Developers often encounter a situation where they do not want to commit all created and modified project files and temporarily ignore them from the staging area. Moreover, they want to keep these changes without updating the repository. In this situation, it is required to temporarily untrack these files. More specifically, the “$ git rm –cached” and “$ git update-index” commands can be helpful for this corresponding purpose.
This post discusses:
- Method 1: How to Untrack Files From Git Temporarily Using “git rm –cached” Command?
- Method 2: How to Untrack Files From Git Temporarily Using “git update-index” Command?
Now, move toward the detail of the above-listed methods!
Method 1: How to Untrack Files From Git Temporarily Using “git rm –cached” Command?
The “$ git rm –cached” command can temporarily remove the specified file from the staging area and untrack it. To implement this operation for better understanding, follow the steps below.
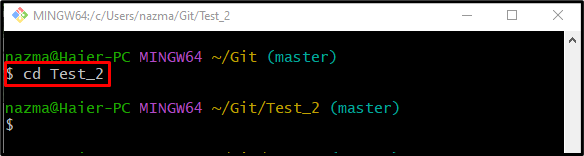
Step 1: Move to Local Repository
First, navigate to the particular Git repository by executing the “cd” command:
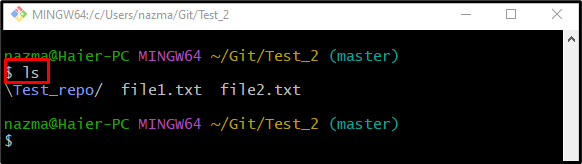
Step 2: List of Content
Run the following command to view the list of current repository content:
Step 3: Make New Text File
To make a new text file in the repository, use the “touch” command:
Step 4: Staged the Untrack File
Next, run the below-provided command to add the text file to the staging area:
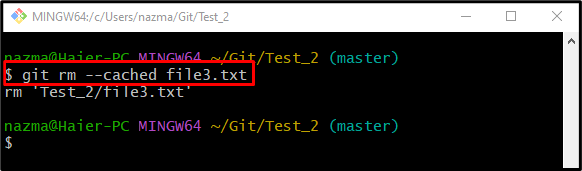
Step 5: Temporarily Remove File From Tracking Area
Now, delete the file from the staging area by executing the “git rm” command along with the “–cached” option and particular file name:
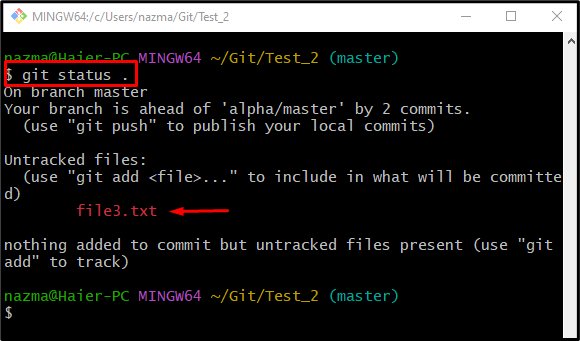
Step 6: Check Repository Status
Run the “git status .” command to check the repository status:
As you can see, the specified file has been temporarily removed the file from the staging index:
Let’s move to the next method to untrack the files from Git temporarily.
Method 2: How to Untrack Files From Git Temporarily Using “git update-index” Command?
Sometimes developers do not want to track all created files in the staging area and want to ignore them temporarily. To do so, follow the below-listed steps.
Step 1: Ignore Particular File
To start ignoring the desired text file with changes, execute the provided command along with desired file path:
Here, the “–assume-unchanged” option will suppose the file is not changed and ignore the modifications:
Step 2: Move to Git Repository
Now, navigate to the particular Git local repository using the following command:
Step 3: Check the Status of ignored Files
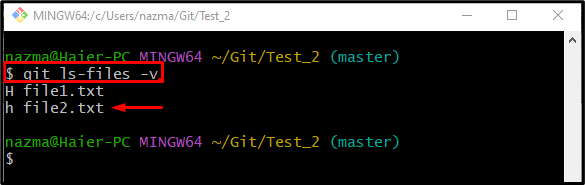
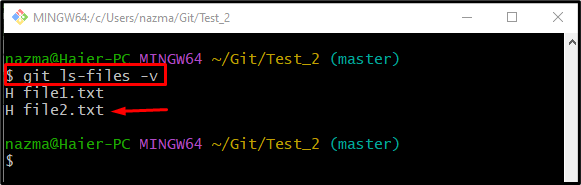
Now, to ensure the specified file is ignored successfully, run the “git ls-files” command with the “-v” option:
Here, the “h” indicates that the file is untracked temporarily from the repository and “H” shows the file is tracked:
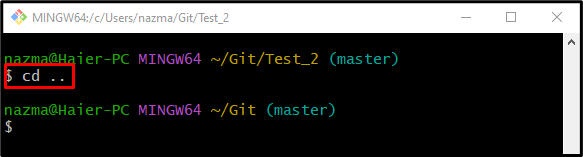
Step 4: Switch Back to Git Root Directory
Next, switch back to the Git root directory using the “cd ..” command:
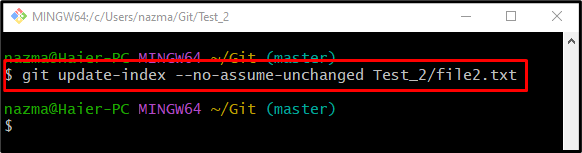
Step 5: Track Particular Ignore File
After performing desired operations on the Git repository, track back the ignore file, and run the following command along with the “–no-assume-unchanged” option:
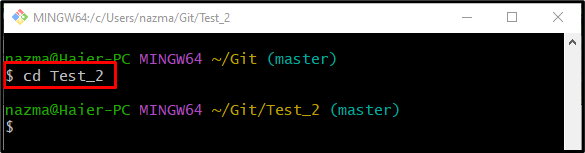
Step 6: Move to Git Repository
Next, navigate to the Git local repository through the provided command:
Step 7: Check File Current Status
Lastly, check the previously ignored file’s status:
As you can see, the below-highlighted file status is “H”, which indicates that the file is tracked successfully:
That’s it! We have provided different ways to untrack files from the Git repository temporarily.
Conclusion
Two different commands are used to untrack files from the Git repository, which are the “$ git rm –cached <file-name>” or the “$ git update-index –assume-unchanged <path/to/file>” command. To track back the ignored file, the “$ git update-index –no-assume-unchanged <path/to/file>” command can be used. This post illustrated the different commands to untrack files from the Git repository temporarily.