through the following mount command:
If you want to verify the changes, you can check the partitions through the following command:
In case your system has the filesystem or more than 2 TB, you can use the inode64 option as it is a benchmark mounting:
Sometimes, XFS contains the write barriers for security. You can use the following command to disable the barrier:
Mount Command Options
You place the different flags in the options section to perform various tasks. To know more about mount command options, you can use the following command:
Here are the brief details about the mount command options that you can use while mounting the XFS file system:
| Options | Description |
| -a flag | It can mount the filesystem which is mentioned in the fstab. |
| -c flag | It does not canonicalize the paths. |
| -f flag | It performs the dry run. |
| -F flag | It forks off for every device. |
| -T flag | It works as an alternative file to the /etc/fstab. |
| -i flag | It does not call the mount helpers. |
| -l flag | It displays the file system labels. |
| -n flag | It does not write to /etc/mtab. |
Conclusion
This article is all about the simple mount options of the XFS file system in Linux. We also explained how the mount works in the XFS filesystem and the different options that are used with the XFS mount. We hope that you get all the essential details about the XFS mount options that you can try.